|
550s BC
This article concerns the period 559 BC–550 BC. Events and trends *Carthage conquers Sicily, Sardinia, and Corsica. * 559 BC—King Cambyses I of Anshan dies and is succeeded by his son Cyrus II the Great. * 558 BC— Hegesias is removed as Archon of Athens. *558 BC—The Chinese state of Jin defeats its rival state of Qin in battle. * 557 BC—The Persians besiege Larissa (Calah) but fail to capture it until a solar eclipse occurs.Solar Eclipses and Ancient History. Jennings, S. Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada, Vol.2, pg. 172 * 556 BC—Pisistratus is exiled from Athens to Euboea. *556 BC—Labashi-Marduk succeeds Neriglissar as king of Babylon. *556 BC—Nabonidus succeeds Labashi-Marduk as king of Babylon. *c. 550 BC—Colonisation of Greeks ends. *550 BC— Abdera is destroyed by the Thracians. *550 BC— Mago I begins his rule of Carthage. *550 BC—The Temple of Artemis is completed in Ephesus. *553-550 BC—Medo-Persian conflict, the Persian king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classical world. It became the capital city of the civilization of Ancient Carthage and later Roman Carthage. The city developed from a Phoenician colony into the capital of a Punic people, Punic empire which dominated large parts of the Southwest Mediterranean during the first millennium BC. The legendary Queen Elissa, Alyssa or Dido, originally from Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre, is regarded as the founder of the city, though her historicity has been questioned. In the myth, Dido asked for land from a local tribe, which told her that she could get as much land as an oxhide could cover. She cut the oxhide into strips and laid out the perimeter of the new city. As Carthage prospered at home, the polity sent colonists abroad as well as magistrates to rule t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season in its new moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to Ecliptic, the plane of Earth's orbit. In a total eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon. In #Types, partial and annular eclipses, only part of the Sun is obscured. Unlike a lunar eclipse, which may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth, a solar eclipse can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world. As such, although total solar eclipses occur somewhere on Earth every 18 months on average, they recur at any given place only once every 360 to 410 years. If the Moon were in a perfectly circular orbit and in the same orbital plane as Earth, there would be total solar eclipses once a month, at every new moon. Instead, because the Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mago I
MagoI, also known as Magon (, ), was the king of the Ancient Carthage from 550 BC to 530 BC and the founding monarch of the Magonid dynasty of Carthage.Carthage . Accessed 30 November 2008 Mago I was originally a . Under Mago, Carthage became preeminent among the Phoenician colonies in the western . Rule Under Mago, Carthage established itself as the dominant n military power in the western |
Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east, it comprises present-day southeastern Bulgaria (Northern Thrace), northeastern Greece (Western Thrace), and the European part of Turkey (East Thrace). Lands also inhabited by ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into Macedonia (region), Macedonia. Etymology The word ''Thrace'', from ancient Greek ''Thrake'' (Θρᾴκη), referred originally to the Thracians (ancient Greek ''Thrakes'' Θρᾷκες), an ancient people inhabiting Southeast Europe. The name ''Europe'' (ancient Greek Εὐρώπη), also at first referred to this region, before that term expanded to include its Europe, modern sense. It has been suggested that the name ''Thrace'' derives from the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
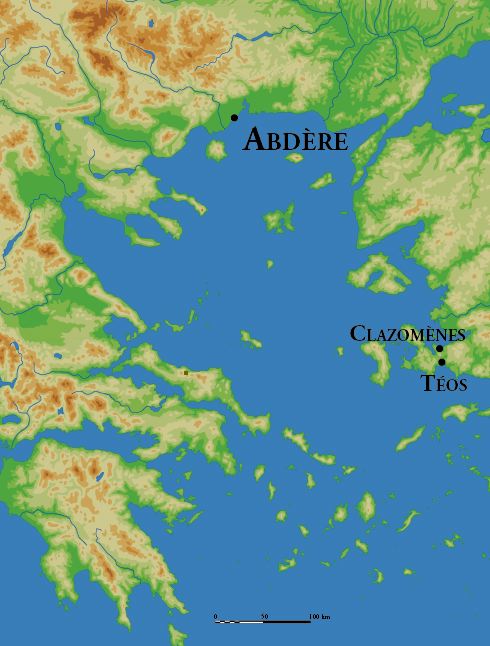
Abdera, Thrace
Abdera () is a municipality in the Xanthi regional unit of Thrace, Greece. In classical antiquity, it was a major Greek ''polis'' on the Thracian coast. The ancient polis is to be distinguished from the municipality, which was named in its honor. The polis lay 17 km east-northeast of the mouth of the Nestos River, almost directly opposite the island of Thasos. It was a colony placed in previously unsettled Thracian territory, not then a part of Hellas, during the age of Greek colonization. The city that developed from it became of major importance in ancient Greece. After the 4th centuryAD it declined, contracted to its acropolis, and was abandoned, never to be reoccupied except by archaeologists. During the Early Middle Ages, a new settlement emerged near the ancient city. It was called Polystylon (), and later considered as the New Abdera (). In 2011 the modern municipality of Abdera was synoecized from three previous municipalities comprising a number of modern settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a lesser extent, other countries surrounding the Eastern Mediterranean and Black Sea. They also form a significant Greek diaspora, diaspora (), with many Greek communities established around the world.. Greek colonies and communities have been historically established on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea, but the Greek people themselves have always been centered on the Aegean Sea, Aegean and Ionian Sea, Ionian seas, where the Greek language has been spoken since the Bronze Age.. Until the early 20th century, Greeks were distributed between the Greek peninsula, the western coast of Asia Minor, the Black Sea coast, Cappadocia in central Anatolia, Egypt, the Balkans, Cyprus, and Constantinople. Many of these regions coincided to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
550 BC
The year 550 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as year 204 ''Ab urbe condita''. The denomination 550 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events * Greek colonization ends (approximate date). * Cyrus II the Great overthrows Astyages of the Medes, establishing the Achaemenid Empire. * Mago I begins his rule of Carthage and founds the Magonid dynasty. * The Kingdom of Colchis is established. * Abdera is destroyed by the Thracians. * The Temple of Artemis is completed in Ephesus. * The Temple of Hera I is built in what is now Paestum, Italy (approximate date). * Siddhartha Gautama founds Buddhism in Northern India after achieving enlightenment after six years of practicing penance and meditation. Births * Aristodemus of Cumae, tyrant of Cumae *Hecataeus of Miletus, early Greek historian *Miltiades, renowned Olympi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabonidus
Nabonidus (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-naʾid'', meaning "May Nabu be exalted" or "Nabu is praised") was the last king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from 556 BC to the fall of Babylon to the Achaemenian Empire under Cyrus the Great in 539 BC. Nabonidus was the last native ruler of ancient Mesopotamia, the end of his reign marking the end of thousands of years of Sumero-Akkadian language, Akkadian states, Monarchy, kingdoms and empires. He was also the last independent king of Babylon. Regarded as one of the most vibrant and individualistic rulers of his time, Nabonidus is characterised by some scholars as an unorthodox religious reformer and as the first archaeologist. The origins of Nabonidus, his connection to previous royalty, and subsequently what claim he had to the throne remain unclear, given that Nabonidus made no genealogical claims of kinship to previous kings. This suggests that he was neither related nor connected to the Chaldean dynasty of Babylonian rulers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
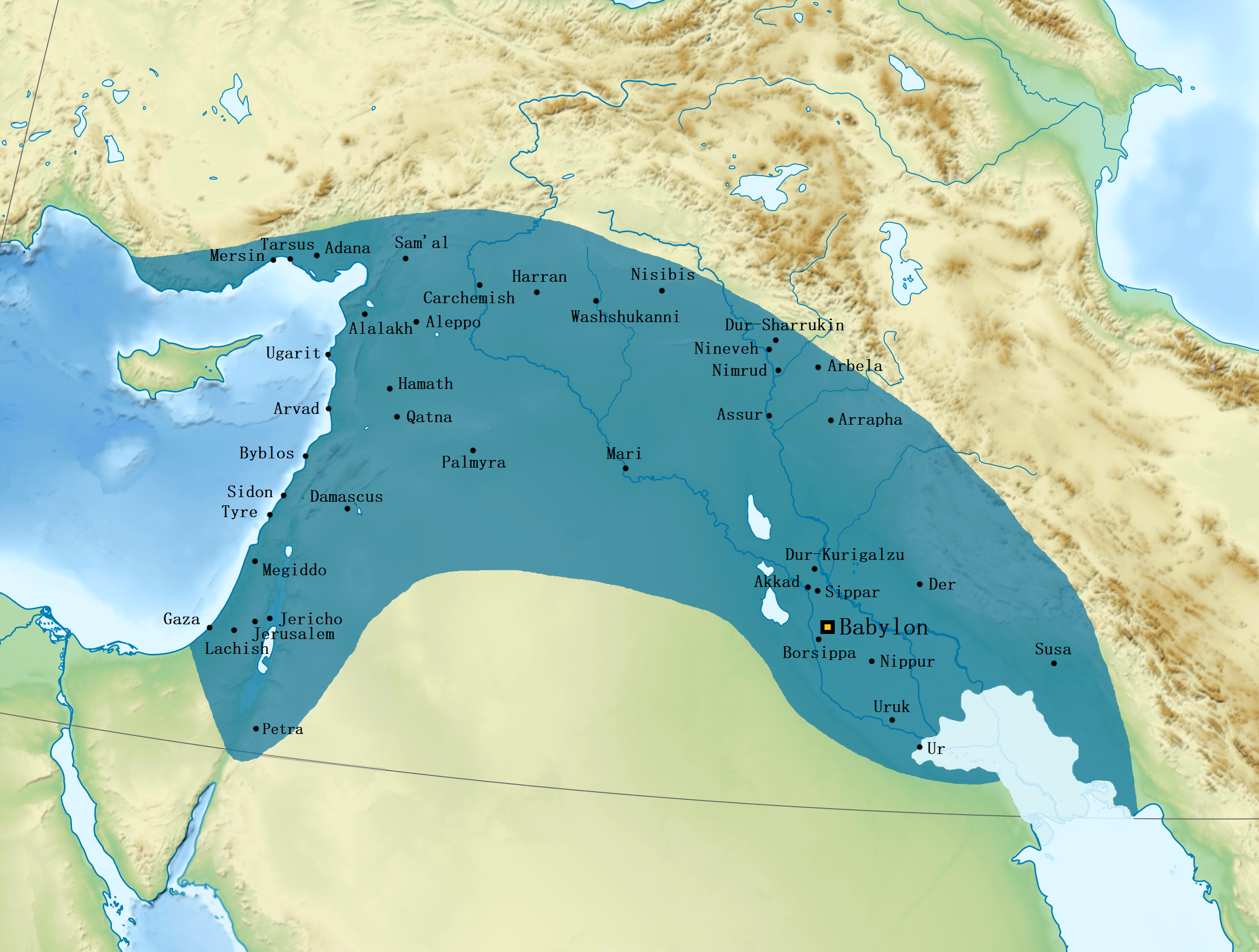
Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-speaking region of Babylonia. Its rulers established two important empires in antiquity, the 19th–16th century BC Old Babylonian Empire, and the 7th–6th century BC Neo-Babylonian Empire. Babylon was also used as a regional capital of other empires, such as the Achaemenid Empire. Babylon was one of the most important urban centres of the ancient Near East, until its decline during the Hellenistic period. Nearby ancient sites are Kish, Borsippa, Dilbat, and Kutha. The earliest known mention of Babylon as a small town appears on a clay tablet from the reign of Shar-Kali-Sharri (2217–2193 BC), of the Akkadian Empire. Babylon was merely a religious and cultural centre at this point and neither an independent state nor a large city, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neriglissar
Neriglissar ( Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nergal-šar-uṣur'' or ''Nergal-šarra-uṣur'', meaning "Nergal, protect the king") was the fourth king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from his usurpation of the throne in 560 BC to his death in 556 BC. Though unrelated to previous Babylonian kings, possibly being of Aramean ancestry, Neriglissar was a prominent official and general in the reign of Nebuchadnezzar II (605–562 BC) and became even more influential through marrying one of Nebuchadnezzar's daughters, possibly Kashshaya. Nebuchadnezzar was initially succeeded by his son, Amel-Marduk, but Amel-Marduk's reign only lasted for two years before Neriglissar usurped the Babylonian throne and put him to death. Through his marriage to Nebuchadnezzar's daughter, possibly significantly older than any of the old king's sons, Neriglissar might have represented a less legitimate but more wealthy and well-established faction of the royal family, even if he himself was not part of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labashi-Marduk
Labashi-Marduk ( or , meaning "O Marduk, may I not come to shame") was the fifth and penultimate king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling in 556 BC. He was the son and successor of Neriglissar. Though classical authors such as Berossus wrote that Labashi-Marduk was just a child when he became king, Babylonian documents indicate that he had been in charge of his own affairs before his rise to the throne, suggesting he was an adult, though possibly still relatively young. Labashi-Marduk's reign was very short, lasting only one to three months, with the last evidence of Neriglissar's life dating in April 556 BC and documents dated to Labashi-Marduk's successor, Nabonidus, appearing in May that same year and becoming widespread in Babylonia by the end of June. Nabonidus's son Belshazzar led a coup against the king, deposing and killing Labashi-Marduk and proclaiming Nabonidus as king. The reason for Labashi-Marduk's deposition is unknown, Berossus simply describes the justificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euboea
Euboea ( ; , ), also known by its modern spelling Evia ( ; , ), is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete, and the sixth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest point). In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to . Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos. It forms most of the regional unit of Euboea, which also includes Skyros and a small area of the Greek mainland. Name Like most of the Greek islands, Euboea was known by other names in antiquity, such as ''Macris'' (Μάκρις) and ''Doliche'' (Δολίχη) from its elongated shape, or ''Ellopia'' (after El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |