|
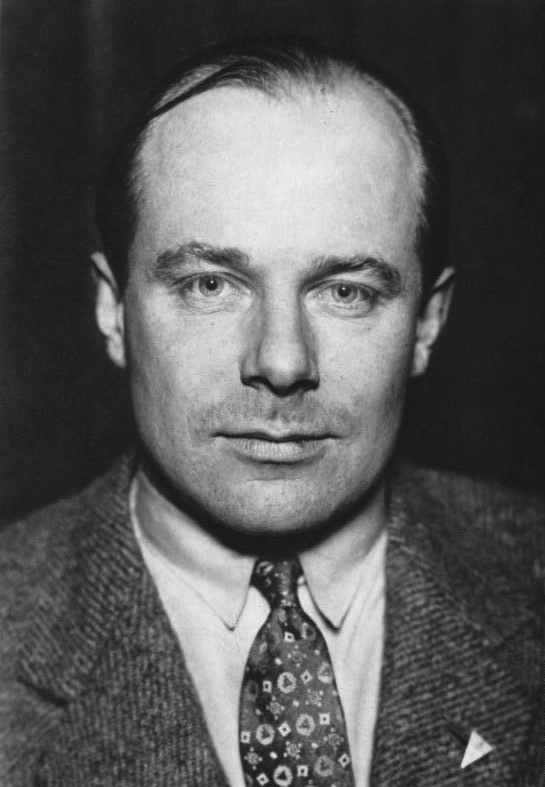
Battle Of Montcornet
The Battle of Montcornet, on 17 May 1940 took place during the Battle of France. The French 4e Division cuirassée (Colonel Charles de Gaulle), attacked the German-held village of Montcornet with over 200 tanks. The French drove off the Germans but later had to retreat due to lack of support and the intervention of the . Background On 10 May 1940, the Third Reich had launched a vast offensive against the Netherlands, Belgium and France. After the German breakthrough in the Battle of Sedan on 13 May, the Germans had driven the French troops to a hasty retreat. Prelude De Gaulle had just taken command of the new (4e DCr) on 12 May as the Germans were fighting to break through. That day, with three tank battalions assembled, less than a third of his paper strength, he was summoned to headquarters and told to attack to gain time for the Sixth Army (General Robert Touchon) to redeploy from the Maginot Line to the Aisne; it was his chance to implement his ideas of tank warfare. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the German invasion of France during the Second World War. On 3 September 1939, France declared war on Germany following the German invasion of Poland. In early September 1939, France began the limited Saar Offensive and by mid-October had withdrawn to their start lines. German armies invaded Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands on 10 May 1940. Italy entered the war on 10 June 1940 and attempted an invasion of France. France and the Low Countries were conquered, ending land operations on the Western Front until the Normandy landings on 6 June 1944. In ''Fall Gelb'' ("Case Yellow"), German armoured units made a surprise push through the Ardennes and then along the Somme valley, cutting off and surrounding the Allied units that had advanced into Belgium to meet the German armies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabteilung'' of the Imperial Navy, had been disbanded in May 1920 in accordance with the terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles which banned Germany from having any air force. During the interwar period, German pilots were trained secretly in violation of the treaty at Lipetsk Air Base in the Soviet Union. With the rise of the Nazi Party and the repudiation of the Versailles Treaty, the ''Luftwaffe''s existence was publicly acknowledged on 26 February 1935, just over two weeks before open defiance of the Versailles Treaty through German rearmament and conscription would be announced on 16 March. The Condor Legion, a ''Luftwaffe'' detachment sent to aid Nationalist forces in the Spanish Civil War, provided the force with a valuable testing grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of French Military Equipment Of World War II
Uniforms and Protective equipment * Adrian helmet * Combat uniform (go to France section) Weapons * List of World War II weapons of France Utility vehicles * P107 * Laffly S15 * Laffly V15 * SOMUA MCG * Citroën U23 * Renault AGx Maginot Line * Maginot LineDonnell, Clayton. The Battle for the Maginot Line, 1940 (Pen and Sword, 2017). Aircraft * List of aircraft of the French Air Force during World War II A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby unio ... Ships * List of Classes of French ships of World War II References {{Reflist Military equipment of World War II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Abbeville
The Battle of Abbeville took place from 27 May to 4 June 1940, near Abbeville during the Battle of France in the Second World War. On 20 May, the 2nd Panzer Division advanced to Abbeville on the English Channel, overran the 25th Infantry Brigade of the 50th (Northumbrian) Infantry Division and captured the town at Only a few British survivors managed to retreat to the south bank of the Somme and at on 21 May, the III Battalion, Rifle Regiment 2 reached the coast, west of Noyelles-sur-Mer. The 1st Armoured Division (Major-General Roger Evans) arrived in France from 15 May without artillery, short of an armoured regiment and the infantry of the 1st Support Group, which had been diverted to Calais. From 27 May to 4 June, attacks by the Franco-British force south of the Abbeville bridgehead, held by the 2nd Panzer Division, then the 57th Infantry Division, recaptured about half of the area; the Allied forces lost many of their tanks and the Germans much of their infantry, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caumont-sur-Durance
Caumont-sur-Durance (, literally ''Caumont on Durance''; oc, Caumont de Durença) is a commune in the Vaucluse department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of Southeastern France. In 2017, it had a population of 4,885. Geography The river Calavon flows into the Durance in the commune. It is home to the Charterhouse of Bonpas (French: ''Chartreuse de Bonpas''), a former Carthusian priory and historic monument. See also * Communes of the Vaucluse department *Avignon – Provence Airport Avignon Provence Airport (french: Aéroport Avignon Provence, ) is an airport located in the city of Avignon and west of Caumont-sur-Durance, in the Vaucluse department of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region in France. Facilities The airp ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Caumontsurdurance Communes of Vaucluse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
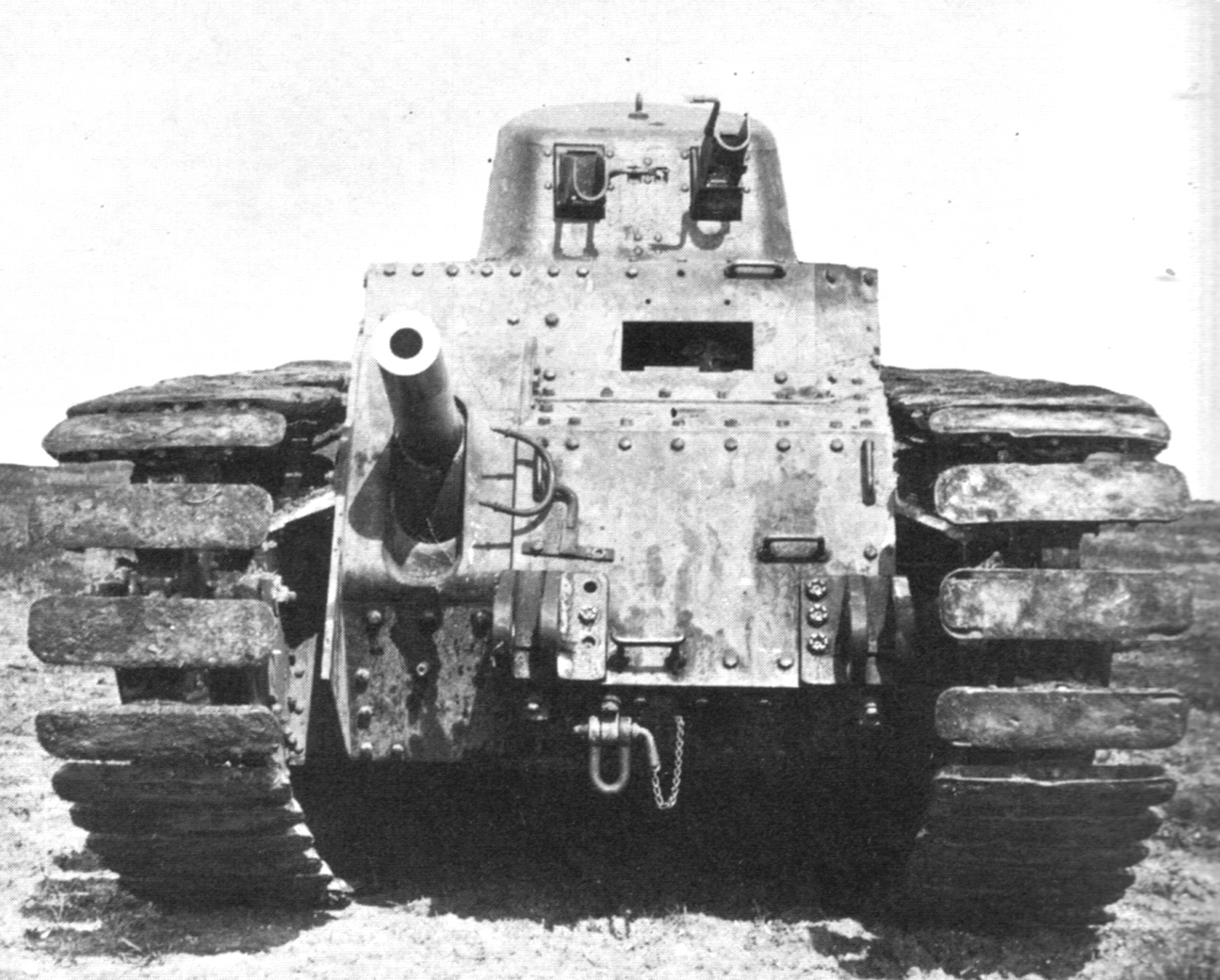
Char D2
The Char D2 was a French medium tank of the interwar period. In 1930, at a time the Char D1 had not even entered production, the Renault company agreed to build a better armoured version called the Char D2. By not using old-fashioned rivets, it was hoped to save weight. The tank should have the potential to serve as an alternative in the role of battle tank for the heavier Char B1, should the latter be forbidden by treaty. The failure of the armament limitation talks resulted in a severe reduction of the projected manufacture, now in the form of an interim tank. Organisational difficulties with Renault caused the actual production of a first series of fifty to be delayed to the years 1936 and 1937. A second series of fifty was ordered in 1938, despite indications that the type was mechanically unreliable, as a possible cheaper addition to the expensive Char B1. With the latter type, in case of war, only a limited number of armoured divisions for the Infantry Arm could be raised; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuka
The Junkers Ju 87 or Stuka (from ''Sturzkampfflugzeug'', "dive bomber") was a German dive bomber and ground-attack aircraft. Designed by Hermann Pohlmann, it first flew in 1935. The Ju 87 made its combat debut in 1937 with the Luftwaffe's Condor Legion during the Spanish Civil War of 1936–1939 and served the Axis in World War II from beginning to end (1939–1945). The aircraft is easily recognisable by its inverted gull wings and fixed spatted undercarriage. Upon the leading edges of its faired main gear legs were mounted ram-air sirens known as ', which became a propaganda symbol of German air power and of the so-called ''Blitzkrieg'' victories of 1939–1942, as well as providing Stuka pilots with audible feedback as to speed. The Stuka's design included several innovations, including automatic pull-up dive brakes under both wings to ensure that the aircraft recovered from its attack dive even if the pilot blacked out from the high g-forces. The Ju 87 operated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Char B1
The Char B1 was a French heavy tank manufactured before World War II. The Char B1 was a specialised break-through vehicle, originally conceived as a self-propelled gun with a 75 mm howitzer in the hull; later a 47 mm gun in a turret was added, to allow it to function also as a , a "battle tank" fighting enemy armour, equipping the armoured divisions of the Infantry Arm. Starting in the early twenties, its development and production were repeatedly delayed, resulting in a vehicle that was both technologically complex and expensive, and already obsolescent when real mass-production of a derived version, the Char B1 "bis", started in the late 1930s. A further up-armoured version, the Char B1 "ter", was only built in two prototypes. Among the most powerfully armed and armoured tanks of its day, the type was very effective in direct confrontations with German armour in 1940 during the Battle of France, but low speed and high fuel consumption made it ill-adapted to the wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth Army (France)
The Sixth Army (french: 6eme Armée) was a field army of the French Army during World War I and World War II. World War I The Sixth Army was formed 26 August 1914, composed of troops from various disparate French armies: two active army corps, the ( 4th and 7th respectively detached from the Third Army and First Army, the 5th and 6th groups of reserve divisions, the 45th and 37th Infantry Divisions, a native brigade and a cavalry corps. After Alexander von Kluck rotated his German First Army away from Paris to reinforce Karl von Bülow's German Second Army, Joseph Gallieni ordered the Sixth Army to attack von Kluck's forces. Although the German First Army counterattacked, this allowed John French's British Expeditionary Force to occupy a twenty-mile salient between the two armies beginning the First Battle of the Marne. France would end up contributing three corps to the opening attack of the Battle of the Somme (the 20th Army Corps, I Colonial and 35th Corps of the Sixth A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Sedan (1940)
The Battle of Sedan or Second Battle of Sedan (12–15 May 1940)Frieser 2005, p. 196. took place in the Second World War during the Battle of France in 1940. It was part of the German ''Wehrmacht''s operational plan codenamed ''Fall Gelb'' (Case Yellow) for an offensive through the hilly and forested Ardennes, to encircle the Allied armies in Belgium and north-eastern France. German Army Group A crossed the Meuse with the intention of capturing Sedan and pushing westwards towards the Channel coast, to trap the Allied forces that were advancing east into Belgium, as part of the Allied Dyle Plan. Sedan is situated on the east bank of the Meuse. Its capture would give the Germans a base from which to take the Meuse bridges and cross the river. The German divisions could then advance across the open and undefended French countryside to the English Channel. On 12 May, Sedan was captured without resistance and the Germans defeated the French defences around Sedan on the west bank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Belgium
The invasion of Belgium or Belgian campaign (10–28 May 1940), often referred to within Belgium as the 18 Days' Campaign (french: Campagne des 18 jours, nl, Achttiendaagse Veldtocht), formed part of the greater Battle of France, an offensive campaign by Germany during the Second World War. It took place over 18 days in May 1940 and ended with the German occupation of Belgium following the surrender of the Belgian Army. On 10 May 1940, Germany invaded Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and Belgium under the operational plan '' Fall Gelb'' (Case Yellow). The Allied armies attempted to halt the German Army in Belgium, believing it to be the main German thrust. After the French had fully committed the best of the Allied armies to Belgium between 10 and 12 May, the Germans enacted the second phase of their operation, a break-through, or sickle cut, through the Ardennes, and advanced toward the English Channel. The German Army ('' Heer'') reached the Channel after five days, encircl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |