|
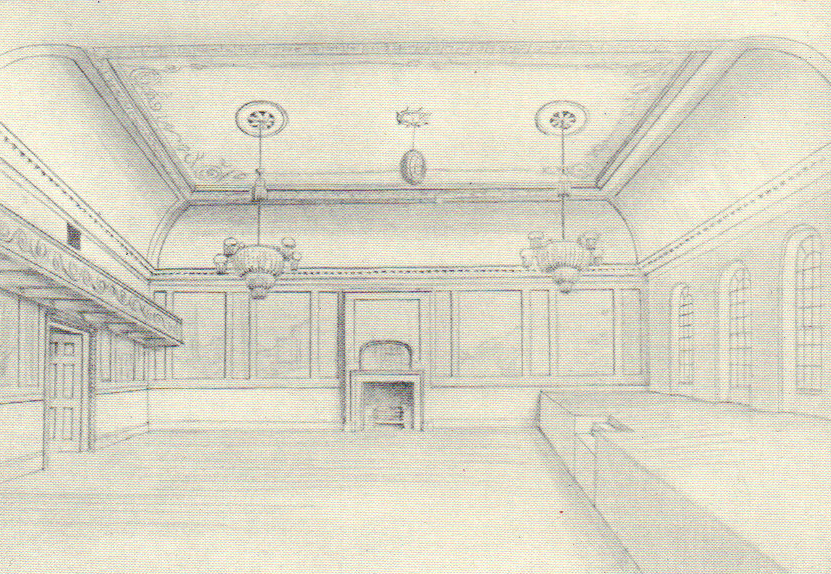
Brechin Town House
Brechin Town House is a municipal structure in the High Street in Brechin, Angus, Scotland. The structure, which was used as a museum from 2003 to 2023, is a Category B listed building. History The first municipal building in the town was a tolbooth which was erected on the current site and dated back at least to the first half of the 15th century. The ground floor was used as a prison and the first floor accommodated the burgh council chamber: it was replaced by a town house in the late 17th century. It was at the mercat cross in front of this building that James Maule, 4th Earl of Panmure proclaimed James Francis Edward Stuart, known as the "Old Pretender", as King James VIII during the Jacobite rising of 1715. By the 1780s, the old town house had become dilapidated, and the burgh council decided to demolish it and build a new town house, financed by public subscription, on the same site: major contributors included the member of parliament, Sir David Carnegie, 4th Baronet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brechin
Brechin (; ) is a town and former royal burgh in Angus, Scotland. Traditionally Brechin was described as a city because of its cathedral and its status as the seat of a pre-Scottish Reformation, Reformation Roman Catholic diocese (which continues today as an Bishop, episcopal seat of the Scottish Episcopal Church), but that status has not been officially recognised in the modern era. Nevertheless, the designation is often used, with examples being the City of Brechin and District Community Council, City of Brechin and Area Partnership, City of Brechin Civic Trust and Brechin City F.C., Brechin City Football Club. Kinnaird Castle, Brechin, Kinnaird Castle is nearby. Brechin is located slightly closer to Dundee than Aberdeen on the A90 road, A90 between the cities. It is the fourth largest settlement of Angus. History In the centre of Brechin is a small museum in the Brechin Town House, and an award-winning tourist attraction, the Caledonian Railway (Brechin), Caledonian Railw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, usually dome-like structure on top of a building often crowning a larger roof or dome. Cupolas often serve as a roof lantern to admit light and air or as a lookout. The word derives, via Italian language, Italian, from lower Latin ''cupula'' (classical Latin ''cupella''), (Latin ''cupa''), indicating a vault resembling an upside-down cup. The cylindrical drum underneath a larger cupola is called a tholobate. Background The cupola evolved during the Renaissance from the older Oculus (architecture), oculus. Being weatherproof, the cupola was better suited to the wetter climates of northern Europe. The chhatri, seen in Architecture of India, Indian architecture, fits the definition of a cupola when it is used atop a larger structure. Cupolas often serve as a Bell tower, belfry, Belvedere (structure), belvedere, or roof lantern above a main roof. In other cases they may crown a spire, tower, or Turret (architecture), turret. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Chambers And Town Halls In Scotland
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agreed definition of the lower boundary for their size. In a narrower sense, a city can be defined as a permanent and densely populated place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organizations, and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving the efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Buildings Completed In 1790
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The main types of modern political systems recognized are democracies, totalitarian regimes, and, sitting between these two, authoritarian regimes with a variety of hybrid regimes. Modern classification systems also include monarchies as a standalone entity or as a hybrid system of the main three. Historically prevalent forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Listed Buildings In Brechin, Angus ...
This is a list of listed buildings in the parish of Brechin in Angus, Scotland. List Key See also * List of listed buildings in Angus Notes References * All entries, addresses and coordinates are based on data froHistoric Scotland This data falls under thOpen Government Licence {{Reflist Brechin Brechin (; ) is a town and former royal burgh in Angus, Scotland. Traditionally Brechin was described as a city because of its cathedral and its status as the seat of a pre-Scottish Reformation, Reformation Roman Catholic diocese (which contin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brechin Cathedral
Brechin Cathedral is a Scottish Church building which dates from the 13th century. It is the former Cathedral of the former Roman Catholic Diocese of Brechin but has not served that function since the Scottish Reformation in the 16th century. It is in the Pointed style, but suffered maltreatment in 1806 at the hands of restorers, whose work was subsequently removed during the restoration completed in 1902. The western gable with its flamboyant window, Gothic architecture, Gothic door and massive square tower, parts of the (much truncated) choir, and the nave pillars and clerestory are all that is left of the original edifice. The modern stained glass in the chancel is reckoned amongst the finest in Scotland. The cathedral is a category A listed building and the attached Round Tower is a scheduled monument. Round Tower Immediately adjoining the cathedral to the southwest stands the Irish round tower, Round Tower, built about A.D. 1000. It is 86 ft.(26.21 m) high, has at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diorama
A diorama is a replica of a scene, typically a three-dimensional model either full-sized or miniature. Sometimes dioramas are enclosed in a glass showcase at a museum. Dioramas are often built by hobbyists as part of related hobbies like military vehicle modeling, miniature figure modeling, or aircraft modeling. In the United States around 1950 and onward, natural history dioramas in museums became less fashionable, leading to many being removed, dismantled, or destroyed. Etymology Artists Louis Daguerre and Charles Marie Bouton coined the name "diorama" for a theatrical system that used variable lighting to give a translucent painting the illusion of depth and movement. It derives from Greek δια- (through) + ὅραμα (visible image) = "see-through image." The first use in reference to museum displays is recorded in 1902, although such displays existed before. Modern The current, popular understanding of the term "diorama" denotes a partially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanics' Institute
Mechanics' institutes, also known as mechanics' institutions, sometimes simply known as institutes, and also called schools of arts (especially in the Australian colonies), were educational establishments originally formed to provide adult education, particularly in technical subjects, to working men in Victorian-era Britain and its colonies. They were often funded by local industrialists on the grounds that they would ultimately benefit from having more knowledgeable and skilled employees. The mechanics' institutes often included libraries for the adult working class, and were said to provide them with an alternative pastime to gambling and drinking in pubs. Many of the original institutes included lending libraries, and the buildings of some continue to be used as libraries. Others have evolved into parts of universities, adult education facilities, theatres, cinemas, museums, recreational facilities, or community halls. Few are still referred to as mechanics' institutes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Adam (architect)
William Adam (1689 – 24 June 1748) was a Scottish architect, mason, and entrepreneur. He was the foremost architect of his time in Scotland,McWilliam, p.57 designing and building numerous country houses and public buildings, and often acting as contractor as well as architect. Among his best known works are Hopetoun House near Edinburgh, and Duff House in Banff. His individual, exuberant style built on the Palladian style, but with Baroque details inspired by Vanbrugh and Continental architecture. In the 18th century, Adam was considered Scotland's "Universal Architect". However, since the early 20th century, architectural critics have taken a more measured view, Colin McWilliam, for instance, finding the quality of his work "varied to an extreme degree". As well as being an architect, Adam was involved in several industrial ventures and improvement schemes, including coal mining, salt panning, stone quarries and mills. In 1731 he began to build up his own estate i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilaster
In architecture, a pilaster is both a load-bearing section of thickened wall or column integrated into a wall, and a purely decorative element in classical architecture which gives the appearance of a supporting column and articulates an extent of wall. As an ornament it consists of a flat surface raised from the main wall surface, usually treated as though it were a column, with a capital at the top, plinth (base) at the bottom, and the various other column elements. In contrast to a Classical pilaster, an engaged column or buttress can support the structure of a wall and roof above. In human anatomy, a pilaster is a ridge that extends vertically across the femur, which is unique to modern humans. Its structural function is unclear. Definition A pilaster is foremost a load-bearing architectural element used widely throughout the world and its history where a structural load is carried by a thickened section of wall or column integrated into a wall. It is also a purel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coved Ceiling
A coved ceiling is a ceiling that has had the visual appearance of the point where the ceiling meets the walls improved by the addition of coving. It can also refer to a ceiling, like in a Mosque A mosque ( ), also called a masjid ( ), is a place of worship for Muslims. The term usually refers to a covered building, but can be any place where Salah, Islamic prayers are performed; such as an outdoor courtyard. Originally, mosques were si .... References Interior design {{Architecturalelement-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |