|
Buccal Pumping
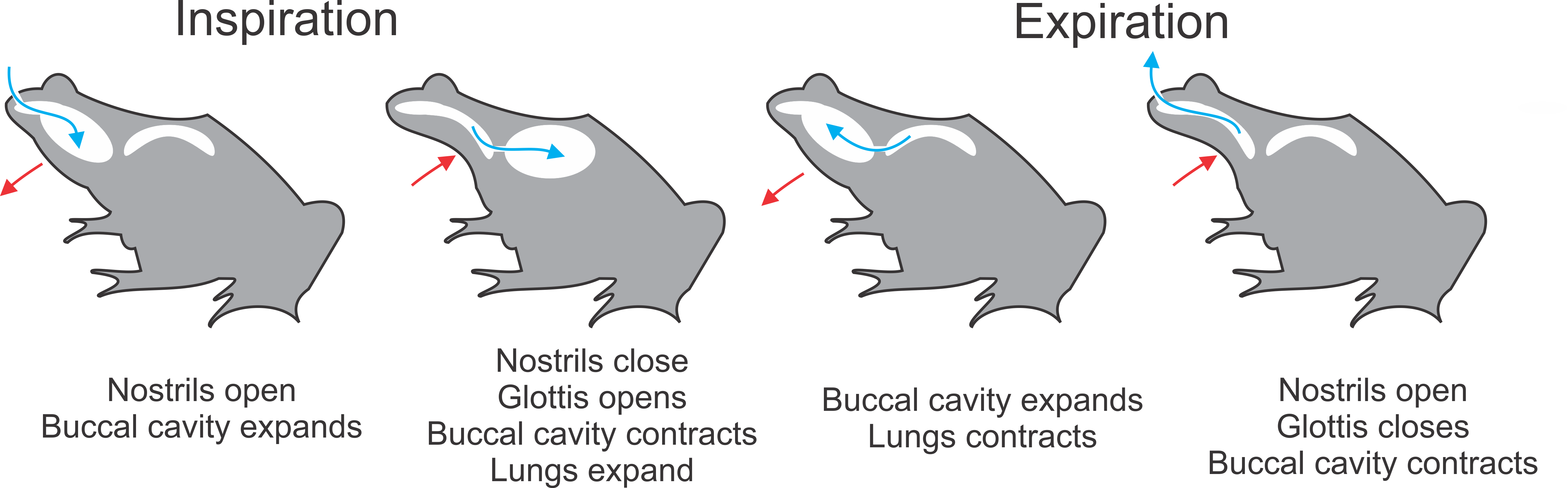
Buccal pumping (/ˈbʌk.əl/...) is "breathing with one's cheeks": a method of ventilation used in respiration in which the animal moves the floor of its mouth in a rhythmic manner that is externally apparent.Brainerd, E. L. (1999). New perspectives on the evolution of lung ventilation mechanisms in vertebrates. Experimental Biology Online 4, 11-28. http://www.brown.edu/Departments/EEB/brainerd_lab/pdf/Brainerd-1999-EBO.pdf It is the sole means of inflating the lungs in amphibians. There are two methods of buccal pumping, defined by the number of movements of the floor of the mouth needed to complete both inspiration and expiration. Four stroke Four-stroke buccal pumping is used by some basal ray-finned fish and aquatic amphibians such as ''Xenopus'' and ''Amphiuma''. This method has several stages. These will be described for an animal starting with lungs in a deflated state: First, the glottis (opening to the lungs) is closed, and the nostrils are opened. The floor of the mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiration (physiology)
In physiology, respiration is the transport of oxygen from the outside environment to the Cell (biology), cells within Tissue (biology), tissues, and the removal of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction to the environment by a respiratory system. The physiological definition of respiration differs from the Cellular respiration, biochemical definition, which refers to a metabolic process by which an organism obtains energy (in the form of ATP and NADPH) by oxidizing nutrients and releasing waste products. Although physiologic respiration is necessary to sustain cellular respiration and thus life in animals, the processes are distinct: cellular respiration takes place in individual cells of the organism, while physiologic respiration concerns the Diffusion#Diffusion vs. bulk flow diffusion, diffusion and transport of metabolites between the organism and the external environment. Exchange of gases in the lung occurs by ventilation and perfusion. Ventilation refers to the in-and-ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excluding the amniotes (tetrapods with an amniotic membrane, such as modern reptiles, birds and mammals). All extant taxon, extant (living) amphibians belong to the monophyletic subclass (biology), subclass Lissamphibia, with three living order (biology), orders: Anura (frogs and toads), Urodela (salamanders), and Gymnophiona (caecilians). Evolved to be mostly semiaquatic, amphibians have adapted to inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living in freshwater ecosystem, freshwater, wetland or terrestrial ecosystems (such as riparian woodland, fossorial and even arboreal habitats). Their biological life cycle, life cycle typically starts out as aquatic animal, aquatic larvae with gills known as tadpoles, but some species have devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenopus
''Xenopus'' () (Gk., ξενος, ''xenos'' = strange, πους, ''pous'' = foot, commonly known as the clawed frog) is a genus of highly aquatic frogs native to sub-Saharan Africa. Twenty species are currently described within it. The two best-known species of this genus are '' Xenopus laevis'' and '' Xenopus tropicalis'', which are commonly studied as model organisms for developmental biology, cell biology, toxicology, neuroscience and for modelling human disease and birth defects. The genus is also known for its polyploidy, with some species having up to 12 sets of chromosomes. Characteristics ''Xenopus laevis'' is a rather inactive creature. It is incredibly hardy and can live up to 15 years. At times the ponds that ''Xenopus laevis'' is found in dry up, compelling it, in the dry season, to burrow into the mud, leaving a tunnel for air. It may lie dormant for up to a year. If the pond dries up in the rainy season, ''Xenopus laevis'' may migrate long di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphiuma
''Amphiuma'' is a genus of aquatic salamanders from the United States, the only Extant taxon, extant genus within the family (biology), family Amphiumidae . They are colloquially known as amphiumas. They are also known to fishermen as "conger eels" or "Congo snakes", which are zoology, zoologically incorrect designations or misnomers, since amphiumas are actually salamanders (and thus amphibians), and not fish, nor reptiles and are not from Congo Basin, Congo. ''Amphiuma'' exhibits one of the largest complements of DNA in the living world, around 25 times more than a human. Taxonomy Numerous phylogenetic studies have indicated that amphiumas form a clade with the families Torrent salamander, Rhyacotritonidae (torrent salamanders) and Plethodontidae (lungless salamanders), with an especially close relationship to Plethodontidae. Despite this possible relationship, the two families must have still diverged very early on. The genus ''Proamphiuma'' from the Cretaceous is the earlies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottis
The glottis (: glottises or glottides) is the opening between the vocal folds (the rima glottidis). The glottis is crucial in producing sound from the vocal folds. Etymology From Ancient Greek ''γλωττίς'' (glōttís), derived from ''γλῶττα'' (glôtta), variant of ''γλῶσσα'' (glôssa, "tongue"). Function Phonation As the vocal folds vibrate, the resulting vibration produces a "buzzing" quality to the speech, called voice or voicing or pronunciation. Sound production that involves moving the vocal folds close together is called ''glottal''. English has a voiceless glottal transition spelled "h". This sound is produced by keeping the vocal folds spread somewhat, resulting in non-turbulent airflow through the glottis. In many accents of English the glottal stop (made by pressing the folds together) is used as a variant allophone of the phoneme (and in some dialects, occasionally of and ); in some languages, this sound is a phoneme of its own. Skilled p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes Animal communication#Auditory, vocalisation including speech possible. Humans have two lungs, a ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nostril
A nostril (or naris , : nares ) is either of the two orifices of the nose. They enable the entry and exit of air and other gasses through the nasal cavities. In birds and mammals, they contain branched bones or cartilages called turbinates, whose function is to warm air on inhalation and remove moisture on exhalation. Fish do not breathe through noses, but they do have two small holes used for smelling, which can also be referred to as nostrils (with the exception of Cyclostomi, which have just one nostril). In humans, the nasal cycle is the normal ultradian cycle of each nostril's blood vessels becoming engorged in swelling, then shrinking. The nostrils are separated by the septum. The septum can sometimes be deviated, causing one nostril to appear larger than the other. With extreme damage to the septum and columella, the two nostrils are no longer separated and form a single larger external opening. Like other tetrapod A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wikti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four-stroke Buccal Pumping
Buccal pumping (/ˈbʌk.əl/...) is "breathing with one's cheeks": a method of ventilation used in respiration in which the animal moves the floor of its mouth in a rhythmic manner that is externally apparent.Brainerd, E. L. (1999). New perspectives on the evolution of lung ventilation mechanisms in vertebrates. Experimental Biology Online 4, 11-28. http://www.brown.edu/Departments/EEB/brainerd_lab/pdf/Brainerd-1999-EBO.pdf It is the sole means of inflating the lungs in amphibians. There are two methods of buccal pumping, defined by the number of movements of the floor of the mouth needed to complete both inspiration and expiration. Four stroke Four-stroke buccal pumping is used by some basal ray-finned fish and aquatic amphibians such as ''Xenopus'' and ''Amphiuma''. This method has several stages. These will be described for an animal starting with lungs in a deflated state: First, the glottis (opening to the lungs) is closed, and the nostrils are opened. The floor of the mout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
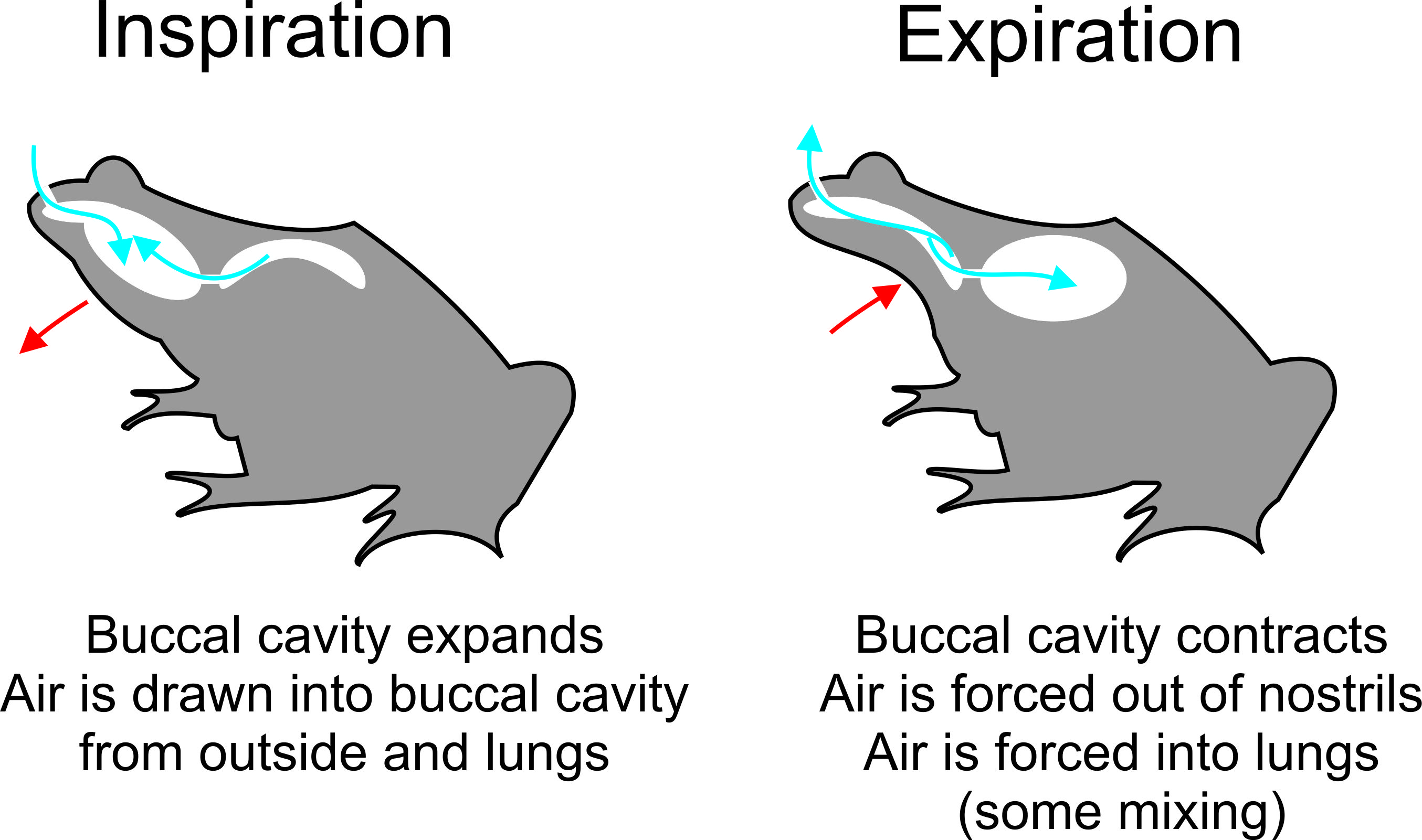
Two Stroke Buccal Pumping
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and the only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultures. Mathematics The number 2 is the second natural number after 1. Each natural number, including 2, is constructed by succession, that is, by adding 1 to the previous natural number. 2 is the smallest and the only even prime number, and the first Ramanujan prime. It is also the first superior highly composite number, and the first colossally abundant number. An integer is determined to be even if it is divisible by two. When written in base 10, all multiples of 2 will end in 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8; more generally, in any even base, even numbers will end with an even digit. A digon is a polygon with two sides (or edges) and two vertices. Two distinct points in a plane are always sufficient to define a unique line in a nontrivial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting Taxonomy, taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern Cladistics, cladistic taxonomy regards that group as Paraphyly, paraphyletic, since Genetics, genetic and Paleontology, paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
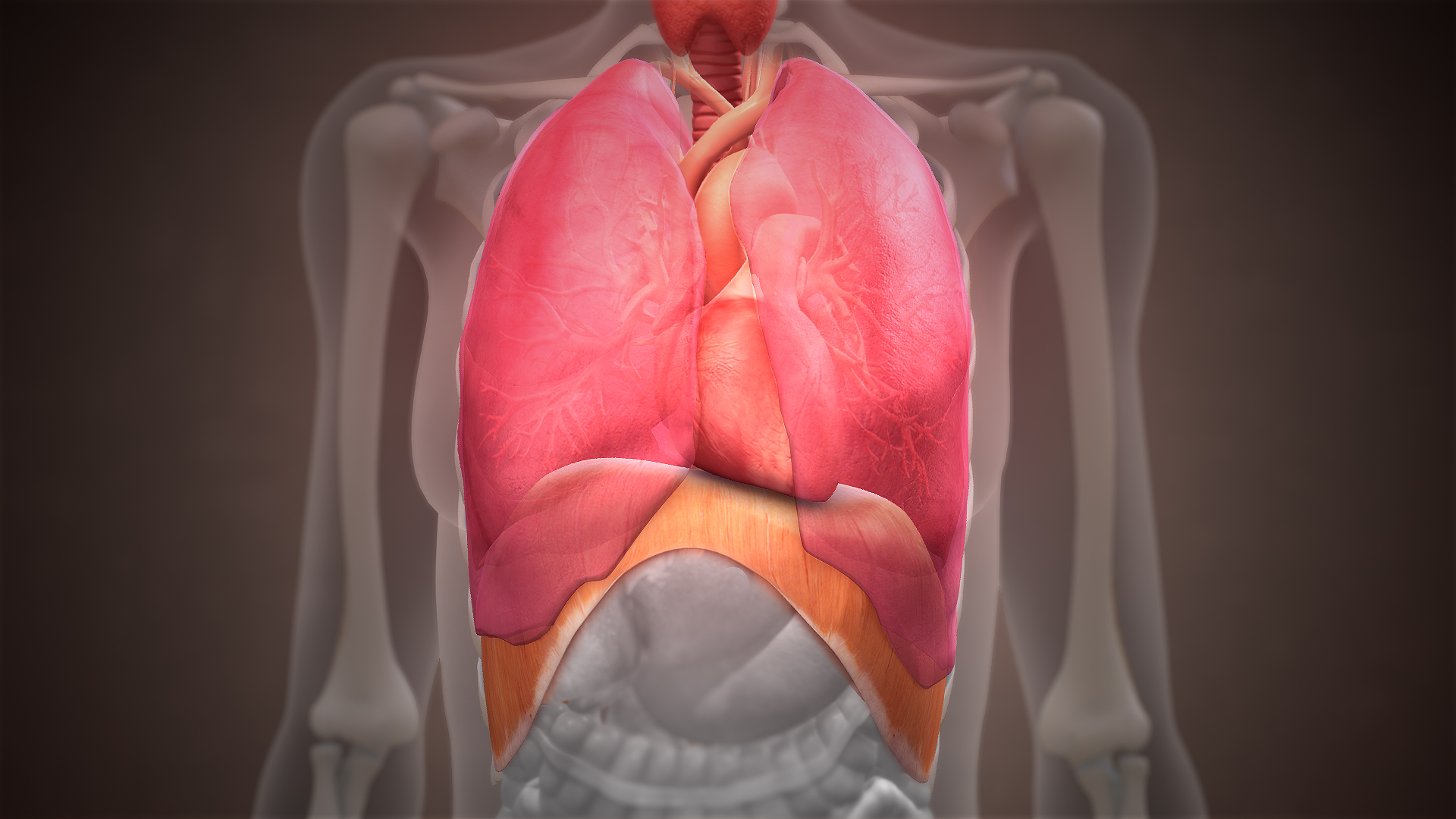
Thoracic Diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm (; ), is a sheet of internal Skeletal striated muscle, skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important Muscles of respiration, muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or Pelvic floor, pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is higher up (superior) to the left half, since th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |