|
Battle Of Spartivento
The Battle of Cape Spartivento, known as the Battle of Cape Teulada in Italy, was a naval battle during the Battle of the Mediterranean in the Second World War, fought between naval forces of the Royal Navy and the Italian ''Regia Marina'' on 27 November 1940. Origins On the night of 11 November 1940, the British incapacitated or destroyed half of the Italian fleet's battleships in a daring aerial assault as they lay at rest at Taranto. Until then, the Italians had left their capital ships in harbour, hoping its mere presence as a fleet in being would deter British shipping through the area, though they would not decline battle if given the opportunity.Greene & Massignani, p. 116 Six days later, on the night of 17 November, an Italian force consisting of two battleships ( and ) and a number of supporting units attempted to intercept two British aircraft carriers, and and their cruiser escorts, who were ''en route'' to Malta in an attempt to provide planes to reinforce that isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Mediterranean
The Battle of the Mediterranean was the name given to the naval campaign fought in the Mediterranean Sea during World War II, from 10 June 1940 to 2 May 1945. For the most part, the campaign was fought between the Kingdom of Italy, Italian Regia Marina, Royal Navy (''Regia Marina''), supported by other Axis Powers, Axis naval and air forces, and the United Kingdom, British Royal Navy, supported by other Allies of World War II, Allied naval forces, such as Australia, the Netherlands, Poland and Kingdom of Greece, Greece. American naval and air units joined the Allied side in 1942. Each side had three overall objectives in this battle. The first was to attack the supply lines of the other side. The second was to keep open the supply lines to their own armies in North Africa. The third was to destroy the ability of the opposing navy to wage war at sea. Outside of the Pacific War, Pacific theatre, the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean saw the largest conventional naval warfare acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleet In Being
In naval warfare, a "fleet in being" is a naval force that extends a controlling influence without ever leaving port. Were the fleet to leave port and face the enemy, it might lose in battle and no longer influence the enemy's actions, but while it remains safely in port, the enemy is forced to continually deploy forces to guard against it. A "fleet in being" can be part of a sea denial doctrine, but not one of sea control. Use of the term The term was first used in 1690 when Lord Torrington, commander of the Royal Navy forces in the English Channel, found himself facing a stronger French fleet. He proposed avoiding a sea battle, except under very favourable conditions, until he could be reinforced. By thus keeping his "fleet in being", he could maintain an active threat which would force the enemy to remain in the area and prevent them from taking the initiative elsewhere. Secondary use Rudyard Kipling published a series of articles about the British Channel Fleet under the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chetaïbi
Chetaïbi ( ar, شطايبي; ber, Ceṭṭaybi) (formerly Herbillon) is a small fishing port in Annaba Province, Algeria located on a peninsula west of Annaba. Geography The commune of Chetaïbi is located about 62 km northwest of the wilayah of Annaba. Chetaïbi has a fishing port. The main beaches of Chetaïbi are Chétaibi, Les sables d'or, Oued Leghnem, Fountaine Romaine, La Baie Ouest and Sidi Akkacha. The population of the town was 8035 in the 2008 census. The postal code of Chetaïbi is 23014. Gallery Chetaibi village.jpg, Village of Chetaïbi Chetaibi vue Aerienne.jpg, Aerial view of Chetaïbi Chetaibi.jpg, Chetaïbi Village chetaibi.jpg , Chetaïbi History During the Roman Empire there was a Roman town called Tacuata and based on the remaining ruins, it was a relatively important city. In Roman times it was the starting point of a road to the west, marked by Muharur ( Sidi Akkacha), Zacca (Cape de Fer), where red porphyry was mined and exported to Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floatplane
A floatplane is a type of seaplane with one or more slender floats mounted under the fuselage to provide buoyancy. By contrast, a flying boat uses its fuselage for buoyancy. Either type of seaplane may also have landing gear suitable for land, making the vehicle an amphibious aircraft. British usage is to call "floatplanes" "seaplanes" rather than use the term "seaplane" to refer to both floatplanes and flying boats. Use Since World War II and the advent of helicopters, advanced aircraft carriers and land-based aircraft, military seaplanes have stopped being used. This, coupled with the increased availability of civilian airstrips, have greatly reduced the number of flying boats being built. However, numerous modern civilian aircraft have floatplane variants, most of these are offered as third-party modifications under a supplemental type certificate (STC), although there are several aircraft manufacturers that build floatplanes from scratch. These floatplanes have found thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IMAM Ro
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, serve as community leaders, and provide religious guidance. Thus for Sunnis, anyone can study the basic Islamic sciences and become an Imam. For most Shia Muslims, the Imams are absolute infallible leaders of the Islamic community after the Prophet. Shias consider the term to be only applicable to the members and descendents of the ''Ahl al-Bayt'', the family of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. In Twelver Shiasm there are 14 infallibles, 12 of which are Imams, the final being Imam Mahdi who will return at the end of times. The title was also used by the Zaidi Shia Imams of Yemen, who eventually founded the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen (1918–1970). Sunni imams Sunni Islam does not have imams in the same sense as the Shi'a, an important di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandria grew rapidly and became a major centre of Hellenic civilisation, eventually replacing Memphis, in present-day Greater Cairo, as Egypt's capital. During the Hellenistic period, it was home to the Lighthouse of Alexandria, which ranked among the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, as well as the storied Library of Alexandria. Today, the library is reincarnated in the disc-shaped, ultramodern Bibliotheca Alexandrina. Its 15th-century seafront Qaitbay Citadel is now a museum. Called the "Bride of the Mediterranean" by locals, Alexandria is a popular tourist destination and an important industrial centre due to its natural gas and oil pipelines from Suez. The city extends about along the northern coast of Egypt, and is the largest city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force H
Force H was a British naval formation during the Second World War. It was formed in 1940, to replace French naval power in the western Mediterranean removed by the French armistice with Nazi Germany. The force occupied an odd place within the naval chain of command. Normal British practice was to have naval stations and fleets around the world, whose commanders reported to the First Sea Lord via a flag officer. Force H was based at Gibraltar but there was already a flag officer at the base, Flag Officer Commanding, North Atlantic. The commanding officer of Force H did not report to this Flag Officer but directly to the First Sea Lord, Admiral of the Fleet Sir Dudley Pound. Operation Catapult One of the first operations that Force H took part in was connected with the reason for its formation. French naval power still existed in the Mediterranean, and the British Government viewed it as a threat to British interests. It was feared that the Vichy government of Philippe Pét ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60 percent of the losses sustained by the Luftwaffe in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined their monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackburn Skua
The Blackburn B-24 Skua was a carrier-based low-wing, two-seater, single- radial engine aircraft by the British aviation company Blackburn Aircraft. It was the first Royal Navy carrier-borne all-metal cantilever monoplane aircraft, as well as the first dive bomber in Fleet Air Arm (FAA) service.Jackson 1968, p. 399. The aircraft took its name from the sea bird which 'divebombs' any potential predators that come too close to its nest. The Skua was designed during the mid-1930s to Specification O.27/34, it was a radical design for the era, combining the functions of a dive bomber and fighter. Its enclosed cockpit and monoplane configuration were obvious shifts from preceding FAA aircraft such as the Hawker Nimrod and Hawker Osprey biplanes. On 9 February 1937, the first prototype performed its maiden flight; it was ordered straight off the drawing board to accelerate its development. In November 1938, the Skua was introduced to FAA service; 33 aircraft were operational by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibraltar
) , anthem = " God Save the King" , song = " Gibraltar Anthem" , image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg , map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe , map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green , mapsize = , image_map2 = Gibraltar map-en-edit2.svg , map_alt2 = Map of Gibraltar , map_caption2 = Map of Gibraltar , mapsize2 = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = , established_title = British capture , established_date = 4 August 1704 , established_title2 = , established_date2 = 11 April 1713 , established_title3 = National Day , established_date3 = 10 September 1967 , established_title4 = Accession to EEC , established_date4 = 1 January 1973 , established_title5 = Withdrawal from the EU , established_date5 = 31 January 2020 , official_languages = English , languages_type = Spoken languages , languages = , capital = Westside, Gibraltar (de facto) , coordinates = , largest_settlement_type = largest district , l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
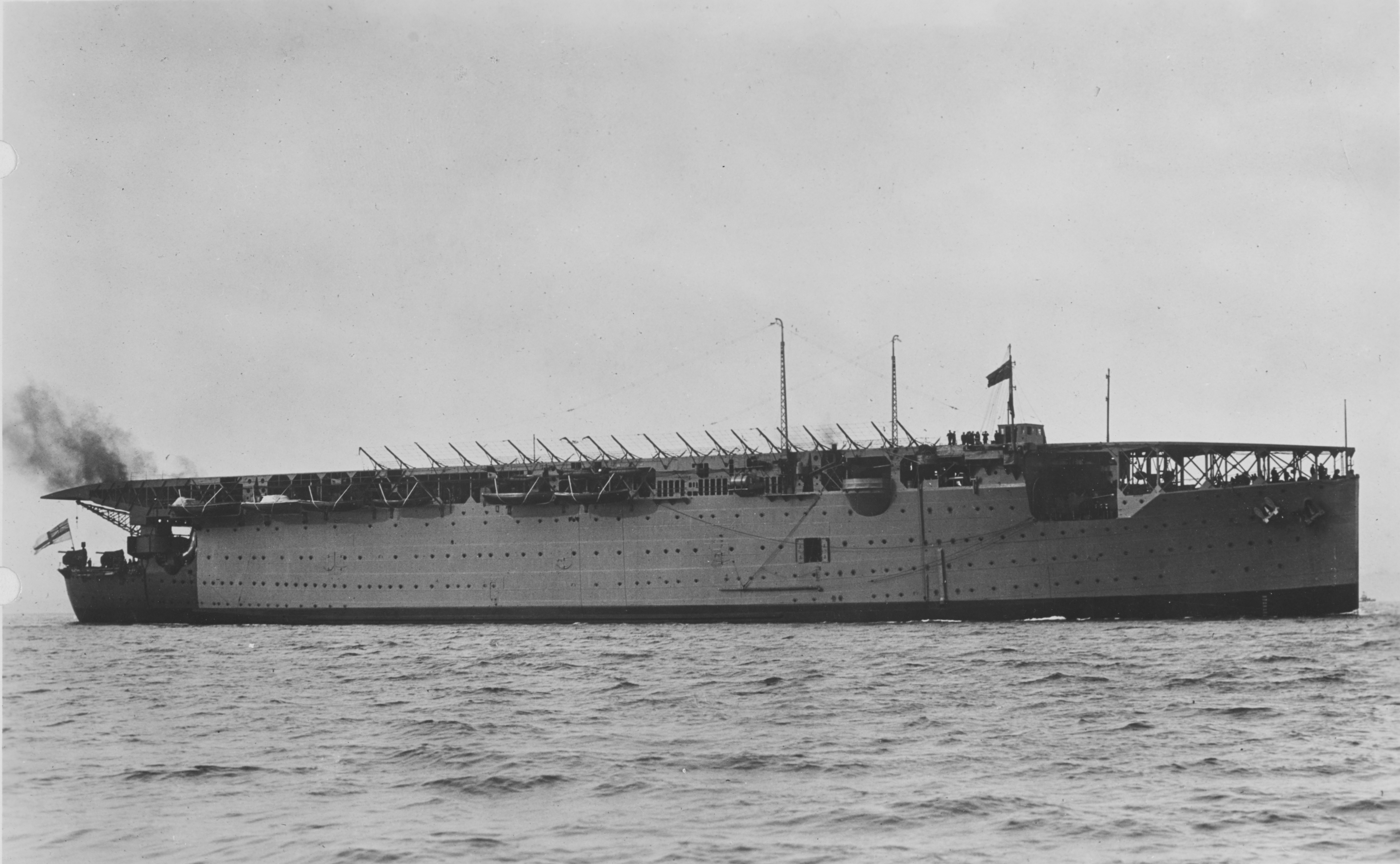
Operation White
Operation White (17 November 1940) was a British attempt to deliver 14 aircraft, 12 Hawker Hurricane fighters and two Blackburn Skua dive bombers, to Malta from the old aircraft carrier . The operation was thwarted by the presence of the Italian Fleet at sea, which prompted a premature take-off of the fighters; this combined with bad weather, led to only five aircraft reaching Malta. White was one of what became known as Club Runs that supplied fighters for the defence of Malta. Background Malta After the entry of Italy in the Second World War on 10 June 1940, the division of responsibility in the Mediterranean between the French Navy () in the west and the British in the eastern Mediterranean ended. To compensate for the withdrawal of the French, the Admiralty established Force H at Gibraltar. The British authorities designed a formal system of aircraft reinforcement to Malta, to assemble an adequate air defence and replace potential losses. Only two routes remained open a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_starboard_bow_view.jpg)


.jpg)