|
Burmese People
Burmese people or the Myanmar people () are citizens from Myanmar (Burma), irrespective of their ethnic or religious background. Myanmar is a multi-ethnic, multi-cultural and multi-lingual country. The Burmese government officially recognises 135 ethnic groups, who are grouped into eight 'national races,' namely the Bamar (Burmans), Shan, Karen, Rakhine (Arakanese), Mon, Kachin, Chin, and Kayah (Karenni). Many ethnic and ethnoreligious communities exist outside these defined groupings, such as the Burmese Chinese and Panthay, Burmese Indians, Anglo-Burmese, and Gurkhas. The 2014 Myanmar Census enumerated 51,486,253 persons. There is also a substantial Burmese diaspora, the majority of whom have settled in neighbouring Asian countries. Refugees and asylum seekers from Myanmar make up one of the world's five largest refugee populations. Terminology The term "Burmese people" is often used to refer to all citizens of Myanmar, regardless of their ethnic background ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burmese Speaking World Map 20250125015808
Burmese may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to Myanmar, a country in Southeast Asia * Burmese people * Burmese language * Burmese alphabet * Burmese cuisine * Burmese culture Animals * Burmese cat * Burmese chicken * Burmese (horse), a horse given to Queen Elizabeth II * Burmese pony, a breed of horse * Burmese python See also * * :Burmese people * Bamar people The Bamar people ( Burmese: ဗမာလူမျိုး, ''ba. ma lu myui:'' ) (formerly known as Burmese people or Burmans) are a Sino-Tibetan-speaking ethnic group native to Myanmar (formerly known as Burma). With an estimated population ..., the majority ethnic group in Myanmar * Burmese English, the dialect of English spoken in Myanmar/Burma * Bernese (other) {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism In Myanmar
Hinduism is the Religion in Myanmar, fourth-largest religion in Myanmar, being practised by 0.5% of the population of Myanmar. Hinduism is practised by about 890,000 people in Myanmar, and has been influenced by elements of Buddhism, with many Hindu temples in Myanmar housing statues of the Buddha. There is a sizable population of Hindus with the Myanmar Tamils and minority Bengali Hindus having the biggest population share. History Hinduism, along with Buddhism, arrived in Burma during ancient times. Both names of the country are rooted in Hinduism; Burma is the British colonial officials' phonetic equivalent for the first half of ''Brahma Desha'', the ancient name of the region.Toʻ Cinʻ Khu, , pp. iv-v Brahma is part of Hindu trinity, a deity with four heads. The name ''Myanmar'' is the regional language transliteration of ''Brahma'', where ''b'' and ''m'' are interchangeable. Arakan Mountains, Arakan (Rakhine) Yoma is a significant natural mountainous barrier between Burma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karenni People
The Karenni (, ), also known as the Kayah () or Kayah Li (Karenni language, Karenni: ), are a Karen people native to the Kayah State of Myanmar (Burma). According to a 1983 census, the Karenni consist of the following groups: Kayah, Geko Karen language, Geko (Kayan Ka Khaung, Gekho, Kayan Kadao), Geba Karen language, Geba (Kayan Gebar, Gaybar), Kayan people (Myanmar), Lahwi (Kayan Lahwi), Bre people, Bre, Manumanaw, Manu-Manau (Kayan Manumanao), Yintale, Yinbaw kayan kangan, Bwe Karen language, Bwe and Pa'O people, Pa'O. Several of the groups (Geko, Geba, Padaung, Yinbaw) belong to Kayan people (Myanmar), Kayan, a subgroup in region of Karenni. The groups Bre and Manu-Manau belong to the Kayaw subgroup. Karenni represent Kayah and the term Karennies is used to represent all nine tribes native to the Kayah state. Karennies consist of nine sub-tribes namely Kayah, Padaung (Kayan)(), Geko(), Geba(), Zayein(), Bre(), Manu-Manau(), Yintale() and Yinbaw(). Karenni States The K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chin People
The Chin peoples (, ) are collection of ethnic groups native to the Chin State, Myanmar that speak the Kuki-Chin-Mizo languages, which are closely related but mutually unintelligible. The Chin identity, as a pan-ethnic identity, is a modern construction, shaped by British rule, Christian missionary influence, and post-independence ethnic politics that has built upon older tribal and regional identities. Ethnonyms Chin (ချင်း, MLCTS: khyang:) is a pseudo-exonym, a Burmese language adaptation of the Asho Chin word ''khlong'' or ''khlaung'', which means "man" or "person." Burmese speakers approximated the Asho Chin word, and began to apply the exonym to all nearby groups residing in the Arakan Mountains and Chin Hills. The Burmese term first appeared in stone inscriptions dating to the reign of King Kyansittha in the 11th century. The term "Chin" is not universally accepted by all groups living in Chin State nor by all Kuki-Chin groups. Groups in the north pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kachin People
The Kachin peoples (, ; , ) are a collection of diverse ethnolinguistic groups inhabiting the Kachin Hills in northern Myanmar's Kachin State, as well as Yunnan Province in China, and the northeastern Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam. Approximately 1.5 million Kachin people live in this region. In contemporary usage, the Kachin peoples typically refer to a specific grouping of four to six ethnicities: the Jingpo, the Zaiwa, the Lashi/Lachik, the Lawngwaw/Maru, and to a lesser extent, the Rawang and the Lisu. Kachin identity is heterogenous and diverse, as it encompasses various ethnolinguistic groups who share overlapping territories, but do not all share coherent cultural practices and integrated social structures. Some definitions distinguish Kachin and Shan (Tai) peoples though some Kachin people have demonstrated the over-simplicity of the concept of lineage-based ethnic identity by culturally "becoming Shans". The most widely spoken Kachin language is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mon People
The Mon (; Thai Mon: ဂကူမည်; , ; , ) are an ethnic group who inhabit Lower Myanmar's Mon State, Kayin State, Kayah State, Tanintharyi Region, Bago Region, the Irrawaddy Delta, and several areas in Thailand (mostly in Pathum Thani province, Phra Pradaeng and Nong Ya Plong). The native language is Mon, which belongs to the Monic branch of the Austroasiatic language family and shares a common origin with the Nyah Kur language, which is spoken by the people of the same name that live in Northeastern Thailand. A number of languages in Mainland Southeast Asia are influenced by the Mon language, which is also in turn influenced by those languages. The Mon were one of the earliest to reside in Southeast Asia, and were responsible for the spread of Theravada Buddhism in Mainland Southeast Asia. The civilizations founded by the Mon were some of the earliest in Thailand as well as Myanmar and Laos. The Mon are regarded as a large exporter of Southeast Asian cultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karen People
The Karen ( ), also known as the Kayin, are an ethnolinguistic group of peoples who speak Karenic languages and are indigenous to southern and southeastern Myanmar, including the Irrawaddy Delta, Irrawaddy delta and Kayin State. The Karen account for around 6.69% of the Burmese population. The Karen consist of approximately 20 subgroups, the largest of whom are the S'gaw people, S'gaw and the Pwo peoples. Other Karenic-speaking peoples like the Pa'O people, Pa'O, Karenni people, Karenni, and the Kayan people (Myanmar), Kayan, have formed distinct identities. The ethnic identity of the Karen peoples has significantly been shaped by British colonial rule, Christian missionaries, Decolonization, decolonisation, and sociopolitical developments in Myanmar. The group as a whole is heterogeneous and disparate, as many Karenic ethnic groups do not share a common language, culture, religion, or material characteristics. A pan-Karen ethnic identity is a relatively modern creation, est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shan People
The Shan people (, , or , ), also known as the Tai Long (တႆးလူင်, ) or Tai Yai, are a Tai ethnic group of Southeast Asia. The Shan are the biggest minority of Burma (Myanmar) and primarily live in the Shan State, but also inhabit parts of Mandalay Region, Kachin State, Kayah State, Sagaing Region and Kayin State, and in adjacent regions of China ( Dai people), Laos, Assam and Meghalaya (Ahom people), Cambodia ( Kula people), Vietnam and Thailand. Though no reliable census has been taken in Burma since 1935, the Shan are estimated to number 4–6 million, with CIA Factbook giving an estimate of five million spread throughout Myanmar which is about 10% of the overall Burmese population. 'Shan' is a generic term for all Tai-speaking peoples within Myanmar (Burma). The capital of Shan State is Taunggyi, the fifth-largest city in Myanmar with about 390,000 people. Other major cities include Thibaw (Hsipaw), Lashio, Kengtung and Tachileik. Etymology The Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamar People
The Bamar people ( Burmese: ဗမာလူမျိုး, ''ba. ma lu myui:'' ) (formerly known as Burmese people or Burmans) are a Sino-Tibetan-speaking ethnic group native to Myanmar (formerly known as Burma). With an estimated population of around 35 million people, they are the largest ethnic group in Myanmar, accounting for 68.78% of the country's total population. The geographic homeland of the Bamar is the Irrawaddy River basin. The Bamar speak the Burmese language which serves as the national language and lingua franca of Myanmar. Ethnonyms In the Burmese language, ''Bamar'' (, also transcribed ''Bama'') and ''Myanmar'' (, also transliterated ''Mranma'' and transcribed ''Myanma'') have historically been interchangeable endonyms. Burmese is a diglossic language; "Bamar" is the diglossic low form of "Myanmar," which is the diglossic high equivalent. The term "Myanmar" is extant to the early 1100s, first appearing on a stone inscription, where it was used as a cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
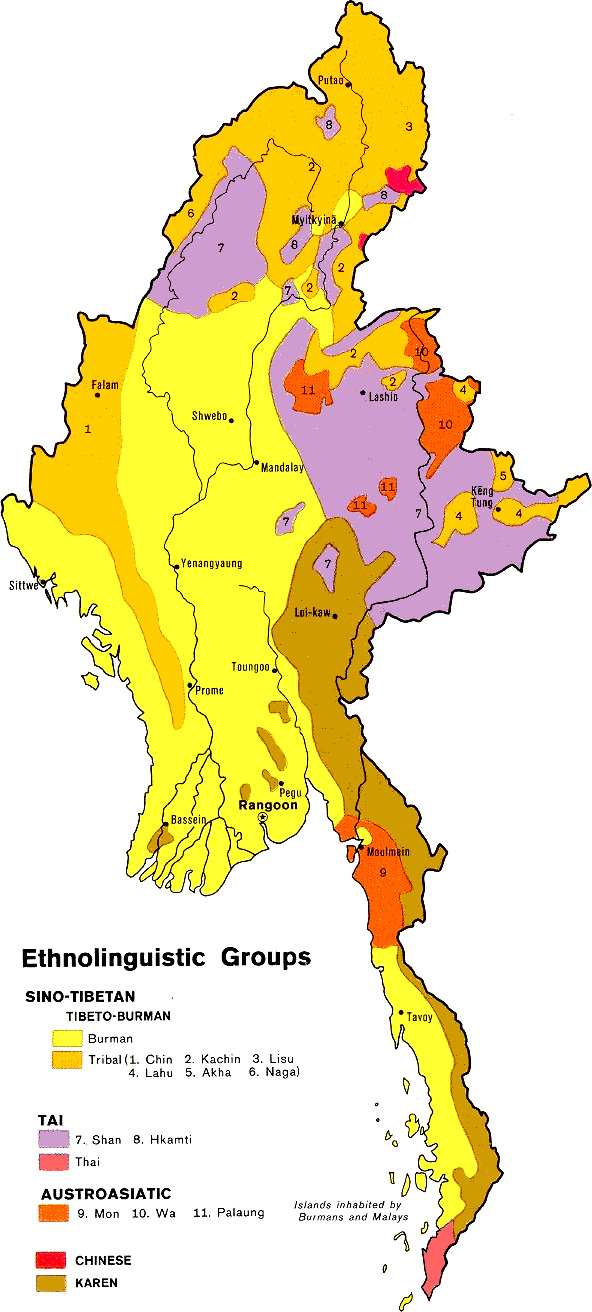
List Of Ethnic Groups In Myanmar
Myanmar (Burma) is an ethnically diverse nation with 135 distinct ethnic groups officially recognised by the Burmese government, which are grouped into eight "major national ethnic races" — the Bamar people, Bamar, Karen people, Kayin, Rohingya people, Arakanese, Shan people, Shan, Mon people, Mon, Chin people, Chin, Kachin people, Kachin, and Karenni people, Karenni. The Bamar (Burman) comprise about 68% of the population, and the rest belonging to numerous major and minor ethnic and language groups. The "major national ethnic races" are grouped primarily according to geographic region rather than ethnolinguistic affiliation. For example, the Shan national race includes 33 ethnic groups that live in Shan State and speak languages in at least four language families. Myanmar's contemporary politics around ethnicity surround treating ethnicity as a minoritising discourse, pitting a "pan-ethnic" national identity against minority groups. Often ethnicity identities in practice ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politics Of Myanmar
Myanmar (Names of Myanmar, formerly Burma) () operates ''de jure'' as a unitary state, unitary assembly-independent republic under its 2008 Constitution of Myanmar, 2008 constitution. On 1 February 2021, Tatmadaw, Myanmar's military took over the government in 2021 Myanmar coup d'état, a coup, causing ongoing 2021 Myanmar protests, anti-coup protests. Political conditions Early history The first known city-states emerged in central Myanmar in the second century AD. They were founded by Tibeto-Burman-speaking migrants from present-day Yunnan. The history of Myanmar as a unified entity, formerly called Burma, began with the Pagan Kingdom in 849. In 1057, Anawrahta, King Anawrahta founded the first unified Myanmar state at Bagan. In 1287, the Bagan Kingdom, Bagan kingdom collapsed following recurring Mongol invasions, leading to 250 years of political divide. In the time period between 1510 and 1752, the area was united as Burma by the Toungoo dynasty, which was the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |