|
Bunyavirales
''Bunyaviricetes'' is a class of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses with mainly tripartite genomes. Member viruses infect arthropods, plants, protozoans, and vertebrates. The name ''Bunyaviricetes'' derives from Bunyamwera, where the virus Bunyamwera virus was first discovered. Bunyaviruses belong to the fifth group of the Baltimore classification, Baltimore classification system, which includes viruses with a Sense (molecular biology), negative-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. They have an Viral envelope, enveloped, spherical virion. Though generally found in arthropods or rodents, certain viruses in this class occasionally infect humans. Some of them also infect plants. In addition, there is a group of bunyaviruses whose replication is restricted to arthropods and is known as insect-specific bunyaviruses. A majority of bunyaviruses are vector-borne. With the exception of Hantaviruses and Arenaviruses, all viruses in the ''Bunyaviricetes'' class are Arbovirus, transmitted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hantavirus
''Orthohantavirus'' is a genus of viruses that includes all hantaviruses (family ''Hantaviridae'') that cause disease in humans. Orthohantaviruses, hereafter referred to as hantaviruses, are naturally found primarily in rodents. In general, each hantavirus is carried by one rodent species and each rodent that carries a hantavirus carries one hantavirus species. Hantaviruses in their natural reservoirs usually cause an asymptomatic, persistent infection. In humans, however, hantaviruses cause two diseases: hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) and hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS). HFRS is mainly caused by hantaviruses in Africa, Asia, and Europe, called Old World hantaviruses, and HPS is usually caused by hantaviruses in the Americas, called New World hantaviruses. Hantaviruses are transmitted mainly through aerosols and droplets that contain rodent excretions, as well as through contaminated food, bites, and scratches. Environmental factors such as rainfall, temperature, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunyamwera
Bunyamwera is a town in Bundibugyo District, Uganda. It lies just outside of Rwenzori Mountains National Park, which is to the south. The town is north of Kagugu, southeast of Bunyana, and southwest of Butama. Other nearby settlements include Bundimbuga, 1½ km north, and Bundikahondo, 2 km northwest. The peak of Busunga is 6 km northwest, Kyabwageya's peak is 10 km east, and Kinera's peak is 10 km east. The nearest hospital, Kasulenge Health Center II, is 9 km northeast. In the 1950s, Bunyamwera was considered a Konzo spur village, and children there went to primary school in the parish of Mutunda. Bunyamwera parish includes two hydropower plants, Ndugutu and Sindila. Bunyamwera is where '' Bunyamwera orthobunyavirus'' was first isolated, and it also lends its name to that virus' genus '' Orthobunyavirus'', its family ''Peribunyaviridae'', and its order ''Bunyavirales ''Bunyaviricetes'' is a class of segmented negative-strand RN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbovirus
Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is Transmission (medicine), transmitted by arthropod Vector (epidemiology), vectors. The term ''arbovirus'' is a portmanteau word (''ar''thropod-''bo''rne ''virus''). ''Tibovirus'' (''ti''ck-''bo''rne ''virus'') is sometimes used to more specifically describe viruses transmitted by ticks, a superorder within the arthropods. Arboviruses can affect both animals (including humans) and plants. In humans, symptoms of arbovirus infection generally occur 3–15 days after exposure to the virus and last three or four days. The most common clinical features of infection are fever, headache, and malaise, but encephalitis and viral hemorrhagic fever may also occur. Signs and symptoms The incubation period – the time between when infection occurs and when symptoms appear – varies from virus to virus, but is usually limited between 2 and 15 days for arboviruses. The majority of infections, however, are asymptomatic. Among cases in which sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is a tick-borne infection caused by '' Dabie bandavirus'' also known as the SFTS virus, first reported between late March and mid-July 2009 in rural areas of Hubei and Henan provinces in Central China. It is an emerging infectious disease causing fever, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of consciousness and heamorrhage. SFTS has fatality rates ranging from 12% to as high as 30% in some areas due to multiple organ failure, thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), leucopenia (low white blood cell count), and elevated liver enzyme levels. Virology SFTS virus (SFTSV) is a virus in the order ''Bunyavirales'', discovered in 2009. Transmission The life cycle of the SFTSV most likely involves arthropod vectors like '' Haemaphysalis longicornis'' ticks and animal hosts. Humans appear to be largely accidental hosts. Person-to-person transmission was not initially noted in the 2011, but occurs via blood or mucus as documented in 2012. Symptoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the self-replication, replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to typical DNA-dependent RNA polymerases, which all organisms use to catalyze the transcription (genetics), transcription of RNA from a DNA template. RdRp is an essential protein encoded in the genomes of most RNA-containing viruses that lack a DNA stage, including SARS-CoV-2. Some eukaryotes also contain RdRps, which are involved in RNA interference and differ structurally from viral RdRps. History Viral RdRps were discovered in the early 1960s from studies on mengovirus and polio virus when it was observed that these viruses were not sensitive to actinomycin D, a drug that inhibits cellular DNA-directed RNA synthesis. This lack of sensitivity suggested the action of a virus-specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative-strand RNA Virus
Negative-strand RNA viruses (−ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have Sense (molecular biology), negative-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid (RNA). They have genomes that act as complementary strands from which messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized by the viral enzyme RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). During replication of the viral genome, RdRp synthesizes a positive-sense antigenome that it uses as a template to create genomic negative-sense RNA. Negative-strand RNA viruses also share a number of other characteristics: most contain a viral envelope that surrounds the capsid, which encases the viral genome, −ssRNA virus genomes are usually linear, and it is common for their genome to be segmented. Negative-strand RNA viruses constitute the phylum ''Negarnaviricota'', in the kingdom ''Orthornavirae'' and realm ''Riboviria''. They are descended from a common ancestor that was a Double-stranded RNA viruses, double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) virus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (biology)
Morphology (from Ancient Greek μορφή (morphḗ) "form", and λόγος (lógos) "word, study, research") is the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. This includes aspects of the outward appearance (shape, structure, color, pattern, size), as well as the form and structure of internal parts like bones and organs, i.e., anatomy. This is in contrast to physiology, which deals primarily with function. Morphology is a branch of life science dealing with the study of the overall structure of an organism or taxon and its component parts. History The etymology of the word "morphology" is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "form", and (), meaning "word, study, research". While the concept of form in biology, opposed to function, dates back to Aristotle (see Aristotle's biology), the field of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the German anatomist and physiologist Karl Fried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
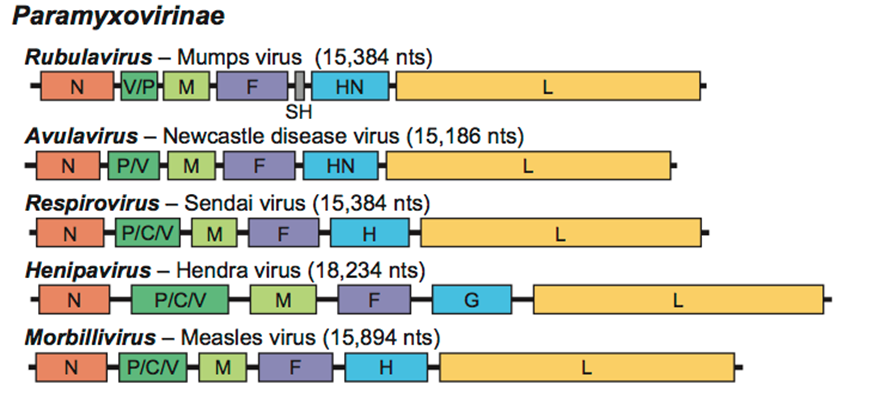
Paramyxoviridae
''Paramyxoviridae'' (from Ancient Greek, Greek ''para-'' “by the side of” and ''myxa'' “mucus”) is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Mononegavirales''. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family include measles, mumps, and respiratory tract infections. The family has nine subfamilies that contain 23 genera. Structure Virions are enveloped and can be spherical or pleomorphic and capable of producing filamentous virions. The diameter is around 150 nm. Genomes are linear, around 15kb in length. Fusion proteins and attachment proteins appear as spikes on the virion surface. Matrix proteins inside the envelope stabilise virus structure. The nucleocapsid core is composed of the genomic RNA, nucleocapsid proteins, phosphoproteins and polymerase proteins. Genome The genome is non-segmented, negative-sense RNA, 15–19 kilobases in length, and contains six to 10 genes. Extracistronic (noncoding) regions include: * A 3’ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the Molecule">molecular scale. The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm), or nanometer (American spelling Despite the various list of dialects of English, English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variati ...), is a units of measurement, unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one billionth (short scale) or one thousand million (long scale) of a metre, meter (0.000000001 m) and to 1000 picometres. One nanometre can be expressed in scientific notation as 1 × 10−9 m and as m. History The nanometre was formerly known as the "''millimicrometre''" – or, more commonly, the "''millimicron''" for short – since it is of a micrometre, micrometer. It was often de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puumala Virus
Puumala virus (PUUV) is the main cause of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in Europe and Russia. Puumala virus is transmitted by the bank vole (''Clethrionomys glareolus''). In its natural reservoir, PUUV causes a persistent infection with few symptoms and is spread through excretions, fighting, and grooming. Humans can become infected by inhaling aerosols that contain rodent saliva, urine, or feces, as well as through bites and scratches. In humans, infection is usually asymptomatic but can lead to a mild form of HFRS often called nephropathia epidemica (NE). Symptoms include fever and headache, impaired vision, as well as the appearance of spots on the skin and renal symptoms such as kidney swelling, excess protein in urine, blood in urine, decreased urine production, and kidney failure. The case fatality rate from infection is less than 1%. The genome of PUUV is about 12 kilobases (kb) in length and segmented into three negative-sense, single-stranded RNA (-ssRNA) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |