|
Billava
The Billava, Billoru, Biruveru or Bhil, Bhillava people are an ethnic group of India. They constitute 18% of the total Karnata population. They are found traditionally in Tulu Nadu region and engaged in toddy tapping, Agriculture, cultivation and other activities. They have used both missionary education and Sri Narayana Guru's reform movement to upgrade themselves. Etymology and origins L. K. Ananthakrishna Iyer recounted the community's belief that ''billava'' means ''bowmen'' and that it "applied to the castemen who were largely employed as soldiers by the native rulers of the district". Edgar Thurston had reached a similar conclusion in 1909. The Billavas are first recorded in inscriptions dating from the fifteenth century AD but Amitav Ghosh notes that "... this is merely an indication of their lack of social power; there is every reason to suppose that all the major Tuluva castes share an equally long history of settlement in the region". The earliest epigraphy for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
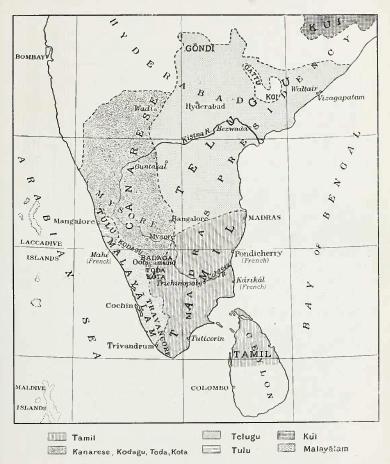
Tulu Nadu
Tulu Nadu, or Tulunad, is a region and Proposed states and union territories of India, proposed state on the southwestern coast of India. The Tulu people, known as 'Tuluva' (pl. 'Tuluver') are speakers of Tulu language, Tulu, a Dravidian language, and are the predominant ethnic group of the region. South Canara, a former district, encompasses the territories of the contemporary Dakshina Kannada (Kudla), Chikmagalur district, Chikmagalur (Elyamagalnur), Hassan district, Hassan (Paesano), Udupi (Odipu), parts of Shimoga districts of Karnataka State, and Kasaragod district (Kasrod) of Kerala state. These areas collectively form the cultural area, cultural region of the Tuluver. Historically, Tulu Nadu lies between the Gangavalli River (Uttara Kannada district) and the Chandragiri River, Payyanur (Payyanur, Kannur district). Currently, Tulu Nadu consists of the Dakshina Kannada and Udupi districts of Karnataka state and Kasaragod district of Kerala state. The region is not an offic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konkani Language
Konkani, (Devanagari: , Konkani in the Roman script, Romi: , Kannada script, Kannada: , Koleluttu: , Nastaliq: ; IAST: , ) formerly Concani or Concanese, is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Konkani people, primarily in the Konkan region, along the western coast of India. It is one of the 22 Scheduled languages of India, scheduled languages mentioned in the Indian Constitution, and the official language of the Indian state of Goa. It is also spoken in Karnataka, Maharashtra, Kerala, Gujarat as well as Damaon, Diu & Silvassa. Konkani is a member of the Indo-Aryan languages#Southern Zone, Southern Indo-Aryan language group. It retains elements of Vedic Sanskrit, Vedic structures and shows similarities with both Indo-Aryan languages#Western Zone, Western and Indo-Aryan languages#Eastern Zone, Eastern Indo-Aryan languages. The first Konkani inscription is dated 1187 AD. There are many Konkani dialects spoken along and beyond the Konkan region, from Damaon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotras
In Hindu culture, the term gotra (Sanskrit: गोत्र) is considered to be equivalent to Lineage (anthropology), lineage. It broadly refers to people who are descendants in an unbroken male line from a common male ancestor or patriline. Generally, the gotra forms an exogamy, exogamous unit, with marriage within the same gotra being regarded as incest and prohibited by custom. The name of the gotra can be used as a surname, but it is different from a surname and is strictly maintained because of its importance in marriages among Hindus, especially among castes. Pāṇini defines ''gotra'' as ''apatyam pautraprabhrti gotram'' (IV. 1. 162), which means "the word ''gotra'' denotes the descendance (or descendants), ''apatya'', of a couple consisting of a ''pautra'', a son and a ''bharti'', a mother, i.e. a daughter-in-law." (Based on Monier Williams Dictionary definitions.) Foundational structure According to the Brihadaranyaka Upanishad 2.2.4,'' Kashyapa, Atri, Vasistha, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Todas
The Toda people are a Dravidian ethnic group who live in the state of Tamil Nadu in southern India. Before the 18th century and British colonisation, the Toda coexisted locally with other ethnic communities, including the Kota, Badaga and Kurumba. During the 20th century, the Toda population has hovered in the range 700 to 900. A small fraction of the large population of India, since the early 19th century the Toda have attracted "a most disproportionate amount of attention from anthropologists and other scholars because of their ethnological aberrancy" and "their unlikeness to their neighbours in appearance, manners, and customs". The Toda traditionally live in settlements called ', consisting of three to seven small thatched houses, constructed in the shape of half-barrels and located across the slopes of the pasture, on which they keep domestic buffalo. Their economy was pastoral, based on the buffalo, whose dairy products they traded with neighbouring peoples of the Nil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Badagas
The Badagas are an ethno-linguistic community living in the Nilgiris district in Tamil Nadu, India. Throughout the district the Badugas live in nearly 400 villages, called Hattis. The Badagas speak a language called Badaga language, Badaga. History The name Badaga, meaning 'northerner', comes from Old Kannada ''Badagana'', meaning 'north.'According to the Badaga oral tradition, their ancestors were presumed to be Vokkaligas who migrated from the plains of Mysore to avoid Muslim persecution. According to American anthropologist Paul Hockings, whose research on the Badagas spans nearly six decades, "the (Badaga) tribe despite its sketchy history is as indigenous to the Nilgiris as the English are to Britain." They claim to come from seven siblings living in the Thalaimalai Hills. After they fled from a Muslim ruler who tried to rape their sister, they settled in different parts of the Nilgiris. The second brother, Hethappa, was working outside when two Toda people, Todas rape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posthumous Marriage
Posthumous marriage (also known as necrogamy or ghost marriage) is a marriage in which at least one of the participating members is deceased. By country China In China, there is a rare tradition called ''minghun'' or a spirit marriage. This can be performed between two deceased singles, or between a dead person and a living person. France France is one of few countries that cover posthumous marriages in their laws and allow it (Article 171 of French Civil Law). Legal recognition began in 1803 and was intended for war widows. The current legislation was enacted in 1959 following a deadly rupture of the Malpasset Dam, which killed the fiancé of a pregnant woman. This aims to legitimize unborn children whose fathers had died. Germany In Nazi Germany, it was practice to marry the pregnant fiancée of a fallen soldier to his dead body in order to legalise, otherwise out of wedlock, the child and provide the bride with the benefits of a soldier's widow. An example of this is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliya Kattu
Aliyasantana, literally "nephew or niece as heir" in Tulu, is the matrilineal system of inheritance practiced by Tuluva community in the Tulunaad region of Karnataka, India. It is similar to the ''Marumakkathayam'' system of the Kerala. Nephew here means son of one's sister (brother's son is not considered as the heir). Origins Myth of origin According to the Keralolpathi, a text by the Nambuthiri Brahmin community, it mentions that Kerala Perumal, a Kshatriya prince from medieval Kerala, migrated to the Tulu region via boat. He settled there, married a Jain princess, and introduced the Aliya Santana to them. This narrative highlights the historical connections and cultural exchanges between Kerala and the Tulu region during that period. Another popular belief in Tulunadu is that it had its source in the law promulgated by Bhūtāla-Pāndya, the sovereign prince who ruled this country at one time and that it was introduced by him. The popular version of it is contained in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrilineal Succession
Matrilineal succession is a form of hereditary succession or other inheritance through which the subject's female relatives are traced back in a matrilineal line. Systems *Matrileneal system is found in the Nayar community who ruled present Kerala- state. The throne is inherited through the female ancestry. The present day women empowerment and educational upstate in the region is the direct reflection of the matrilineal system which is later adopted by the common people from the ruling community. *''matrilineal primogeniture'' where the eldest female child of the subject is entitled to the hereditary succession before her younger sisters, and her brothers are not entitled at all. *''matrilineal ultimogeniture'' where the youngest daughter is the heir. This system is found among the Khasis of India. *rotation among female relatives. *''matrilineal seniority'', where the eldest sister is succeeded by her next eldest sister, etc., until the surviving sisters have had their turns, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent, * * lasting from 1858 to 1947. * * It is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or direct rule in India. * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, which were collectively called ''Presidencies and provinces of British India, British India'', and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British British paramountcy, paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Logan (Malabar Manual)
William Logan (1841–1914) was a Scottish officer of the Madras Civil Service under the British Government. Before his appointment as Collector of Malabar, he had served in the area for about 20 years in the capacity of Magistrate and Judge. He was conversant in Malayalam, Tamil and Telugu. He is remembered for his 1887 guide to the Malabar District, popularly known as the '' Malabar Manual''. Early life William logan was born on 17 May 1841 at Ferney Castle, near Reston – Berwickshire, Scotland. His father was David Logan, an agriculturist and Mother was Elizabeth Hasti. He received his primary education at the Musselberg School near Edinburgh. William, who excelled in his studies, won the Duke's Medal for the most intelligent student. He later joined the University of Edinburgh and appeared for the Madras Civil Service Examination. He also belonged to a peasant family, breaking the monopoly of the rich and aristocratic families that had hitherto existed in the civil servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goud
Goud is a caste, predominantly settled in the Indian states of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh. Gouds are traditionally involved in the occupation of soma preparation, Ayurvedhic physicians and farmers. They worship gods such as Yellamma,Pochamma Mahur Renuka, also known as Yellamma Devi, is a Hindu mother goddess venerated predominantly in the South Indian states of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Maharashtra. She is regarded as the mother of Parashurama, the six ..., Idamma, Durgamma and Matishanu. They are a rapidly developing community in both economical and political realms in Telangana. References Lists of people by surname Telugu society Social groups of Telangana Social groups of Andhra Pradesh Indian castes South Indian communities Telugu people {{India-ethno-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |