|
Bulat Steel
Bulat is a type of steel alloy known in Russia from medieval times; it was regularly mentioned in Russian legends as the material of choice for cold steel. The name ' is a Russian transliteration of the Persian word ', meaning steel. This type of steel was used by the armies of nomadic peoples. Bulat steel was the main type of steel used for swords in the armies of Genghis Khan. Bulat steel is generally agreed to be a Russian name for wootz steel, the production method of which has been lost for centuries, and the bulat steel used today makes use of a more recently developed technique. History The secret of bulat manufacturing had been lost by the beginning of the 19th century. It is known that the process involved dipping the finished weapon into a vat containing a special liquid of which Ononis spinosa, spiny restharrow extract was a part (the plant's name in Russian, ', reflects its historical role), then holding the sword aloft while galloping on a horse, allowing it to dry a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kard Dagger (cropped)
A kard () is the equivalent in the Persian language for knife. In the specialist jargon, Kard is considered a type of knife found in the Persianate societies like Persia, Turkey, Armenia and all the way to India. Mostly used in the 18th century and before, it has a straight single edged blade and is usually no longer than in length. It has no guard, and usually the handle was bone, ivory, or horn. It was mostly a stabbing weapon, and commonly the point would be reinforced to penetrate chain mail Mail (sometimes spelled maille and, since the 18th century, colloquially referred to as chain mail, chainmail or chain-mail) is a type of armour consisting of small metal rings linked together in a pattern to form a mesh. It was in common milita .... A major characteristic of a kard is that the hilt is only partially covered by the sheath. References {{Knives Knives Indo-Persian weaponry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
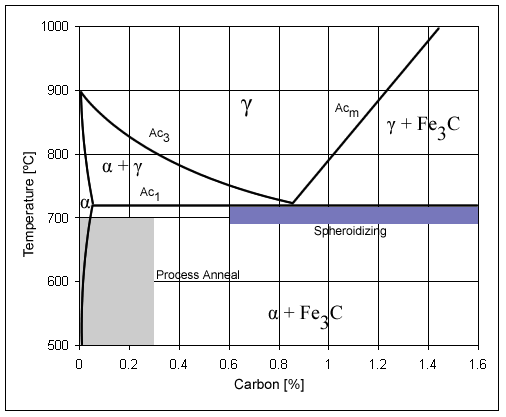
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states: * no minimum content is specified or required for chromium, cobalt, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, zirconium, or any other element to be added to obtain a desired alloying effect; * the specified minimum for copper does not exceed 0.40%; * or the specified maximum for any of the following elements does not exceed: manganese 1.65%; silicon 0.60%; and copper 0.60%. As the carbon content percentage rises, steel has the ability to become harder and stronger through heat treating; however, it becomes less ductile. Regardless of the heat treatment, a higher carbon content reduces weldability. In carbon steels, the higher carbon content lowers the melting point. The term may be used to reference steel that is not stainless steel; in this use carbon steel may include alloy st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Steel Industry Of Russia
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high elastic modulus, yield strength, fracture strength and low raw material cost, steel is one of the most commonly manufactured materials in the world. Steel is used in structures (as concrete reinforcing rods), in bridges, infrastructure, tools, ships, trains, cars, bicycles, machines, electrical appliances, furniture, and weapons. Iron is always the main element in steel, but other elements are used to produce various grades of steel demonstrating altered material, mechanical, and microstructural properties. Stainless steels, for example, typically contain 18% chromium and exhibit improved corrosion and oxidation resistance versus its carbon steel counterpart. Under atmospheric pressures, steels generally take on two crystalline forms: body-centered cubic and face-centered cubic, however depending on the thermal history and alloying, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it, with more than 150 Nobel Prize-winners being featured since its inception. In print since 1845, it is the oldest continuously published magazine in the United States. ''Scientific American'' is owned by Springer Nature, which is a subsidiary of Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. History ''Scientific American'' was founded by inventor and publisher Rufus Porter (painter), Rufus Porter in 1845 as a four-page weekly newspaper. The first issue of the large-format New York City newspaper was released on August 28, 1845. Throughout its early years, much emphasis was placed on reports of what was going on at the United States Patent and Trademark Office, U.S. Patent Office. It also reported on a broad range of inventions including perpetual motion machines, an 1860 devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tamahagane Steel
is a type of steel made in the Japanese tradition. The word means 'precious', and the word means 'steel'. is used to make Japanese swords, daggers, knives, and other kinds of tools. The carbon content of the majority of analyzed Japanese swords historically lies between a mass of 0.5–0.7%; however, the range extends up to 1.5%. Production is made of an found in Shimane, Japan. There are two main types of iron sands: and . is lower quality, is better quality. The (furnace master) decides the amount of the mixing parts. Depending on the desired result, the mixes one or more types of sands. The iron sand is put in a , a clay tub furnace. The clay tub measures about tall, long and wide. The tub is dried and heated to about . Then, it is mixed with charcoal to add carbon to the steel so it can be hardened. The process of making continues for 36–72 hours (a day and a half to three days), depending on how many people work and how much metal is to be obtained. Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Noric Steel
Noric steel is a historical steel from Noricum, a kingdom located in modern Austria and Slovenia. The proverbial hardness of Noric steel is expressed by Ovid: ''"...durior ..ferro quod noricus excoquit ignis..."'' which roughly translates to "...harder than iron which Noric fire tempers Anaxarete.html" ;"title="as Anaxarete">as Anaxarete towards the advances of Iphis]..." and it was widely used for the weapons of the Roman military after Noricum joined the Empire in 16 BC. The iron ore was quarried at two mountains in modern Austria still called ''Erzberg'' "ore mountain" today, one at Hüttenberg, Carinthia and the other at Eisenerz, Styria, separated by . The latter is the site of the modern Erzberg mine. Buchwald identifies a sword of found in Krenovica, Moravia as an early example of Noric steel due to a chemical composition consistent with Erzberg ore. A more recent sword, dating to and found in Zemplin, eastern Slovakia, is of extraordinary length for the period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wootz Steel
Wootz steel is a crucible steel characterized by a pattern of bands and high carbon content. These bands are formed by sheets of microscopic carbides within a tempered martensite or pearlite matrix in higher-carbon steel, or by ferrite and pearlite banding in lower-carbon steels. It was a pioneering steel alloy developed in southern India in the mid-1st millennium BC and exported globally. History Wootz steel originated in the mid-1st millennium BC in India, wootz steel was made in Golconda in Telangana, Karnataka, Tamilnadu and Sri Lanka. The steel was exported as cakes of steely iron that came to be known as "wootz". The method was to heat black magnetite ore in the presence of carbon in a sealed clay crucible inside a charcoal furnace to completely remove slag. An alternative was to smelt the ore first to give wrought iron, then heat and hammer it to remove slag. The carbon source was bamboo and leaves from plants such as Avārai. Locals in Sri Lanka adopted the productio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Toledo Steel
Toledo steel, historically known for being unusually hard, is from Toledo, Spain, which has been a traditional sword-making, metal-working center since about the Roman period, and came to the attention of Rome when used by Hannibal in the Punic Wars. It soon became a standard source of weaponry for Roman legions. Toledo steel was famed for its high quality alloy. History The name "Toledo steel" comes from the city where these special steel products were most-notably crafted: Toledo, Spain. Toledo steel forging techniques were developed from ancient customs associated with culture in the Iberian Peninsula, and used to forge many different types of weapons over the course of many centuries. In simple terms, the Toledo steel technique consisted of a steel blade that enveloped a wrought iron strip, thus preventing the steel from bending or cracking. As such, the strong and durable Toledo steel weapons were said to have had a "soul of iron". In ancient Iberia, blacksmiths in Tol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brinell Hardness Test
The Brinell hardness test (pronounced /brəˈnɛl/) measures the indentation hardness of materials. It determines hardness through the scale of penetration of an indenter, loaded on a material test-piece. It is one of several definitions of hardness in materials science. The hardness scale is expressed in terms of a Brinell hardness value, sometimes referred to as the Brinell hardness number but formally expressed as HBW (Hardness Brinell Wolfram – Wolfram being an alternative name for the tungsten carbide ball indenter used during the test). The test was named after Johan August Brinell (1849-1925) who developed the method at the end of the 19th century. History Premiered by Swedish engineer Johan August Brinell at the 1900 Paris Exposition, it was the first widely used and standardised hardness test in engineering and metallurgy. The large size of indentation and thus possible damage to test-pieces limits its usefulness. However, it also had the useful feature that the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (metalworking), pressing or abrasion (mechanical), abrasion. In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard metals such as titanium and beryllium are harder than soft metals such as sodium and metallic tin, or wood and common plastics. Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular bonds, but the behavior of solid materials under force is complex; therefore, hardness can be measured in different ways, such as scratch hardness, indentation hardness, and rebound hardness. Hardness is dependent on ductility, elasticity (physics), elastic stiffness, plasticity (physics), plasticity, deformation (mechanics), strain, strength of materials, strength, toughness, viscoelasticity, and viscosity. Common examples of hard matter are cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, carbon-12, C and carbon-13, C being stable, while carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the timeline of chemical element discoveries#Pre-modern and early modern discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the abundance of the chemical elements, fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |