|
CD8
CD8 (cluster of differentiation 8) is a transmembrane protein, transmembrane glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). Along with the TCR, the CD8 co-receptor plays a role in T cell Cell signaling, signaling and aiding with cytotoxic T cell-antigen interactions. Like the TCR, CD8 binds to a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecule, but is specific for the MHC class I protein. However, while the TCR interacts with the antigen-binding region of MHC-I, the CD8 molecule binds to the α3 domain, a non-variant region of MHC-I located away from the antigen-binding site. There are two Protein isoform, isoforms of the protein, alpha (CD8A) and beta (CD8B), each encoded by a different gene. In humans, both genes are located on chromosome 2 in position 2p12. CD8A is composed of 235 amino acid residues while CD8B consists of 210 residues, these two molecules share only 25 conserved residues. Both CD8 chains are type I membrane proteins, each with three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotoxic T Cell
A cytotoxic T cell (also known as TC, cytotoxic T lymphocyte, CTL, T-killer cell, cytolytic T cell, CD8+ T-cell or killer T cell) is a T lymphocyte (a type of white blood cell) that kills cancer cells, cells that are infected by intracellular pathogens such as viruses or bacteria, or cells that are damaged in other ways. Most cytotoxic T cells express T-cell receptors (TCRs) that can recognize a specific antigen. An antigen is a molecule capable of stimulating an immune response and is often produced by cancer cells, viruses, bacteria or intracellular signals. Antigens inside a cell are bound to class I MHC molecules, and brought to the surface of the cell by the class I MHC molecule, where they can be recognized by the T cell. If the TCR is specific for that antigen, it binds to the complex of the class I MHC molecule and the antigen, and the T cell destroys the cell. In order for the TCR to bind to the class I MHC molecule, the former must be accompanied by a glycoprotei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD8A
T-cell surface glycoprotein CD8 alpha chain (Cluster of Differentiation 8a), is a protein encoded by ''CD8A'' gene. Function The CD8 protein is a cell surface glycoprotein found on most cytotoxic T lymphocytes that mediates efficient cell-cell interactions within the immune system. The CD8, acting as a coreceptor, and the T-cell receptor on the T lymphocyte recognize antigen displayed by an antigen-presenting cell (APC) in the context of class I MHC molecules. The functional coreceptor is either a homodimer composed of two alpha chains, or a heterodimer composed of one alpha and one beta chain. Both alpha and beta chains share significant homology to variable domain of immunoglobulin light chains. This gene encodes the CD8 alpha chain isoforms. Two alternative transcripts encoding distinct isoforms, one membrane associated and one secreted, have been identified. Interactions CD8A has been shown to interact with: * CD3D, * HLA-A, and * HLA-G. See also * Clus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymocyte
A thymocyte is an immune cell present in the thymus, before it undergoes transformation into a T cell. Thymocytes are produced as stem cells in the bone marrow and reach the thymus via the blood. Thymopoiesis describes the process which turns thymocytes into mature T cells according to either negative or positive selection. This selection process is vitally important in shaping the population of thymocytes into a peripheral pool of T cells that are able to respond to foreign pathogens but remain tolerant towards the body's own antigens. Positive selection selects cells which are able to bind MHC class I or II molecules with at least a weak affinity. This eliminates (by a process called "death by neglect") those T cells which would be non-functional due to an inability to bind MHC. Negative selection destroys thymocytes with a high affinity for self peptides or MHC. This eliminates cells which would direct immune responses towards self-proteins in the periphery. Negative selection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in tissues that are in contact with the body's external environment, such as the skin, and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature and mature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes, where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the '' dendrites,'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance to the dendrites of neurons, these are structures distinct from them. Immature dendr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
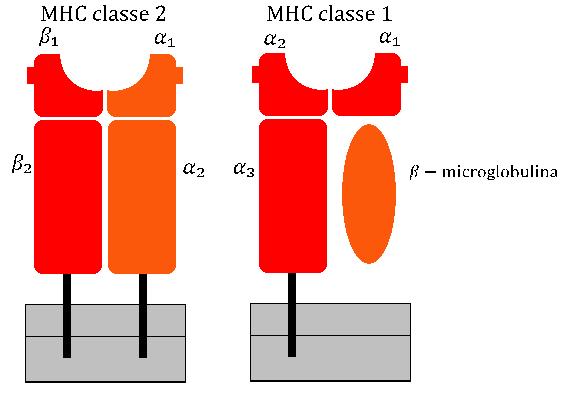
Major Histocompatibility Complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large Locus (genetics), locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for Cell (biology), cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. Its name comes from its discovery during the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules, which is to bind an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bring the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T cell, T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own pheno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosin-protein Kinase Lck
Tyrosin-protein kinase Lck (or lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase) is a 56 kDa protein that is found inside lymphocytes and encoded in the human by the ''LCK'' gene. The Lck is a member of Src kinase family (SKF) and is important for the activation of T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling in both naive T cells and effector T cells. The role of Lck is less prominent in the activation or in the maintenance of memory CD8 T cells in comparison to CD4 T cells. In addition, the constitutive activity of the mouse Lck homolog varies among memory T cell subsets. It seems that in mice, in the effector memory T cell (TEM) population, more than 50% of Lck is present in a constitutively active conformation, whereas less than 20% of Lck is present as active form in central memory T cells. These differences are due to differential regulation by SH2 domain–containing phosphatase-1 (Shp-1) and C-terminal Src kinase. Lck is responsible for the initiation of the TCR signaling cascade insi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunological Synapse
In immunology, an immunological synapse (or immune synapse) is the interface between an antigen-presenting cell or target cell and a lymphocyte such as a T cell, B cell, or natural killer cell. The interface was originally named after the neuronal synapse, with which it shares the main structural pattern. An immunological synapse consists of molecules involved in T cell activation, which compose typical patterns—activation clusters. Immunological synapses are the subject of much ongoing research. Structure and function The immune synapse is also known as the supramolecular activation cluster or SMAC. This structure is composed of concentric rings each containing segregated clusters of proteins—often referred to as the bull’s-eye model of the immunological synapse: * c-SMAC (central-SMAC) composed of the θ isoform of protein kinase C, CD2, CD4, CD8, CD28, Lck, and Fyn. * p-SMAC (peripheral-SMAC) within which the lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 ( LFA-1) and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clusters Of Differentiation
The cluster of differentiation (also known as cluster of designation or classification determinant and often abbreviated as CD) is a protocol used for the identification and investigation of cell surface molecules providing targets for immunophenotyping of cells. In terms of physiology, CD molecules can act in numerous ways, often acting as receptors or ligands important to the cell. A signal cascade is usually initiated, altering the behavior of the cell (see cell signaling). Some CD proteins do not play a role in cell signaling, but have other functions, such as cell adhesion. CD for humans is numbered up to 371 (). Nomenclature The CD nomenclature was proposed and established in the 1st International Workshop and Conference on Human Leukocyte Differentiation Antigens (HLDA), held in Paris in 1982. This system was intended for the classification of the many monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) generated by different laboratories around the world against epitopes on the surface mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Co-receptor
A co-receptor is a cell surface receptor that binds a signalling molecule in addition to a primary receptor in order to facilitate Ligand (biochemistry), ligand recognition and initiate biological processes, such as entry of a pathogen into a host cell. Properties The term co-receptor is prominent in literature regarding signal transduction, the process by which external stimuli regulate internal cellular functioning.Gomperts, BD.; Kramer, IM. Tatham, PER. (2002). Signal transduction. Academic Press. ISBN. The key to optimal cellular functioning is maintained by possessing specific machinery that can carry out tasks efficiently and effectively. Specifically, the process through which intermolecular reactions forward and amplify extracellular signals across the cell surface has developed to occur by two mechanisms. First, cell surface receptors can directly transduce signals by possessing both serine and threonine or simply serine in the cytoplasmic domain. They can also transmit s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-cell Receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex, located on the surface of T cells (also called T lymphocytes). They are responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The binding between TCR and antigen peptides is of relatively low affinity and is biologically degenerate (that is, many TCRs recognize the same antigen peptide, and many antigen peptides are recognized by the same TCR). The TCR is composed of two different protein chains (that is, it is a hetero dimer). In humans, in 95% of T cells the TCR consists of an alpha (α) chain and a beta (β) chain (encoded by '' TRA'' and ''TRB'', respectively), whereas in 5% of T cells the TCR consists of gamma and delta (γ/δ) chains (encoded by '' TRG'' and '' TRD'', respectively). This ratio changes during ontogeny and in diseased states (such as leukemia). It also differs between species. Orthologues of the 4 loci have been mapped in various speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |