|
Błażowa
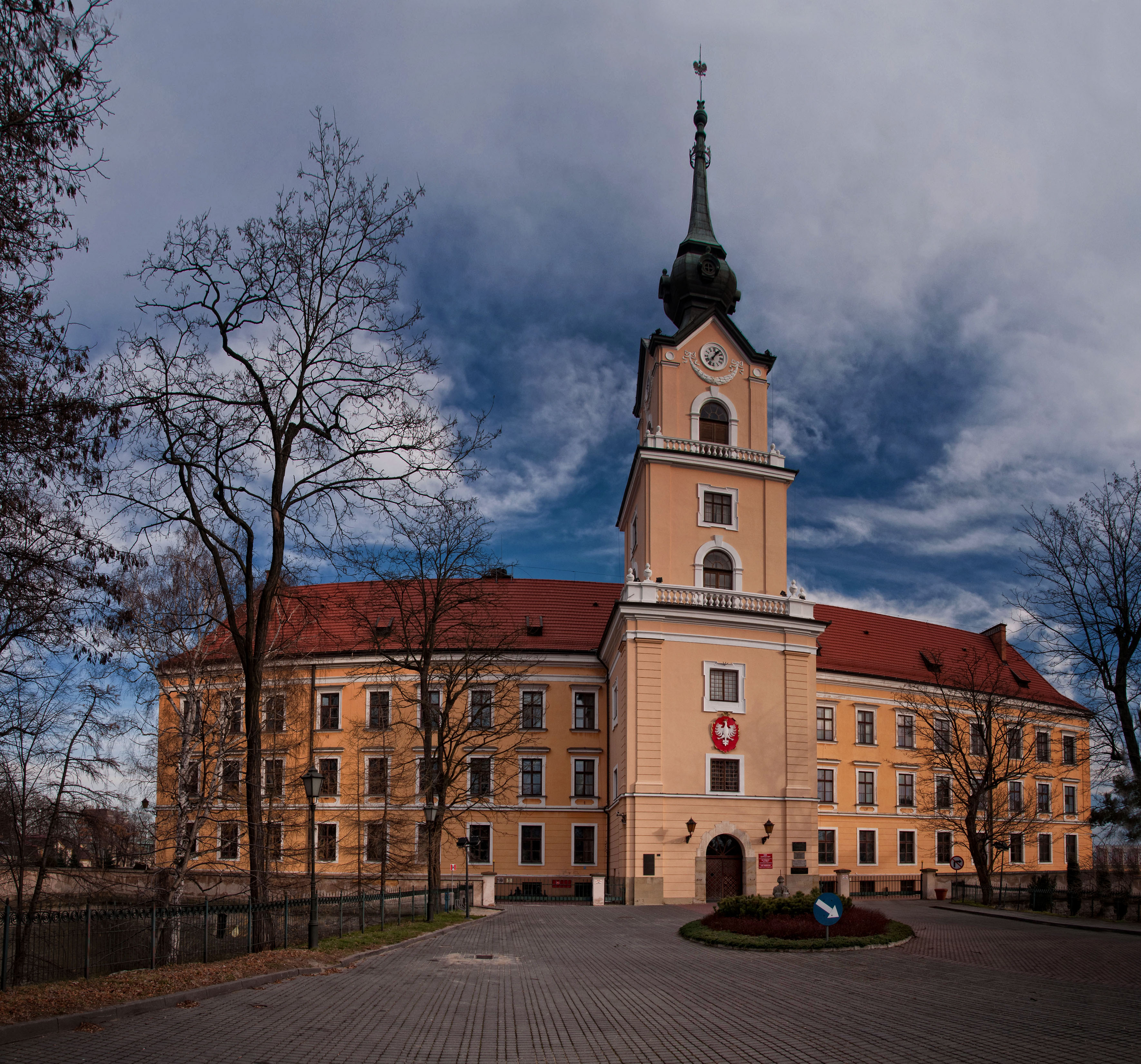
Błażowa ( yi, בלאזשאוו ''Blazhov'') is a town in Rzeszów County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, Poland, with a population of 2,149 as of December 2021. History The area of the gmina of Błażowa in the past was located along the border of Red Ruthenia and Lesser Poland. In the early 14th century, it was part of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia. In 1340 Błażowa was annexed by Polish King Kazimierz Wielki, who created the Sanok Land (1366) and Przemyśl Land, and established several towns in the area (Rzeszów 1354, Brzozow 1359, Tyczyn 1368). Błażowa remained a village located in Sanok Land. In 1624 the whole area was raided by the Crimean Tatars and another devastating Tatar raid took place in 1672. In 1655 – 56, during the Swedish invasion of Poland, Błażowa was burned down by Swedish and then Transilvanian-Cossack soldiers. Further destruction was brought by the Great Northern War. It is not known when exactly Błażowa received town charter, probably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina Błażowa
__NOTOC__ Gmina Błażowa is an urban-rural gmina (administrative district) in Rzeszów County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland. Its seat is the town of Błażowa, which lies approximately south-east of the regional capital Rzeszów. The gmina covers an area of , and as of 2006 its total population is 10,593, of which the population of Błażowa is 2,110, and the population of the rural part of the gmina is 8,483. Villages Apart from the town of Błażowa, Gmina Błażowa contains the villages and settlements of Białka, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, Białka, Błażowa Dolna, Błażowa Górna, Futoma, Kąkolówka, Lecka, Mokłuczka, Nowy Borek, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, Nowy Borek, Piątkowa, Rzeszów County, Piątkowa and Ujazdy, Rzeszów County, Ujazdy. Neighbouring gminas Gmina Błażowa is bordered by the gminas of Gmina Domaradz, Domaradz, Gmina Dynów, Dynów, Gmina Hyżne, Hyżne, Gmina Lubenia, Lubenia, Gmina Niebylec, Niebylec, Gmina Nozdrzec, Nozdrzec a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rzeszów County
__NOTOC__ Rzeszów County ( pl, powiat rzeszowski) is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the city of Rzeszów, although the city is not part of the county (it constitutes a separate city county). The county contains six towns: Dynów, south-east of Rzeszów, Boguchwała, south-west of Rzeszów, Głogów Małopolski, north of Rzeszów, Sokołów Małopolski, north of Rzeszów, Tyczyn, south of Rzeszów, and Błażowa, south-east of Rzeszów. The county covers an area of . As of 2019 its total population is 168,614, out of which the population of Boguchwała is 6,179, that of Głogów Małopolski is 6,654, that of Sokołów Małopolski is 4,193, that of Tyczyn is 3,824, that of Błażowa is 2,139, and the rural population is 139,496. Neighbouring counties Apart fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcarpathian Voivodeship
Subcarpathian Voivodeship or Subcarpathia Province (in pl, Województwo podkarpackie ) is a voivodeship, or province, in the southeastern corner of Poland. Its administrative capital and largest city is Rzeszów. Along with the Marshall, it is governed by the Subcarpathian Regional Assembly. Historically, most of the province's territory was part of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria and the Ruthenian Voivodeship. In the interwar period, it was part of the Lwów Voivodeship. The voivodeship was created on 1 January 1999 out of the former Rzeszów, Przemyśl, Krosno and (partially) Tarnów and Tarnobrzeg Voivodeships, pursuant to the Polish local-government reforms adopted in 1998. The name derives from the region's location near the Carpathian Mountains, and the voivodeship comprises areas of two historic regions of Eastern Europe — Lesser Poland (western and northwestern counties) and Red Ruthenia. During the interwar period (1918-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivodeships Of Poland
A voivodeship (; pl, województwo ; plural: ) is the highest-level administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as "province". The Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998, which went into effect on 1 January 1999, created sixteen new voivodeships. These replaced the 49 former voivodeships that had existed from 1 July 1975, and bear a greater resemblance (in territory, but not in name) to the voivodeships that existed between 1950 and 1975. Today's voivodeships are mostly named after historical and geographical regions, while those prior to 1998 generally took their names from the cities on which they were centered. The new units range in area from under (Opole Voivodeship) to over (Masovian Voivodeship), and in population from nearly one million (Opole Voivodeship) to over five million (Masovian Voivodeship). Administrative authority at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partitions Of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 123 years. The partitions were conducted by the Habsburg monarchy, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire, which divided up the Commonwealth lands among themselves progressively in the process of territorial seizures and annexations. The First Partition was decided on August 5, 1772 after the Bar Confederation lost the war with Russia. The Second Partition occurred in the aftermath of the Polish–Russian War of 1792 and the Targowica Confederation of 1792 when Russian and Prussian troops entered the Commonwealth and the partition treaty was signed during the Grodno Sejm on January 23, 1793 (without Austria). The Third Partition took place on October 24, 1795, in reaction to the unsuccessful Polish Kościuszko Uprising the previ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyczyn
Tyczyn is a town in southern Poland with a population of 3,353 inhabitants (02.06.2009). It is located in the Rzeszów County of the Subcarpathian Voivodeship. History Bartold Tyczner, a merchant from Moravia, founded Tyczyn in 1368 during the reign of King Casimir III of Poland. The Jews migrated into the area during the 15th and 16th centuries. Tyczyn is located in the lower Carpathian foothills, about halfway between the two large towns of Kraków to the west and Lviv (Lwów) to the east. The center of town is on top of a hill surrounded by numerous farming villages. To the north of town is the Strug River. The town grew and dominated the area until the mid-17th century when it was destroyed first by a Tatar and later by a Cossack invasion. During the years 1792 to 1918 Tyczyn and the southern part of Poland, known as Polish Galicia, became part of the Austrian-Hungarian Empire. During those years the area of Tyczyn came under administrative control of Rzeszów, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
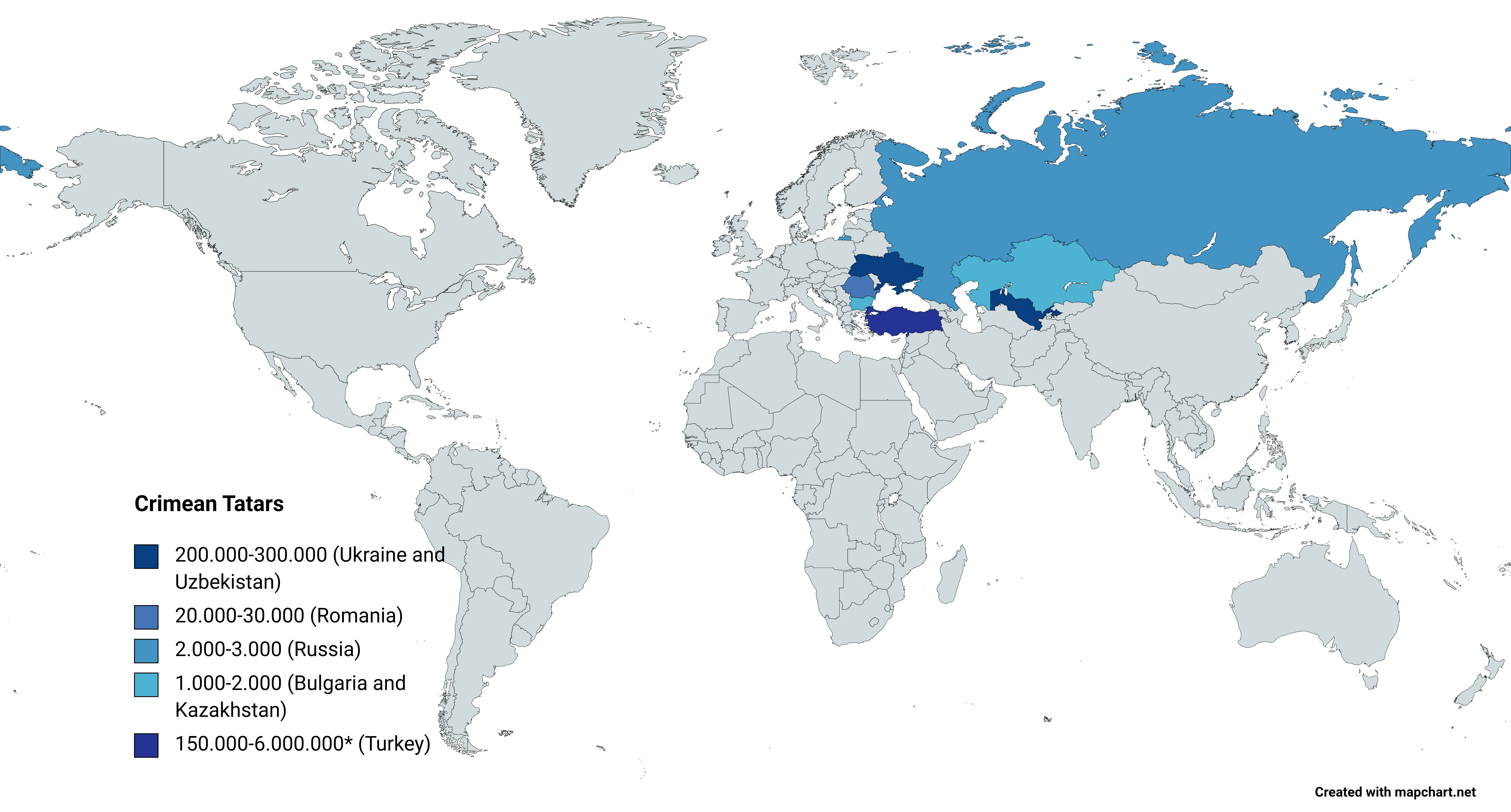
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg , flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars , image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg , caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace , poptime = , popplace = , region1 = , pop1 = 3,500,000 6,000,000 , ref1 = , region2 = * , pop2 = 248,193 , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 239,000 , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 24,137 , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 2,449 , ref5 = , region7 = , pop7 = 1,803 , ref7 = , region8 = , pop8 = 1,532 , ref8 = , region9 = *() , pop9 = 7,000(500–1,000) , ref9 = , region10 = Total , pop10 = 4.024.114 (or 6.524.11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deluge (history)
The Deluge ( pl, potop szwedzki, lt, švedų tvanas) was a series of mid-17th-century military campaigns in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In a wider sense it applies to the period between the Khmelnytsky Uprising of 1648 and the Truce of Andrusovo in 1667, thus comprising the Polish theatres of the Russo-Polish War (1654–1667), Russo-Polish and Second Northern Wars. In a stricter sense, the term refers to the Swedish Empire, Swedish invasion and occupation of the Commonwealth as a theatre of the Second Northern War (1655–1660) only; in Poland and Lithuania this period is called the Swedish Deluge ( pl, potop szwedzki, sv, Svenska syndafloden), or less commonly the Russo–Swedish Deluge ( pl, Potop szwedzko-rosyjski) due to the simultaneous Russo-Polish War (1654–1667), Russo-Polish War. The term "deluge" (''potop'' in Polish) was popularized by Henryk Sienkiewicz in his novel ''The Deluge (novel), The Deluge'' (1886). During the wars the Commonwealth lost approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I of Russia, Frederick IV of Denmark–Norway and Augustus II the Strong of Saxony– Poland–Lithuania. Frederick IV and Augustus II were defeated by Sweden, under Charles XII, and forced out of the alliance in 1700 and 1706 respectively, but rejoined it in 1709 after the defeat of Charles XII at the Battle of Poltava. George I of Great Britain and the Electorate of Hanover joined the coalition in 1714 for Hanover and in 1717 for Britain, and Frederick William I of Brandenburg-Prussia joined it in 1715. Charles XII led the Swedish army. Swedish allies included Holstein-Gottorp, several Polish magnates under Stanislaus I Leszczyński (1704–1710) and Cossacks under the Ukrainian Hetman Ivan Mazepa (1708–17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Gothic
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly serious and learned admirers of the neo-Gothic styles sought to revive medieval Gothic architecture, intending to complement or even supersede the neoclassical styles prevalent at the time. Gothic Revival draws upon features of medieval examples, including decorative patterns, finials, lancet windows, and hood moulds. By the middle of the 19th century, Gothic had become the preeminent architectural style in the Western world, only to fall out of fashion in the 1880s and early 1890s. The Gothic Revival movement's roots are intertwined with philosophical movements associated with Catholicism and a re-awakening of high church or Anglo-Catholic belief concerned by the growth of religious nonconformism. Ultimately, the "Anglo-Catholicism" tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities that were ruled by the House of Habsburg, especially the dynasty's Austrian branch. The history of the Habsburg monarchy can be traced back to the election of Rudolf I as King of Germany in 1273 and his acquisition of the Duchy of Austria for the Habsburg in 1282. In 1482, Maximilian I acquired the Netherlands through marriage. Both realms passed to his grandson and successor, Charles V, who also inherited the Spanish throne and its colonial possessions, and thus came to rule the Habsburg empire at its greatest territorial extent. The abdication of Charles V in 1556 led to a division within the dynasty between his son Philip II of Spain and his brother Ferdinand I, who had served as his lieutenant and the elected king of Hungary and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galicia (Eastern Europe)
Galicia ()"Galicia" ''Collins English Dictionary'' ( uk, Галичина, translit=Halychyna ; pl, Galicja; yi, גאַליציע) is a historical and geographic region spanning what is now southeastern Poland and western Ukraine, long part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.See also: It covers much of such historic regions as Red Ruthenia (centered on Lviv) and Lesser Poland (centered on Kraków). The name of the region derives from the medieval city of Halych, and was first mentioned in Hungarian historical chronicles in the year 1206 as ''Galiciæ''. The eastern part of the region was controlled by the medieval Kingdom of Galicia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_in_1655.png)
