|
Battle Of Aba
The Battle of Aba, which took place on August 12, 1881, was the opening battle of the Mahdist War. The incident saw Mahdist rebels, led by Muhammad Ahmad, who had proclaimed himself the Mahdi, rout Egyptian troops who had landed on Aba Island. Background In March 1881, Muhammad Ahmad, living on Aba Island on the White Nile, before his "inner circle" (which included Abdallahi ibn Muhammad, who would become known as "the Khalifa"), announced that he was the Mahdi. He based this off of a dream he had where he was visited by the Prophet Muhammad and Jesus Christ. The Governor-General of the Sudan, Ra'uf Pasha, soon sent Mohammad Bey Abu Sa'ud to investigate the situation. Arriving on Aba Island on August 7, 1881, Abu Sa'ud requested that Muhammad Ahmad come to Khartoum (the capital of Sudan) to meet with the Governor-General. The Mahdi refused and Abu Sa'ud warned him that he "must give up his claim to be the Mahdi" and then left the island. Battle After that meeting, an "arrest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahdist War
The Mahdist War ( ar, الثورة المهدية, ath-Thawra al-Mahdiyya; 1881–1899) was a war between the Mahdist Sudanese of the religious leader Muhammad Ahmad bin Abd Allah, who had proclaimed himself the "Mahdi" of Islam (the "Guided One"), and the forces of the Khedivate of Egypt, initially, and later the forces of Britain. Eighteen years of war resulted in the nominally joint-rule state of the Anglo-Egyptian Sudan (1899–1956), a ''de jure'' condominium of the British Empire and the Kingdom of Egypt in which Britain had ''de facto'' control over the Sudan. The Sudanese launched several unsuccessful invasions of their neighbours, expanding the scale of the conflict to include not only Britain and Egypt but also the Italian Empire, the Congo Free State and the Ethiopian Empire. The British participation in the war is called the Sudan campaign. Other names for this war include the Mahdist Revolt, the Anglo–Sudan War and the Sudanese Mahdist Revolt. Background Foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious leader; he is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religion. Most Christians believe he is the incarnation of God the Son and the awaited Messiah (the Christ) prophesied in the Hebrew Bible. Virtually all modern scholars of antiquity agree that Jesus existed historically. Research into the historical Jesus has yielded some uncertainty on the historical reliability of the Gospels and on how closely the Jesus portrayed in the New Testament reflects the historical Jesus, as the only detailed records of Jesus' life are contained in the Gospels. Jesus was a Galilean Jew who was circumcised, was baptized by John the Baptist, began his own ministry and was often referred to as "rabbi". Jesus debated with fellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving Sudan
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of The Mahdist War
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1881 In Sudan
Events January–March * January 1– 24 – Siege of Geok Tepe: Russian troops under General Mikhail Skobelev defeat the Turkomans. * January 13 – War of the Pacific – Battle of San Juan and Chorrillos: The Chilean army defeats Peruvian forces. * January 15 – War of the Pacific – Battle of Miraflores: The Chileans take Lima, capital of Peru, after defeating its second line of defense in Miraflores. * January 24 – William Edward Forster, chief secretary for Ireland, introduces his Coercion Bill, which temporarily suspends habeas corpus so that those people suspected of committing an offence can be detained without trial; it goes through a long debate before it is accepted February 2. * January 25 – Thomas Edison and Alexander Graham Bell form the Oriental Telephone Company. * February 13 – The first issue of the feminist newspaper ''La Citoyenne'' is published by Hubertine Auclert. * February 16 – The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
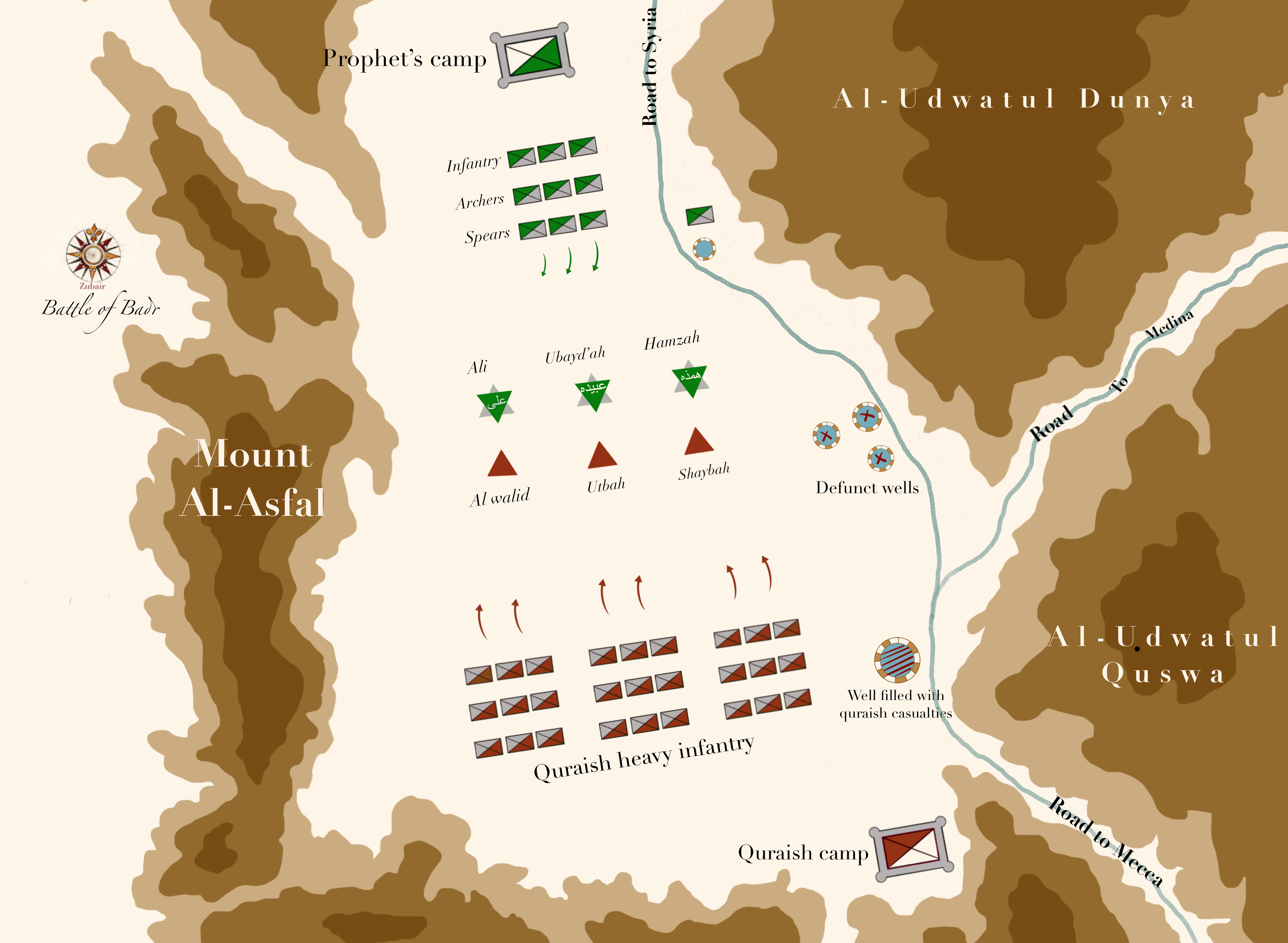
Battle Of Badr
The Battle of Badr ( ar, غَزْوَةُ بَدِرْ ), also referred to as The Day of the Criterion (, ) in the Qur'an and by Muslims, was fought on 13 March 624 CE (17 Ramadan, 2 AH), near the present-day city of Badr, Al Madinah Province in Saudi Arabia. Muhammad, commanding an army of his Sahaba, defeated an army of the Quraysh led by Amr ibn Hishām, better known as Abu Jahl. The battle marked the beginning of the six-year war between Muhammad and his tribe. Prior to the battle, the Muslims and the Meccans had fought several smaller skirmishes in late 623 and early 624. Muhammad took keen interest in capturing Meccan caravans after his migration to Medina, seeing it as repayment for his people, the Muhajirun. A few days before the battle, when he learnt of a Makkan caravan returning from the Levant led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb, Muhammad gathered a small expeditionary force to capture it. Abu Sufyan, learning of the Muslim plan to ambush his caravan, changed cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed tip. A slashing sword is more likely to be curved and to have a sharpened cutting edge on one or both sides of the blade. Many swords are designed for both thrusting and slashing. The precise definition of a sword varies by historical epoch and geographic region. Historically, the sword developed in the Bronze Age, evolving from the dagger; the earliest specimens date to about 1600 BC. The later Iron Age sword remained fairly short and without a crossguard. The spatha, as it developed in the Late Roman army, became the predecessor of the European sword of the Middle Ages, at first adopted as the Migration Period sword, and only in the High Middle Ages, developed into the classical arming sword with crossguard. The word '' sword'' conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastened to the shaft, such as bone, flint, obsidian, iron, steel, or bronze. The most common design for hunting or combat spears since ancient times has incorporated a metal spearhead shaped like a triangle, lozenge, or leaf. The heads of fishing spears usually feature barbs or serrated edges. The word '' spear'' comes from the Old English '' spere'', from the Proto-Germanic ''speri'', from a Proto-Indo-European root ''*sper-'' "spear, pole". Spears can be divided into two broad categories: those designed for thrusting as a melee weapon and those designed for throwing as a ranged weapon (usually referred to as javelins or darts). The spear has been used throughout human history both as a hunting and fishing tool and as a weapon. Along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoe (tool)
A hoe is an ancient and versatile agricultural and horticultural hand tool used to shape soil, remove weeds, clear soil, and harvest root crops. Shaping the soil includes piling soil around the base of plants (hilling), digging narrow furrows ( drills) and shallow trenches for planting seeds or bulbs. Weeding with a hoe includes agitating the surface of the soil or cutting foliage from roots, and clearing the soil of old roots and crop residues. Hoes for digging and moving soil are used to harvest root crops such as potatoes. Types There are many kinds of hoes of varied appearances and purposes. Some offer multiple functions while others have only a singular and specific purpose. There are two general types of hoe: draw hoes for shaping soil and scuffle hoes for weeding and aerating soil. A draw hoe has a blade set at approximately a right angle to the shaft. The user chops into the ground and then pulls (draws) the blade towards them. Altering the angle of the handl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merchant
A merchant is a person who trades in commodities produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Historically, a merchant is anyone who is involved in business or trade. Merchants have operated for as long as industry, commerce, and trade have existed. In 16th-century Europe, two different terms for merchants emerged: referred to local traders (such as bakers and grocers) and ( nl, koopman) referred to merchants who operated on a global stage, importing and exporting goods over vast distances and offering added-value services such as credit and finance. The status of the merchant has varied during different periods of history and among different societies. In modern times, the term ''merchant'' has occasionally been used to refer to a businessperson or someone undertaking activities (commercial or industrial) for the purpose of generating profit, cash flow, sales, and revenue using a combination of human, financial, intellectual and physical capita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing north from Lake Victoria, and the Blue Nile, flowing west from Lake Tana in Ethiopia. The place where the two Niles meet is known as ''al-Mogran'' or ''al-Muqran'' (; English: "The Confluence"). From there, the Nile continues north towards Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea. Divided by these two parts of the Nile, Khartoum is a tripartite metropolis with an estimated population of over five million people, consisting of Khartoum proper, and linked by bridges to Khartoum North ( ) and Omdurman ( ) to the west. Khartoum was founded in 1821 as part of Egypt, north of the ancient city of Soba. While the United Kingdom exerted power over Egypt, it left administration of the Sudan to it until Mahdist forces took over Khartoum. The British at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ra'uf Pasha
Muhammad Rauf Pasha (c.1832 – 1888) was an Egyptian soldier and colonial administrator who served in turn as governor of Equatoria and Harar, and governor general of Sudan. He was ineffective and did little to prevent the Mahdist movement develop in the Sudan, leading to establishment of the Mahdist State. Early career Mohammed Rauf Pasha had a Nubian father and an Abyssinian mother, and came from the menial underclass of Egypt. He rose in the army, accepting posts in a difficult region that most Egyptian officers did their best to avoid but which he saw as presenting opportunity. Rauf Pasha became a general in the Egyptian army. He had considerable experience in Sudan, but was considered mediocre by the British. One historian said dryly that he was envied "for his skill at baccarat". While a young officer Rauf Bey was chief of staff to Samuel Baker in Equatoria. On 23 January 1872 Baker left Rauf Bey with 340 men to garrison Ismailia while he undertook an expedition to the fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |