|
Boyko People
The Boykos or Boikos (; ; ; ), or simply Highlanders (; ), are an ethnolinguistic group located in the Carpathian Mountains of Ukraine, Slovakia, Hungary, and Poland. Along with the neighbouring Lemkos and Hutsuls, the Boykos are a regional subgroup of Ukrainians.[Richard T.Schaefer (ed.), 2008, ''Encyclopedia of Race, Ethnicity, and Society, Volume 1'', Sage Publications, p. 1341. James Stuart Olson, Lee Brigance Pappas & Nicholas Charles Pappas, 1994, ''An Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires'', Greenwood Publishing Group, pp. 109–110. However, the diaspora outside of western Ukraine are often considered a sub-group of Rusyns who speak a distinct East Slavic languages, East Slavic dialect. Boykos differ from their neighbors in dialect, dress, folk architecture, and customs. Etymology Regarding the origin of the name Boyko there exist several etymological hypotheses, but it is generally considered, as explained by priest Joseph Levytsky in his ''Hram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maniava
Maniava or Manyava (, ) is a village of about 3,500 people located on the banks of the Maniavka River in Ivano-Frankivsk Raion, Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast of Western Ukraine. It is situated in the Ukrainian Carpathian Mountains. Maniava belongs to Solotvyn settlement hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Until 18 July 2020, Maniava belonged to Bohorodchany Raion. The raion was abolished in July 2020 as part of the administrative reform of Ukraine, which reduced the number of raions of Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast to six. The area of Bohorodchany Raion was merged into Ivano-Frankivsk Raion. The famous Orthodox Maniava Skete monastery is located on its outskirts, and the Maniava waterfall, with a height of 20 meters one of the highest waterfalls in Ukraine's Carpathian Mountains. * Postal code is 77772 * Telephone code is +380 3471 References Sources * ''Maniava, Western Ukraine'' {{Authority control Villages in Ivano-Frankivsk Raion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolyna Local History Museum Of Tatiana And Omelan Antonovych 1
Dolyna (, ; ; ) is a city in Kalush Raion, Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast, south-western Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Dolyna urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: In 2001, population was around 20,900. History The city's history reaches the 10th century, making it one of oldest in the region. By the 14th century Dolyna became renowned for its salt mine. In 1349 the city came under the rule of the Kingdom of Poland, where it remained until 1772 (see Partitions of Poland). In 1525 Dolyna, or Dolina, as it is called in Polish, was granted city rights under the Magdeburg law and the right to trade salt similar to that of Kolomyia. In 1740 in the city there was a riot of '' opryshky'' (Ukrainian rebels). In 1772 the city fell to Austrians and in 1791 it lost its status. During the second half of the 19th century a segment of the Archduke Albrecht Railway linking Stryi with Stanislaviv was led through the city, later becoming a part of the Galician Transve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historically it could also refer to a wider area consisting of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the List of Bohemian monarchs, Bohemian kings, including Moravia and Czech Silesia, in which case the smaller region is referred to as Bohemia Proper as a means of distinction. Bohemia became a part of Great Moravia, and then an independent principality, which became a Kingdom of Bohemia, kingdom in the Holy Roman Empire. This subsequently became a part of the Habsburg monarchy and the Austrian Empire. After World War I and the establishment of an History of Czechoslovakia (1918–1938), independent Czechoslovak state, the whole of Bohemia became a part of Czechoslovakia, defying claims of the German-speaking inhabitants that regions with German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mykhailo Hrushevsky
Mykhailo Serhiiovych Hrushevsky (; – 24 November 1934) was a Ukrainian academician, politician, historian and statesman who was one of the most important figures of the Ukrainian national revival of the early 20th century. Hrushevsky is often considered the country's greatest modern historian, the foremost organiser of scholarship, the leader of the pre-revolution Ukrainian national movement, the head of the Tsentral'na Rada, Central Rada (Ukraine's 1917–1918 revolutionary parliament), and a leading cultural figure in the Ukrainian SSR during the 1920s. Biography Early life Hrushevsky was born on 29 September 1866 to a Ukrainian noble family in Kholm (Chełm), in Congress Poland, an autonomous polity in the Russian Empire. Hrushevsky grew up in Tiflis, where he attended a local school. His spiritual native land became Podillia, in the area of the village of Sestrynivka, Podolia Governorate, Podillia Governorate. There, his mother, Glafira Zakharivna Okopova, was born in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Administrando Imperio
(; ) is a Greek-language work written by the 10th-century Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII. It is a domestic and foreign policy manual for the use of Constantine's son and successor, the Emperor Romanos II. It is a prominent example of Byzantine encyclopaedism. Author and background The emperor Constantine VII "Porphyrogenitus" (905–959) was only surviving son of the emperor Leo VI the Wise (886–912). Leo VI gave the crown to young Constantine VII in 908 and he became the co-emperor. Leo VI died in May 912, and his brother and co-emperor Alexander became the ruler of Constantinople, but Alexander died in 913. Constantine VII was too young to rule on his own, and the governorship was created. Later in May 919 Constantine VII married Helena Lekapene, daughter of Romanos Lekapenos. In December 920, Romanos I Lekapenos (920–944) was crowned a co-emperor, but he really took over the imperial reign in Constantinople. From 920, Constantine VII become increasingly distant f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Serbia
White Serbia ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Бела Србија, Bela Srbija; ), also called Boiki (; sr-Cyrl-Latn, link=no, Бојка, Bojka), is the name applied to the assumed homeland of the Sorbs (tribe), White Serbs ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, link=no, Бели Срби, Beli Srbi), a tribal subgroup of Wends, a mixed and the westernmost group of Early Slavs. They are the ancestors of the modern Sorbs in Saxony and possibly Serbs in Serbia. Location Sources The Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII () in ''De Administrando Imperio'' of the mid-10th century recounts in Chapter 31: "These same White Croats, Croats arrived as refugees to the emperor of the [Emperor Heraclius, ] before the Serbs came as refugees to the same Emperor Heraclius"; and mainly in Chapter 32: "It should be known that the Serbs are descended from the unbaptized Serbs, also called ‘white’, who live beyond Hungary, in a region called by them Boïki, where their neighbor is Francia, as is also White Croatia, Megali Croatia, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Hoyle Howorth
Sir Henry Hoyle Howorth (1 July 1842 – 15 July 1923) was a British Conservative politician, barrister and amateur historian and geologist.''Obituary: Sir Henry Howorth, A Life of Wide Interests, Politics, Science, and Art'', The Times, 17 July 1923, p.14 Career He was born in Lisbon, Portugal, the son of Henry Howorth, a merchant in that city. He was educated at Rossall School before studying law. He was called to the bar by the Inner Temple in 1867, and practised on the Northern Circuit. He was also the maternal great uncle of anthropologist Sir Edmund Ronald Leach. He was a Unionist in politics, and was elected as Conservative Member of Parliament for Salford South in 1886. He was re-elected in 1892 and 1895 before retiring from the Commons at the 1900 general election. Apart from the law and politics, Howorth was deeply interested in archaeology, history, numismatics and ethnography. He was a prolific writer, contributing articles to a number of journals. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franjo Rački
Franjo Rački (25 November 1828 – 13 February 1894) was a Croatian historian, politician, writer, and Catholic priest. He compiled important collections of old Croatian diplomatic and historical documents, wrote some pioneering historical works, and was a key founder of the Yugoslav Academy of Sciences and Arts. Biography Historian Rački was born in Fužine, near Rijeka in 1828. He completed his secondary education in Senj and Varaždin. He graduated in theology in Senj, where he was ordained Catholic priest in 1852. He received his PhD in theology in Vienna in 1855. His career as a historian began as soon as he started working as a teacher in Senj. He organized the research of Glagolitic documents on the islands of Kvarner. He went to the village of Baška on Krk, the location of the famous Baška Tablet where he analyzed them, and published ''Viek i djelovanje sv. Cirilla i Methoda slavjamkih apošlolov'' (''The Age and Activities of Saints Cyril and Methodius, the Apo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
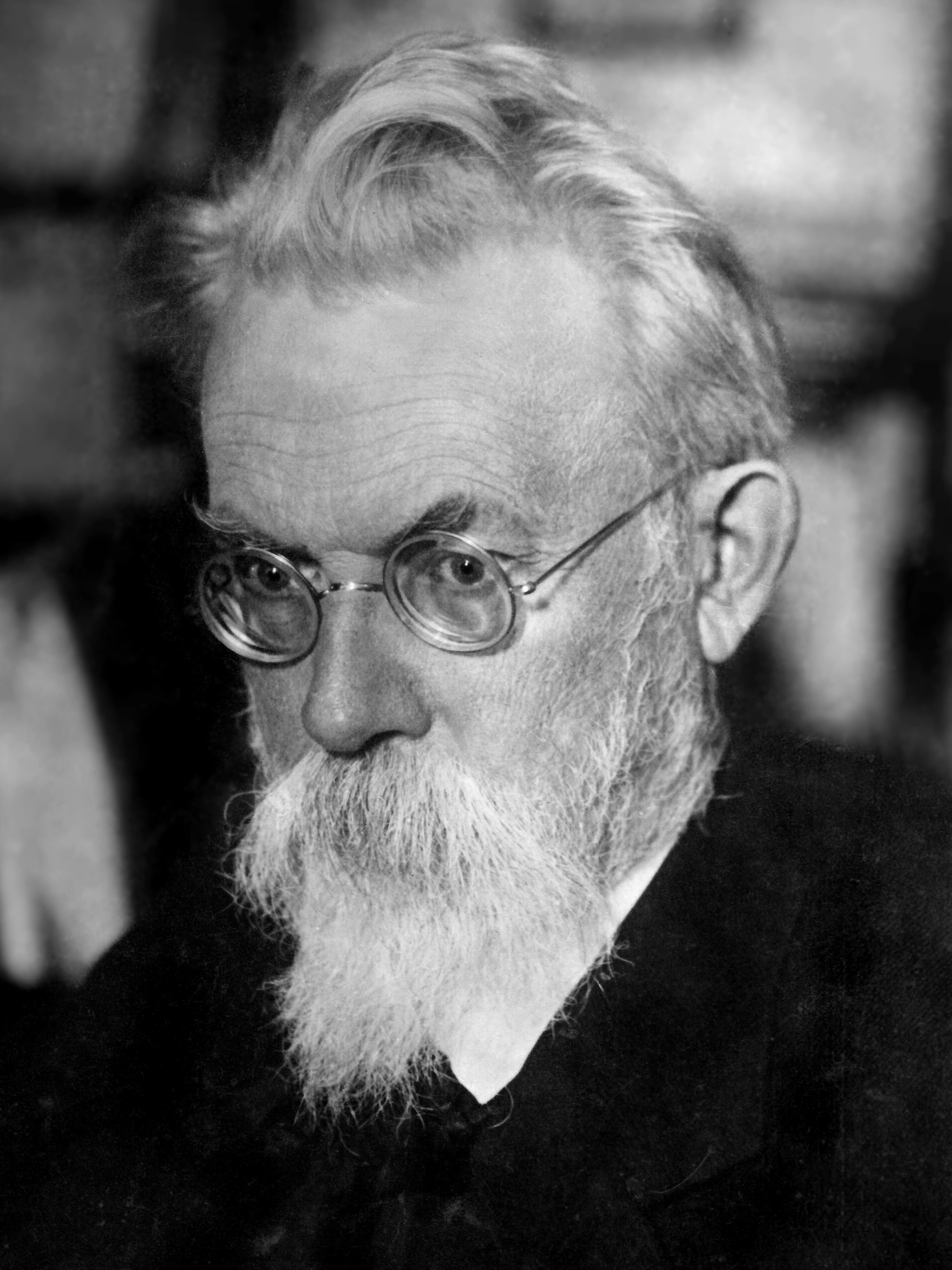
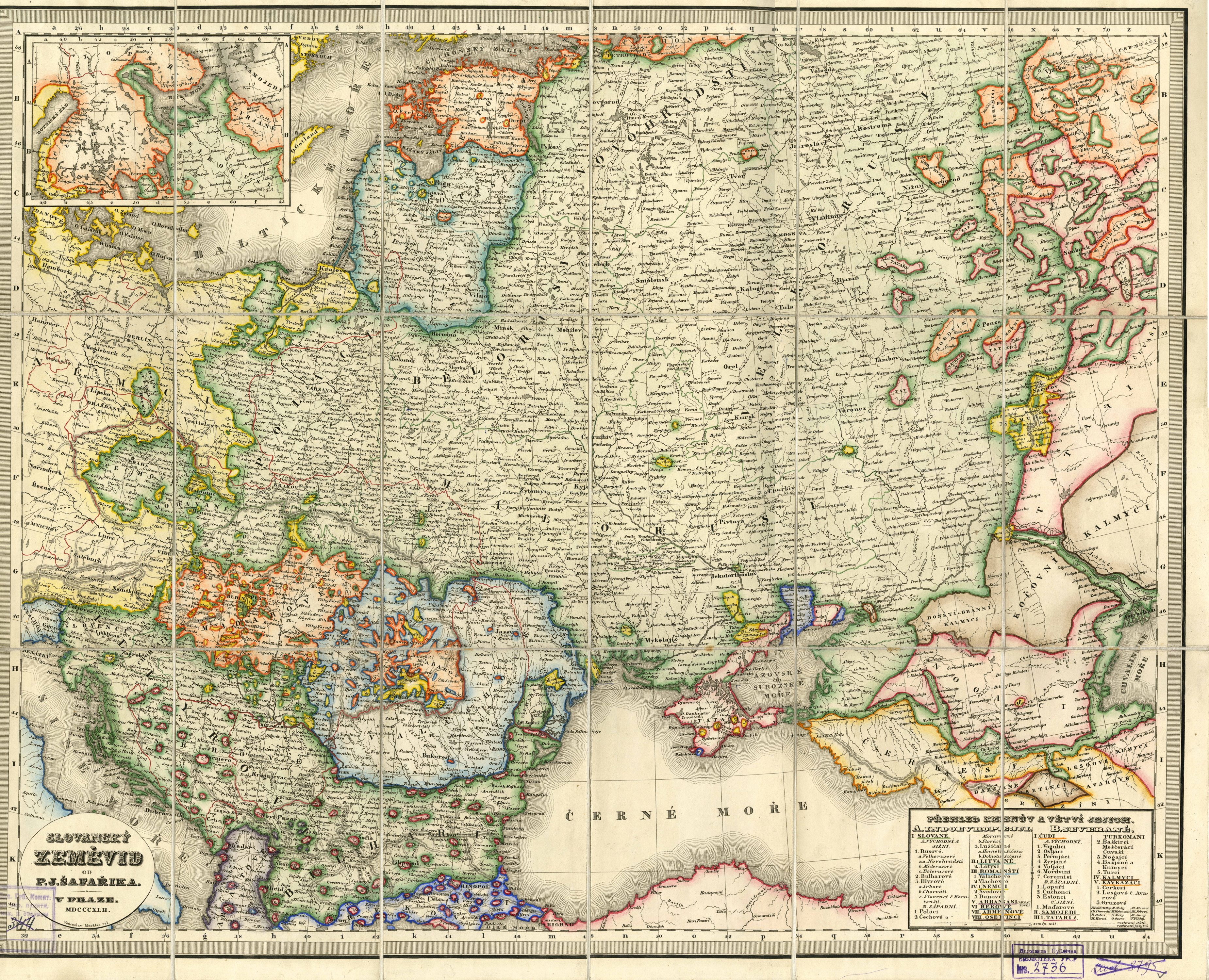
Pavel Jozef Šafárik
Pavel Jozef Šafárik (; 13 May 1795 – 26 June 1861) was a Slovak philologist, poet, literary historian, historian and ethnographer in the Kingdom of Hungary. He was one of the first scientific Slavists. Family His father Pavol Šafárik (1761–1831) was a Protestant clergyman in Kobeliarovo and before that a teacher in Štítnik, where he was also born. His mother, Katarína Káresová (1764–1812) was born in a poor lower gentry family in Hanková and had several jobs in order to help the family in the poor region of Kobeliarovo. P.J. Šafárik had two elder brothers and one elder sister. One brother, Pavol Jozef as well, died before Šafárik was born. In 1813, after Katarína's death, Šafárik's father married the widow Rozália Drábová, although Šafárik and his brothers and sister were against this marriage. The local teacher provided Šafárik with Czech books. On 17 June 1822, when he was in Novi Sad (see below), P. J. Šafárik married 19-year-old Júlia Ambr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Sciences Of Ukraine
The National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine (NASU; , ; ''NAN Ukrainy'') is a self-governing state-funded organization in Ukraine that is the main center of development of Science and technology in Ukraine, science and technology by coordinating a system of research institutes in the country. It is the main research oriented organization along with the five other academies in Ukraine specialized in various scientific disciplines. NAS Ukraine consists of numerous departments, sections, research institutes, scientific centers and various other supporting scientific organizations. The Academy reports on the annual basis to the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine. The presidium of the academy is located at vulytsia Volodymyrska, 54, across the street from the Ukrainian Club Building, Building of Pedagogical Museum, which was used to host the Central Rada, Central Council during the independence period of 1917-18. In 1919–1991 it was a republican branch of the Academy of Sciences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Toronto Press
The University of Toronto Press is a Canadian university press. Although it was founded in 1901, the press did not actually publish any books until 1911. The press originally printed only examination books and the university calendar. Its first scholarly book was a work by a classics professor at University College, Toronto. The press took control of the university bookstore in 1933. It employed a novel typesetting method to print issues of the ''Canadian Journal of Mathematics'', founded in 1949. The press has always had close ties with University of Toronto Libraries. The press was partially located in the library from 1910-1920. The University Librarian Hugh Hornby Langton, the lead librarian of the University of Toronto Libraries, served as the first general editor of the University of Toronto Press. Sidney Earle Smith, president of the University of Toronto in the late 1940s and 1950s, instituted a new governance arrangement for the press modelled on the governing structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Ukraine
The ''Encyclopedia of Ukraine'' (), published from 1984 to 2001, is a fundamental work of Ukrainian Studies. Development The work was created under the auspices of the Shevchenko Scientific Society in Europe (Sarcelles, near Paris). As the ''Encyclopedia of Ukrainian Studies'' it conditionally consists of two parts, the first being a general part that consists of a three volume reference work divided in to subjects or themes. The second part is a 10 volume encyclopedia with entries arranged alphabetically. The editor-in-chief of Volumes I and II (published in 1984 and 1988 respectively) was Volodymyr Kubijovyč. The concluding three volumes, with Danylo Husar Struk as editor-in-chief, appeared in 1993. The encyclopedia set came with a 30-page ''Map & Gazetteer of Ukraine'' compiled by Kubijovyč and Arkadii Zhukovsky. It contained a detailed fold-out map (scale 1:2,000,000). A final volume, ''Encyclopedia of Ukraine: Index and Errata'', containing only the index and a list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |