|
Bragg Grating
A fiber Bragg grating (FBG) is a type of distributed Bragg reflector constructed in a short segment of optical fiber that reflects particular wavelengths of light and transmits all others. This is achieved by creating a periodic variation in the refractive index of the fiber core, which generates a wavelength-specific dielectric mirror. Hence a fiber Bragg grating can be used as an inline optical fiber to block certain wavelengths, can be used for sensing applications, or it can be used as wavelength-specific reflector. History The first in-fiber Bragg grating was demonstrated by Ken Hill in 1978. Initially, the gratings were fabricated using a visible laser propagating along the fiber core. In 1989, Gerald Meltz and colleagues demonstrated the much more flexible transverse holographic inscription technique where the laser illumination came from the side of the fiber. This technique uses the interference pattern of ultraviolet laser light to create the periodic structure of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Bragg Grating
A fiber Bragg grating (FBG) is a type of distributed Bragg reflector constructed in a short segment of optical fiber that reflects particular wavelengths of light and transmits all others. This is achieved by creating a periodic variation in the refractive index of the fiber core, which generates a wavelength-specific dielectric mirror. Hence a fiber Bragg grating can be used as an inline optical fiber to block certain wavelengths, can be used for sensing applications, or it can be used as wavelength-specific reflector. History The first in-fiber Bragg grating was demonstrated by Ken Hill in 1978. Initially, the gratings were fabricated using a visible laser propagating along the fiber core. In 1989, Gerald Meltz and colleagues demonstrated the much more flexible transverse holographic inscription technique where the laser illumination came from the side of the fiber. This technique uses the interference pattern of ultraviolet laser light to create the periodic structure o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surfaces with which it comes into contact. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upper limit of audio frequencies and the lower limit of infrared frequencies; these are the frequencies at which energy from an oscillating current can radiate off a conductor into space as radio waves. Different sources specify different upper and lower bounds for the frequency range. Electric current Electric currents that oscillate at radio frequencies (RF currents) have special properties not shared by direct current or lower audio frequency alternating current, such as the 50 or 60 Hz current used in electrical power distribution. * Energy from RF currents in conductors can radiate into space as electromagnetic waves ( radio waves). This is the basis of radio technology. * RF current does not penetrate deeply into ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addressed Fiber Bragg Structure
An addressed fiber Bragg structure (AFBS) is a fiber Bragg grating, the optical frequency response of which includes two narrowband components with the frequency spacing between them (which is the address frequency of the AFBS) being in the radio frequency (RF) range. The frequency spacing (the address frequency) is unique for every AFBS in the interrogation circuit and does not change when the AFBS is subjected to strain or temperature variation. An addressed fiber Bragg structure can perform triple function in fiber-optic sensor systems: a sensor, a shaper of double-frequency probing radiation, and a multiplexor. The key feature of AFBS is that it enables the definition of its central wavelength without scanning its spectral response, as opposed to conventional fiber Bragg gratings (FBG), which are probed using optoelectronic interrogators. An interrogation circuit of AFBS is significantly simplified in comparison with conventional interrogators and consists of a broadband ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-period Fiber Grating
A long-period fiber grating couples light from a guided mode into forward propagating cladding modes where it is lost due to absorption and scattering. The coupling from the guided mode to cladding modes is wavelength dependent so we can obtain a spectrally selective loss. It is an optical fiber structure with the properties periodically varying along the fiber, such that the conditions for the interaction of several copropagating modes are satisfied. The period of such a structure is of the order of a fraction of a millimeter. In contrast to the fiber Bragg gratings, LPFGs couple copropagating modes with close propagation constants; therefore, the period of such a grating can considerably exceed the wavelength of radiation propagating in the fiber. Because the period of an LPFG is much larger than the wavelength, LPFGs are relatively simple to manufacture. Since LPFGs couple copropagating modes, their resonances can only be observed in transmission spectra. The transmission spect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
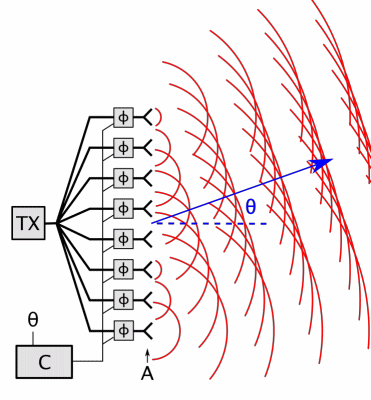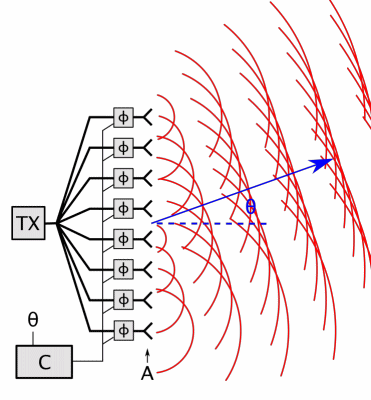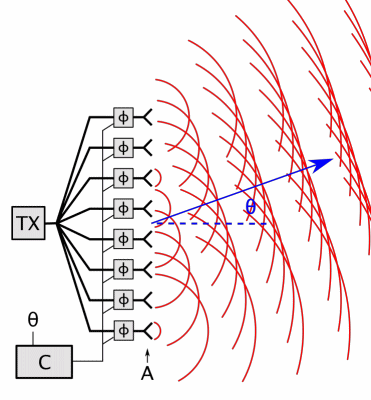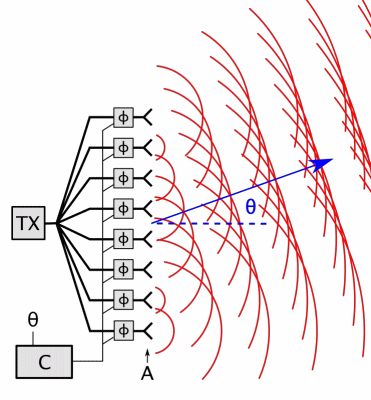
Phased-array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antennas. In a simple array antenna, the radio frequency current from the transmitter is fed to multiple individual antenna elements with the proper phase relationship so that the radio waves from the separate elements combine ( superpose) to form beams, to increase power radiated in desired directions and suppress radiation in undesired directions. In a phased array, the power from the transmitter is fed to the radiating elements through devices called ''phase shifters'', controlled by a computer system, which can alter the phase or signal delay electronically, thus steering the beam of radio waves to a different direction. Since the size of an antenna array must extend many wavelengths to achieve the high gain needed for narrow be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dispersion (optics)
In optics, and by analogy other branches of physics dealing with wave propagation, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency; sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used for specificity to optics in particular. A medium having this common property may be termed a dispersive medium (plural ''dispersive media''). Although the term is used in the field of optics to describe light and other electromagnetic waves, dispersion in the same sense can apply to any sort of wave motion such as acoustic dispersion in the case of sound and seismic waves, and in gravity waves (ocean waves). Within optics, dispersion is a property of telecommunication signals along transmission lines (such as microwaves in coaxial cable) or the pulses of light in optical fiber. Physically, dispersion translates in a loss of kinetic energy through absorption. In optics, one important and familiar consequence of dispersion is the change in the angle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirp
A chirp is a signal in which the frequency increases (''up-chirp'') or decreases (''down-chirp'') with time. In some sources, the term ''chirp'' is used interchangeably with sweep signal. It is commonly applied to sonar, radar, and laser systems, and to other applications, such as in spread-spectrum communications (see chirp spread spectrum). This signal type is biologically inspired and occurs as a phenomenon due to dispersion (a non-linear dependence between frequency and the propagation speed of the wave components). It is usually compensated for by using a matched filter, which can be part of the propagation channel. Depending on the specific performance measure, however, there are better techniques both for radar and communication. Since it was used in radar and space, it has been adopted also for communication standards. For automotive radar applications, it is usually called linear frequency modulated waveform (LFMW). In spread-spectrum usage, surface acoustic wave (SA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theory
A theory is a rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the results of such thinking. The process of contemplative and rational thinking is often associated with such processes as observational study or research. Theories may be scientific, belong to a non-scientific discipline, or no discipline at all. Depending on the context, a theory's assertions might, for example, include generalized explanations of how nature works. The word has its roots in ancient Greek, but in modern use it has taken on several related meanings. In modern science, the term "theory" refers to scientific theories, a well-confirmed type of explanation of nature, made in a way consistent with the scientific method, and fulfilling the criteria required by modern science. Such theories are described in such a way that scientific tests should be able to provide empirical support for it, or empirical contradiction (" falsify") of it. Scientific theories are the most reliable, rigorous, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Laser
A fiber laser (or fibre laser in British English) is a laser in which the active gain medium is an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as erbium, ytterbium, neodymium, dysprosium, praseodymium, thulium and holmium. They are related to doped fiber amplifiers, which provide light amplification without lasing. Fiber nonlinearities, such as stimulated Raman scattering or four-wave mixing can also provide gain and thus serve as gain media for a fiber laser. Advantages and applications An advantage of fiber lasers over other types of lasers is that the laser light is both generated and delivered by an inherently flexible medium, which allows easier delivery to the focusing location and target. This can be important for laser cutting, welding, and folding of metals and polymers. Another advantage is high output power compared to other types of laser. Fiber lasers can have active regions several kilometers long, and so can provide very high optical gain. They can s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |