|
Boerdijk–Coxeter Helix
The Boerdijk–Coxeter helix, named after H. S. M. Coxeter and A. H. Boerdijk, is a linear stacking of regular tetrahedra, arranged so that the edges of the complex that belong to only one tetrahedron form three intertwined helices. There are two chiral forms, with either clockwise or counterclockwise windings. Unlike any other stacking of Platonic solids, the Boerdijk–Coxeter helix is not rotationally repetitive in 3-dimensional space. Even in an infinite string of stacked tetrahedra, no two tetrahedra will have the same orientation, because the helical pitch per cell is not a rational fraction of the circle. However, modified forms of this helix have been found which are rotationally repetitive, and in 4-dimensional space this helix repeats in rings of exactly 30 tetrahedral cells that tessellate the 3-sphere surface of the 600-cell, one of the six regular convex polychora. Buckminster Fuller named it a ''tetrahelix'' and considered them with regular and irregular tetrahe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coxeter Helix 3 Colors
Harold Scott MacDonald "Donald" Coxeter, (9 February 1907 – 31 March 2003) was a British and later also Canadian geometer. He is regarded as one of the greatest geometers of the 20th century. Biography Coxeter was born in Kensington to Harold Samuel Coxeter and Lucy (). His father had taken over the family business of Coxeter & Son, manufacturers of surgical instruments and compressed gases (including a mechanism for anaesthetising surgical patients with nitrous oxide), but was able to retire early and focus on sculpting and baritone singing; Lucy Coxeter was a portrait and landscape painter who had attended the Royal Academy of Arts. A maternal cousin was the architect Sir Giles Gilbert Scott. In his youth, Coxeter composed music and was an accomplished pianist at the age of 10. Roberts, Siobhan, ''King of Infinite Space: Donald Coxeter, The Man Who Saved Geometry'', Walker & Company, 2006, He felt that mathematics and music were intimately related, outlining his ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
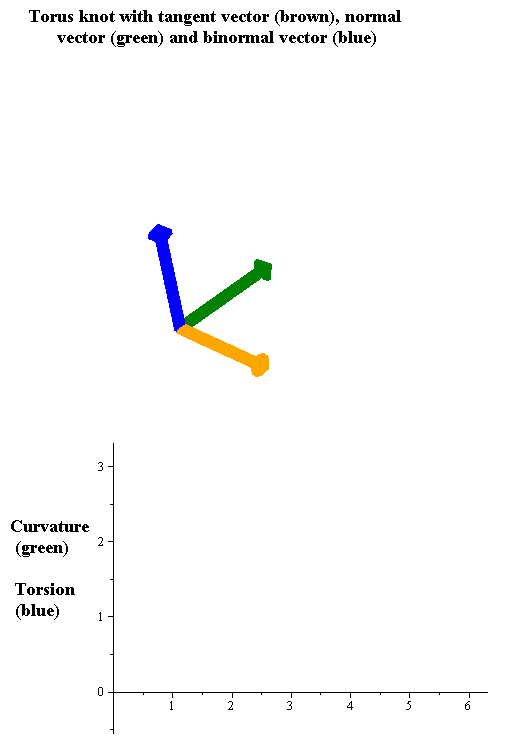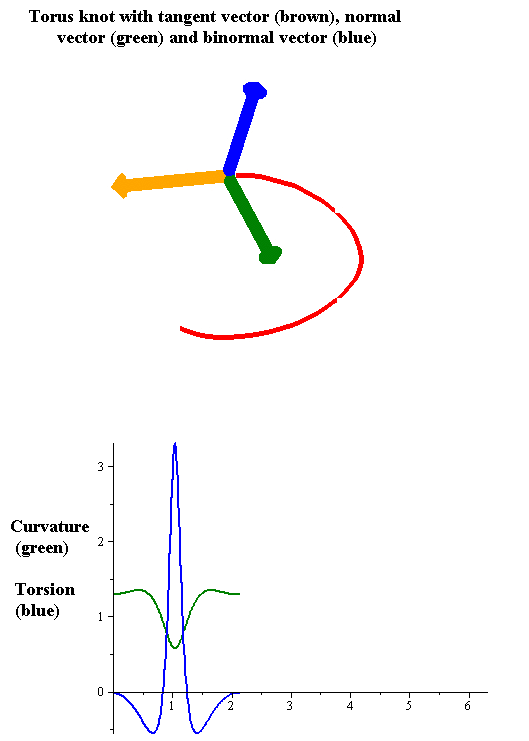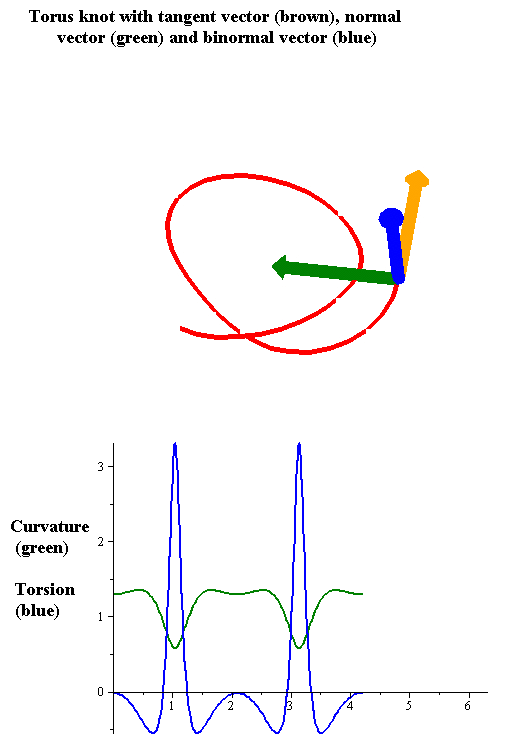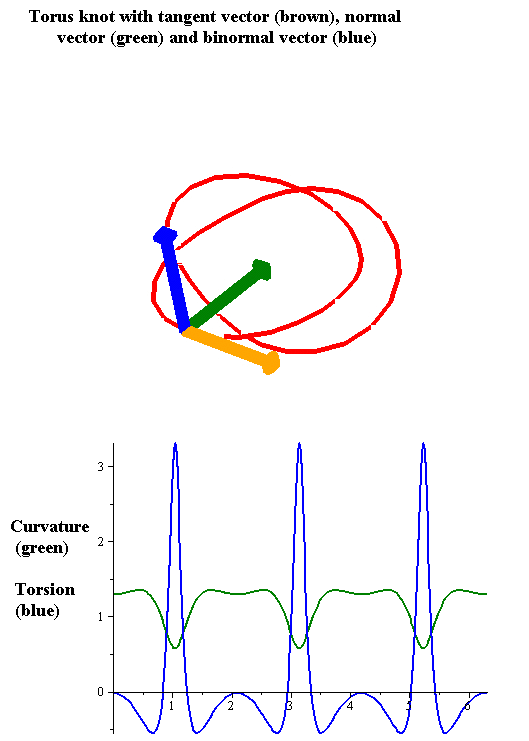
Torsion Of A Curve
In the differential geometry of curves in three dimensions, the torsion of a curve measures how sharply it is twisting out of the osculating plane. Taken together, the curvature and the torsion of a space curve are analogous to the curvature of a plane curve. For example, they are coefficients in the system of differential equations for the Frenet frame given by the Frenet–Serret formulas. Definition Let be a space curve parametrized by arc length and with the unit tangent vector . If the curvature of at a certain point is not zero then the principal normal vector and the binormal vector at that point are the unit vectors : \mathbf=\frac, \quad \mathbf=\mathbf\times\mathbf respectively, where the prime denotes the derivative of the vector with respect to the parameter . The torsion measures the speed of rotation of the binormal vector at the given point. It is found from the equation : \mathbf' = -\tau\mathbf. which means : \tau = -\mathbf\cdot\mathbf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroidal Polyhedron
In geometry, a toroidal polyhedron is a polyhedron which is also a toroid (a -holed torus), having a topological genus () of 1 or greater. Notable examples include the Császár and Szilassi polyhedra. Variations in definition Toroidal polyhedra are defined as collections of polygons that meet at their edges and vertices, forming a manifold as they do. That is, each edge should be shared by exactly two polygons, and at each vertex the edges and faces that meet at the vertex should be linked together in a single cycle of alternating edges and faces, the link of the vertex. For toroidal polyhedra, this manifold is an orientable surface. Some authors restrict the phrase "toroidal polyhedra" to mean more specifically polyhedra topologically equivalent to the (genus 1) torus. In this area, it is important to distinguish embedded toroidal polyhedra, whose faces are flat polygons in three-dimensional Euclidean space that do not cross themselves or each other, from abstract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penta Pyramid Helix
Penta may refer to: Places * , an Italian hamlet (') of Fisciano, Salerno * Penta-di-Casinca, a French municipality of Corsica * Penta, Chhattisgarh, a town in Dantewada district of Chhattisgarh, India * , a small river in Lithuania Other * Penta, a video game character in ''Antarctic Adventure'' * Penta Penguin, a video game character in the ''Crash Bandicoot'' series * Pena Transportes Aéreos, a defunct Brazilian airline * Penta engine, a piston engine design * Pentagón Jr., a luchador also called Penta El Zero Miedo * Penta Water, a brand of bottled water * Volvo Penta, a subsidiary of Volvo * Penta Investments, a Slovak private equity and investment group * The herbaceous vine ''Gynostemma pentaphyllum'', or ''jiaogulan'' * penta-, Greek numeral prefix meaning "five" * Pentachlorophenol Pentachlorophenol (PCP) is an organochlorine compound used as a pesticide and a disinfectant. First produced in the 1930s, it is marketed under many trade names. It can be found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentagonal Pyramid
In geometry, a pentagonal pyramid is a pyramid with a pentagonal base upon which are erected five triangular faces that meet at a point (the apex). Like any pyramid, it is self- dual. The ''regular'' pentagonal pyramid has a base that is a regular pentagon and lateral faces that are equilateral triangles. It is one of the Johnson solids (). It can be seen as the "lid" of an icosahedron; the rest of the icosahedron forms a gyroelongated pentagonal pyramid, More generally an order-2 vertex-uniform pentagonal pyramid can be defined with a regular pentagonal base and 5 isosceles triangle sides of any height. Cartesian coordinates The pentagonal pyramid can be seen as the "lid" of a regular icosahedron; the rest of the icosahedron forms a gyroelongated pentagonal pyramid, ''J''11. From the Cartesian coordinates of the icosahedron, Cartesian coordinates for a pentagonal pyramid with edge length 2 may be inferred as :(1,0,\tau),\,(-1,0,\tau),\,(0,\tau,1),\,(\tau,1,0),(\tau, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Pyramid Helix
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90- degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length adjacent sides. It is the only regular polygon whose internal angle, central angle, and external angle are all equal (90°), and whose diagonals are all equal in length. A square with vertices ''ABCD'' would be denoted . Characterizations A convex quadrilateral is a square if and only if it is any one of the following: * A rectangle with two adjacent equal sides * A rhombus with a right vertex angle * A rhombus with all angles equal * A parallelogram with one right vertex angle and two adjacent equal sides * A quadrilateral with four equal sides and four right angles * A quadrilateral where the diagonals are equal, and are the perpendicular bisectors of each other (i.e., a rhombus with equal diagonals) * A convex quadrilateral with success ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectified 600-cell
In geometry, the rectified 600-cell or rectified hexacosichoron is a convex uniform 4-polytope composed of 600 regular octahedra and 120 icosahedra cells. Each edge has two octahedra and one icosahedron. Each vertex has five octahedra and two icosahedra. In total it has 3600 triangle faces, 3600 edges, and 720 vertices. Containing the cell realms of both the regular 120-cell and the regular 600-cell, it can be considered analogous to the polyhedron icosidodecahedron, which is a rectified icosahedron and rectified dodecahedron. The vertex figure of the rectified 600-cell is a uniform pentagonal prism. Semiregular polytope It is one of three semiregular 4-polytopes made of two or more cells which are Platonic solids, discovered by Thorold Gosset in his 1900 paper. He called it a ''octicosahedric'' for being made of octahedron and icosahedron cells. E. L. Elte identified it in 1912 as a semiregular polytope, labeling it as tC600. Alternate names * octicosahedric (Thorold Gos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex Configuration
In geometry, a vertex configurationCrystallography of Quasicrystals: Concepts, Methods and Structures by Walter Steurer, Sofia Deloudi, (2009) pp. 18–20 and 51–53Physical Metallurgy: 3-Volume Set, Volume 1 edited by David E. Laughlin, (2014) pp. 16–20 is a shorthand notation for representing the of a or |
Square Pyramid
In geometry, a square pyramid is a pyramid having a square base. If the apex is perpendicularly above the center of the square, it is a right square pyramid, and has symmetry. If all edge lengths are equal, it is an equilateral square pyramid, the Johnson solid General square pyramid A possibly oblique square pyramid with base length ''l'' and perpendicular height ''h'' has volume: :V=\frac l^2 h. Right square pyramid In a right square pyramid, all the lateral edges have the same length, and the sides other than the base are congruent isosceles triangles. A right square pyramid with base length ''l'' and height ''h'' has surface area and volume: :A=l^2+l\sqrt, :V=\frac l^2 h. The lateral edge length is: :\sqrt; the slant height is: :\sqrt. The dihedral angles are: :*between the base and a side: :::\arctan \left(\right); :*between two sides: :::\arccos \left(\right). Equilateral square pyramid, Johnson solid J1 If all edges have the same length, then the sides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-cell 5-ring Net
In geometry, the 5-cell is the convex 4-polytope with Schläfli symbol . It is a 5-vertex four-dimensional object bounded by five tetrahedral cells. It is also known as a C5, pentachoron, pentatope, pentahedroid, or tetrahedral pyramid. It is the 4-simplex (Coxeter's \alpha_4 polytope), the simplest possible convex 4-polytope, and is analogous to the tetrahedron in three dimensions and the triangle in two dimensions. The 5-cell is a 4-dimensional pyramid with a tetrahedral base and four tetrahedral sides. The regular 5-cell is bounded by five regular tetrahedra, and is one of the six regular convex 4-polytopes (the four-dimensional analogues of the Platonic solids). A regular 5-cell can be constructed from a regular tetrahedron by adding a fifth vertex one edge length distant from all the vertices of the tetrahedron. This cannot be done in 3-dimensional space. The regular 5-cell is a solution to the problem: ''Make 10 equilateral triangles, all of the same size, using 10 matc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16-cell 8-ring Net4
In geometry, the 16-cell is the regular convex 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol . It is one of the six regular convex 4-polytopes first described by the Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli in the mid-19th century. It is also called C16, hexadecachoron, or hexdecahedroid .Matila Ghyka, ''The Geometry of Art and Life'' (1977), p.68 It is a part of an infinite family of polytopes, called cross-polytopes or ''orthoplexes'', and is analogous to the octahedron in three dimensions. It is Coxeter's \beta_4 polytope. Conway's name for a cross-polytope is orthoplex, for ''orthant complex''. The dual polytope is the tesseract (4-cube), which it can be combined with to form a compound figure. The 16-cell has 16 cells as the tesseract has 16 vertices. Geometry The 16-cell is the second in the sequence of 6 convex regular 4-polytopes (in order of size and complexity). Each of its 4 successor convex regular 4-polytopes can be constructed as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
600-cell Coxeter Helix-ring
6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number. In mathematics Six is the smallest positive integer which is neither a square number nor a prime number; it is the second smallest composite number, behind 4; its proper divisors are , and . Since 6 equals the sum of its proper divisors, it is a perfect number; 6 is the smallest of the perfect numbers. It is also the smallest Granville number, or \mathcal-perfect number. As a perfect number: *6 is related to the Mersenne prime 3, since . (The next perfect number is 28.) *6 is the only even perfect number that is not the sum of successive odd cubes. *6 is the root of the 6-aliquot tree, and is itself the aliquot sum of only one other number; the square number, . Six is the only number that is both the sum and the product of three consecutive positive numbers. Unrelated to 6's being a perfect number, a Golomb ruler of length 6 is a "perfect ruler". Six is a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |