|
Biomineralising Polychaetes
Biomineralising polychaetes are polychaetes that produce minerals to harden or stiffen their own tissues (biomineralize). The most important biomineralizing polychaetes are serpulids, sabellids and cirratulids. They secrete tubes of calcium carbonate. Serpulids have most advanced biomineralization system among the annelids. Serpulids possess very diverse tube ultrastructures. Serpulid tubes are composed of aragonite, calcite Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ... or mixture of both polymorphs. In addition to the tubes, some serpulid species secrete calcareous opercula. Some sabellids and cirratulids can secrete aragonitic tubes. Sabellid and cirratulid tubes have a spherulitic prismatic ultrastructure. There are thin organic sheets in serpulid tube mineral structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpula Israelitica
''Serpula'' (also known as calcareous tubeworm, serpulid tubeworm, fanworm, or plume worm) is a genus of sessile, marine annelid tube worms that belongs to the family Serpulidae. Serpulid worms are very similar to tube worms of the closely related sabellid family, except that the former possess a cartilaginous '' operculum'' that occludes the entrance to their protective tube after the animal has withdrawn into it. The most distinctive feature of worms of the genus ''Serpula'' is their colorful fan-shaped "crown". The crown, used by these animals for respiration and alimentation, is the structure that is most commonly seen by scuba divers and other casual observers. Taxonomy Following is a brief description of the cladistics and taxonomic classification of ''Serpula'': ;Higher taxonomic ranks * The genus ''Serpula'' belongs to the family Serpulidae, also known as serpulid worms or tubeworms. * Family Serpulidae is one of 31 described families of the order Canalipalpata, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
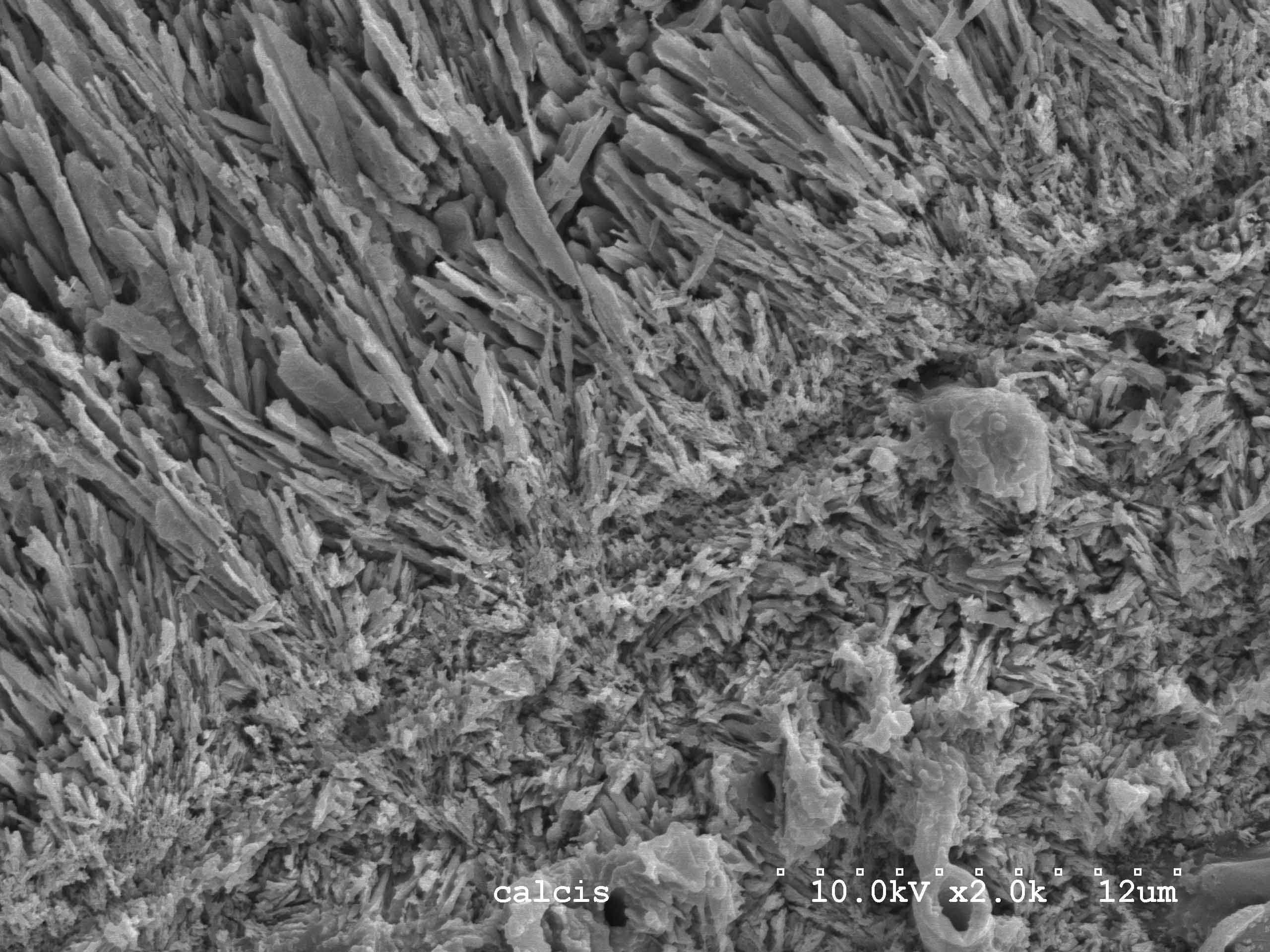
Glomerula Piloseta Tube Microstructure
''Glomerula'' is a genus of polychaete worm in the family Sabellidae. It differs from all other Sabellidae in having a calcareous tube and spinose setae. Only one living species, ''G. piloseta'', is known from Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. The oldest fossils of ''Glomerula'' are known from the Early Jurassic The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ... and their tube microstructure has remained unchanged since then. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q2153277 Sabellida Extant Early Jurassic first appearances Annelid genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm (''Arenicola marina'') and the Alitta virens, sandworm or Alitta succinea, clam worm ''Alitta''. Polychaetes as a class are robust and widespread, with species that live in the coldest ocean temperatures of the abyssal plain, to forms which tolerate the extremely high temperatures near hydrothermal vents. Polychaetes occur throughout the Earth's oceans at all depths, from forms that live as plankton near the surface, to a 2- to 3-cm specimen (still unclassified) observed by the robot ocean probe Nereus (underwater vehicle), ''Nereus'' at the bottom of the Challenger Deep, the deepest known spot in the Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomineralization
Biomineralization, also written biomineralisation, is the process by which living organisms produce minerals, often resulting in hardened or stiffened '' mineralized tissues''. It is an extremely widespread phenomenon: all six taxonomic kingdoms contain members that can form minerals, and over 60 different minerals have been identified in organisms. Examples include silicates in algae and diatoms, carbonates in invertebrates, and calcium phosphates and carbonates in vertebrates. These minerals often form structural features such as sea shells and the bone in mammals and birds. Organisms have been producing mineralized skeletons for the past 550 million years. Calcium carbonates and calcium phosphates are usually crystalline, but silica organisms (such as sponges and diatoms) are always non-crystalline minerals. Other examples include copper, iron, and gold deposits involving bacteria. Biologically formed minerals often have special uses such as magnetic sensors in magnetota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpulidae
The Serpulidae are a family of sessile, tube-building annelid worms in the class Polychaeta. The members of this family differ from other sabellid tube worms in that they have a specialized operculum that blocks the entrance of their tubes when they withdraw into the tubes. In addition, serpulids secrete tubes of calcium carbonate. Serpulids are the most important biomineralizers among annelids. About 300 species in the family Serpulidae are known, all but one of which live in saline waters. The earliest serpulids are known from the Permian ( Wordian to late Permian), and possibly the upper Permian south China The blood of most species of serpulid and sabellid worms contains the oxygen-binding pigment chlorocruorin. This is used to transport oxygen to the tissues. It has an affinity for carbon monoxide which is 570 times as strong as that of the haemoglobin found in human blood. Empty serpulid shells can sometimes be confused with the shells of a family of marine gastropo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabellidae
Sabellidae, or feather duster worms, are a family of marine polychaete tube worms characterized by protruding feathery branchiae. Sabellids build tubes out of a tough, parchment-like exudate, strengthened with sand and bits of shell. Unlike the other sabellids, the genus '' Glomerula'' secretes a tube of calcium carbonate instead. Sabellidae can be found in subtidal habitats around the world. Their oldest fossils are known from the Early Jurassic. Characteristics Feather-duster worms have a crown of feeding appendages or radioles in two fan-shaped clusters projecting from their tubes when under water. Each radiole has paired side branches making a two-edged comb for filter feeding. Most species have a narrow collar below the head. The body segments are smooth and lack parapodia. The usually eight thoracic segments bear capillaries dorsally and hooked chaetae (bristles) ventrally. The abdominal segments are similar, but with the position of the capillaries and chaetae reversed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirratulidae
Cirratulidae is a family of marine polychaete worms. Members of the family are found worldwide, mostly living in mud or rock crevices. Most are deposit feeders, but some graze on algae or are suspension feeders. Although subject to multiple revisions over time, cirratulids are among the few polychaete clades with a verified fossil record. Description Cirratulids vary in size from one to twenty centimetres long. They are mostly burrowers in soft sediments but some live in rock crevices. The head is conical or wedge-shaped and has no antennae. The body is generally cylindrical, tapering at both ends. Cirratulids are characterised by a large number of simple elongate filaments along the body. Some of these occur as an anterior cluster of tentacles, grooved for deposit-feeding, but the majority, the branchiae, are found one pair per segment, and do not have grooves. The chaetae (bristles) are simple capillaries, usually with hooks, and emerge directly from the body wall. There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skeletons and pearls. Materials containing much calcium carbonate or resembling it are described as calcareous. Calcium carbonate is the active ingredient in agricultural lime and is produced when calcium ions in hard water react with carbonate ions to form limescale. It has medical use as a calcium supplement or as an antacid, but excessive consumption can be hazardous and cause hypercalcemia and digestive issues. Chemistry Calcium carbonate shares the typical properties of other carbonates. Notably, it: *reacts with acids, releasing carbonic acid which quickly disintegrates into carbon dioxide and water: : *releases carbon dioxide upon heating, called a thermal decomposition reaction, or calcination (to above 840 °C in the case of ), t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annelid
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecologies – some in marine environments as distinct as tidal zones and hydrothermal vents, others in fresh water, and yet others in moist terrestrial environments. The annelids are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate, invertebrate organisms. They also have parapodia for locomotion. Most textbooks still use the traditional division into polychaetes (almost all marine), oligochaetes (which include earthworms) and leech-like species. Cladistic research since 1997 has radically changed this scheme, viewing leeches as a sub-group of oligochaetes and oligochaetes as a sub-group of polychaetes. In addition, the Pogonophora, Echiura and Sipuncula, previously regarded as separate phyla, are now regarded as sub-grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aragonite
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral and one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate (), the others being calcite and vaterite. It is formed by biological and physical processes, including precipitation from marine and freshwater environments. The crystal lattice of aragonite differs from that of calcite, resulting in a different crystal shape, an orthorhombic crystal system with acicular crystal. Repeated twinning results in pseudo-hexagonal forms. Aragonite may be columnar or fibrous, occasionally in branching helictitic forms called ''flos-ferri'' ("flowers of iron") from their association with the ores at the Carinthian iron mines. Occurrence The type location for aragonite is Molina de Aragón in the Province of Guadalajara in Castilla-La Mancha, Spain, for which it was named in 1797. Aragonite is found in this locality as cyclic twins inside gypsum and marls of the Keuper facies of the Triassic. This type of aragoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on Scratch hardness, scratch hardness comparison. Large calcite crystals are used in optical equipment, and limestone composed mostly of calcite has numerous uses. Other polymorphs of calcium carbonate are the minerals aragonite and vaterite. Aragonite will change to calcite over timescales of days or less at temperatures exceeding 300 °C, and vaterite is even less stable. Etymology Calcite is derived from the German , a term from the 19th century that came from the Latin word for Lime (material), lime, (genitive ) with the suffix ''-ite'' used to name minerals. It is thus a Doublet (linguistics), doublet of the word ''wikt:chalk, chalk''. When applied by archaeology, archaeologists and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |