|
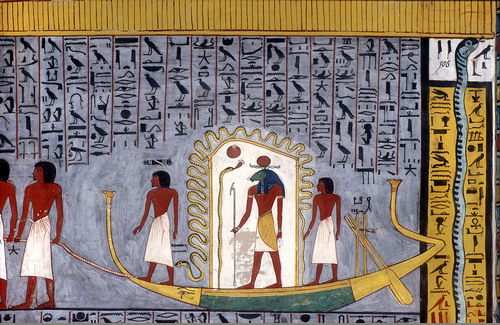
Book Of Gates
The Book of Gates is an ancient Egyptian funerary text dating from the New Kingdom. The ''Book of Gates'' is long and detailed, consisting of one hundred scenes. It narrates the passage of a newly deceased soul into the next world journeying with the sun god, Ra, through the underworld during the hours of the night towards his resurrection. The soul is required to pass through a series of 'gates' at each hour of the journey. Each gate is guarded by a different serpent deity that is associated with a different goddess. It is important that the deceased knows the names of each guardian. Depictions of the judgment of the dead are shown in the last three hours. The text implies that some people will pass through unharmed, but others will suffer torment in a lake of fire. At the end of Ra's journey through the underworld, he emerges anew to take his place back in the sky. History The text was not named by the Egyptians. It was named by French Egyptologist Gaston Maspero who ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Barque
thumb Solar barques were the vessels used by the sun god Ra in ancient Egyptian mythology. During the day, Ra was said to use a vessel called the Mandjet () or the Boat of Millions of Years (), and the vessel he used during the night was known as the Mesektet (). Myth According to Egyptian myth, when Ra became too old and weary to reign on earth he relinquished and went to the skies. Ra was said to travel through the sky on the barge, providing light to the world. Each twelfth of his journey formed one of the twelve Egyptian hours of the day, each overseen by a protective deity. When the sun set and twilight came, he and his vessel passed through the ''akhet'', the horizon, in the west, and traveled to the underworld.At times the horizon is described as a gate or door that leads to the Duat. There he would have to sail on the subterrestrial Nile and cross through the twelve gates and regions,Hart 1986, pp. 68–72. with each hour of the night considered a gate overseen by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Funerary Texts
The literature that makes up the ancient Egyptian funerary texts is a collection of religious documents that were used in ancient Egypt, usually to help the spirit of the concerned person to be preserved in the afterlife. They evolved over time, beginning with the Pyramid Texts in the Old Kingdom through the Coffin Texts of the Middle Kingdom and into several books, most famously the Book of the Dead, in the New Kingdom and later times. Old Kingdom The funerary texts of the Old Kingdom were initially reserved for the king only. Towards the end of the period, the texts appeared in the tombs of royal wives. Middle Kingdom These are a collection of ancient Egyptian funerary spells written on coffins beginning in the First Intermediate Period. Nearly half of the spells in the Coffin Texts derive from those in the Pyramid Texts. New Kingdom *Book of the Dead * Amduat * Spell of the Twelve Caves * The Book of Gates * Book of the Netherworld *Book of Caverns * Book of the Earth * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophagus
A sarcophagus (: sarcophagi or sarcophaguses) is a coffin, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word ''sarcophagus'' comes from the Greek language, Greek wikt:σάρξ, σάρξ ' meaning "flesh", and wikt:φαγεῖν, φαγεῖν ' meaning "to eat"; hence ''sarcophagus'' means "flesh-eating", from the phrase ''lithos sarkophagos'' (wikt:λίθος, λίθος wikt:σαρκοφάγος, σαρκοφάγος), "flesh-eating stone". The word also came to refer to a particular kind of limestone that was thought to rapidly facilitate the corpse decomposition, decomposition of the flesh of corpses contained within it due to the chemical properties of the limestone itself. History of the sarcophagus Sarcophagi were most often designed to remain above ground. The earliest stone sarcophagi were used by Pharaoh, Egyptian pharaohs of the 3rd dynasty, which reigned from about 2686 to 2613 BC. The Hagia Triada sarcoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God Form
A divine embodiment or godform refers to the visualized appearance of the deity assumed in theurgical, tantric, and other mystical practices. This process of ritual embodiment is aimed at transforming the practitioner, aligning them with divine powers for spiritual ascent or transformation. The concept is found across diverse traditions, including Western esotericism, Eastern spirituality, and mysticism, where it serves as a method for achieving personal enlightenment, union with the divine, or other spiritual goals. In Western esotericism, divine embodiment is most commonly associated with theurgy, particularly in the works of Neoplatonists like Iamblichus, where the practitioner assumes a divine form through ritual or meditation to transcend the material world and reach higher spiritual realms. This concept was influenced by ancient Greek practices of invoking gods and embodying divine forces, seen in both the public cults and private rituals. The idea was later adapted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Gates, 4th Division, 5th Hour, Tomb Of Seti I With Eng
A book is a structured presentation of recorded information, primarily verbal and graphical, through a medium. Originally physical, electronic books and audiobooks are now existent. Physical books are objects that contain printed material, mostly of writing and images. Modern books are typically composed of many pages bound together and protected by a cover, what is known as the ''codex'' format; older formats include the scroll and the tablet. As a conceptual object, a ''book'' often refers to a written work of substantial length by one or more authors, which may also be distributed digitally as an electronic book (ebook). These kinds of works can be broadly classified into fiction (containing invented content, often narratives) and non-fiction (containing content intended as factual truth). But a physical book may not contain a written work: for example, it may contain ''only'' drawings, engravings, photographs, sheet music, puzzles, or removable content like paper dol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sia (god)
Sia or Saa, an ancient Egyptian god, was the deification of perception in the Heliopolitan Ennead cosmogony and is probably equivalent to the "intellectual energies of the heart of Ptah in the Memphite theology." He also had a connection with writing and was often shown in anthropomorphic form holding a papyrus scroll. This papyrus was thought to embody intellectual achievements. The god personifies the perceptive mind. In ancient Egyptian mythology, Sia was believed to have been created from blood that dripped from the phallus of Ra. In the Old Kingdom, Sia was often depicted on the right side of Ra, holding his sacred papyrus. In the New Kingdom, Sia is depicted in the solar barque thumb Solar barques were the vessels used by the sun god Ra in ancient Egyptian mythology. During the day, Ra was said to use a vessel called the Mandjet () or the Boat of Millions of Years (), and the vessel he used during the night was known ... in the underworld texts and tomb decorations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heka (god)
Heka (; ; Coptic: hik'; also transliterated Hekau) was the deification of magic and medicine in ancient Egypt. The name is the Egyptian word for "magic". According to Egyptian literature (Coffin text, spell 261), Heka existed "before duality had yet come into being''.''" The term ''ḥk3'' was also used to refer to the practice of magical rituals. Name The name Heka is identical with the Egyptian word ''ḥkꜣ(w)'' "magic". This hieroglyphic spelling includes the symbol for the word ''ka'' (''kꜣ''), the ancient Egyptian concept of the vital force. Due to the importance placed onto names in ancient Egypt Heka was often incorporated into personal names. Some examples include: Hekawy, Hekaf, or simply Heka. The goddess Isis is also sometimes affiliated with Heka being titled Weret Hekau, Great Lady of magic. Beliefs The Old Kingdom Pyramid Texts depict ''Heka'' as a supernatural energy that the gods possess. The "cannibal pharaoh" must devour other gods to gain this m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uraeus
drawing of a Uraeus The Uraeus () or Ouraeus (Ancient Greek: , ; Egyptian: ', "rearing cobra", plural: ''Uraei'') is the stylized, upright form of an Egyptian cobra, used as a symbol of sovereignty, royalty, deity and divine authority in ancient Egypt. Symbolism The Uraeus is a symbol for the goddess Wadjet.Egyptian-Gods She was one of the earliest Egyptian deities and was often depicted as a cobra, as she is the serpent goddess. The center of her cult was in Per-Wadjet, later called Buto by the Greeks. She became the patroness of the Nile Delta and the protector of all of Lower Egypt. The pharaohs wore the uraeus as a head ornament: either with the body of Wadjet atop the head, or as a crown encircling the head; this indicated Wadjet's protection and reinforced the pharaoh's claim over the land. In whatever manner that the Uraeus was displayed upon the pharaoh's head, it was, in effect, part of the pharaoh's crown. The pharaoh was recognized only by wearing the Uraeus, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amduat
The ''Amduat'' (, () is an important Ancient Egyptian funerary texts, ancient Egyptian funerary text of the New Kingdom of Egypt. Similar to previous funerary texts, such as the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom's Pyramid Texts, or the First Intermediate Period of Egypt, First Intermediate Period's Coffin Texts, the ''Amduat'' was found carved on the internal walls of a pharaoh's tomb. Unlike other funerary texts, however, it was reserved almost exclusively for Pharaoh, pharaohs until the Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt, Twenty-first Dynasty, or very select nobility. The ''Amduat'' tells the story of Ra, the Egyptian sun god who makes a daily journey through the underworld, from the time when the sun sets in the west till it rises again in the east. This is associated with imagery of continual death and rebirth, as the sun 'dies' when it sets, and through the trials of rebirth in the underworld, it is once again 'reborn' at the beginning of a new day. It is said that the deceased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of The Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' is the name given to an Ancient Egyptian funerary texts, ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom (around 1550 BC) to around 50 BC. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the ''Duat'', or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. In 1842, the Egyptologist Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name ''Todtenbuch'' (modern spelling ''Totenbuch''), translated to English as 'Book of the Dead'. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated , is translated as ''Spells of Coming Forth by Day''. The ''Book of the Dead'', which was placed in the coffin or burial chamber of the deceased, was part of a tradition of funerary texts which includes the earlier Pyramid Texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amun
Amun was a major ancient Egyptian deity who appears as a member of the Hermopolitan Ogdoad. Amun was attested from the Old Kingdom together with his wife Amunet. His oracle in Siwa Oasis, located in Western Egypt near the Libyan Desert, remained the only oracle of Amun throughout. With the 11th Dynasty ( BC), Amun rose to the position of patron deity of Thebes by replacing Montu. Initially possibly one of eight deities in the Hermapolite creation myth, his worship expanded. After the rebellion of Thebes against the Hyksos and with the rule of Ahmose I (16th century BC), Amun acquired national importance, expressed in his fusion with the Sun god, Ra, as Amun-Ra (alternatively spelled Amon-Ra or Amun-Re). On his own, he was also thought to be the king of the gods. Amun-Ra retained chief importance in the Egyptian pantheon throughout the New Kingdom (with the exception of the " Atenist heresy" under Akhenaten). Amun-Ra in this period (16th–11th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tjanefer
Tjanefer (fl. 1008 BCE) was an ancient Egyptian priest during the reign of the Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt. Description His father was Nesipaherenmut, the Fourth Prophet of Amun, and his mother was Isetemheb. According to the ''Karnak Priestly Annals'', Tjanefer served as the Fourth Prophet of Amun in the 40th regnal year of Psusennes I ( 1008 BCE). He was later promoted to Third Prophet, as it is mentioned in a papyrus found in his tomb at Bab el-Gasus (which is now housed in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...). He married Gautseshen, the daughter of High Priest Menkheperre and Princess Isetemkheb. They had two sons, Pinedjem, later Fourth Prophet, and Menkheperre, Third Prophet of Amun.Dodson & Hilton, pp.200-201, 207-209 Refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |