|
Beta Lomatogona
''Beta lomatogona'' is a species of wild beet in the family Amaranthaceae, native to Cyprus, Turkey, the Transcaucasus, and Iran. A diploid, it is being studied for its cold and drought resistance in an effort to improve the sugar beet A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and that is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris''). Together with .... References lomatogona Flora of Cyprus Flora of Turkey Flora of the Transcaucasus Flora of Iran Plants described in 1838 {{Amaranthaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Ernst Ludwig Von Fischer
Friedrich Ernst Ludwig Fischer (20 February 1782, Halberstadt – 17 June 1854) was a Russian botanist, born in the Holy Roman Empire. He was director of the St Petersburg botanical garden from 1823 to 1850. In 1804 he obtained his medical doctorate from the University of Halle, afterwards working as director of Count Razumoffsky's botanical garden in Gorenki (near Moscow). In 1808 he produced a catalogue of plants of the garden. In 1823, he was appointed director of the imperial botanical garden in St. Petersburg by Alexander I of Russia, Alexander I. Here, he was involved with establishing a herbarium and library, as well as the planning of numerous scientific expeditions into the interior of Russia. During his final years, he served as a medical councillor for the Ministry of the Interior. In 1815, he was elected a corresponding member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. In 1841, his status was changed to that of foreign member. Selected works * ''Catalogue du Jardin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Anton Von Meyer
Carl Anton von Meyer (in Russian: Карл Анто́нович фон Ме́йер, ''Karl Antonovich von Meyer'') (1 April 1795 – 24 February 1855) was a Germans, German, Russified botanist and explorer. Meyer was born in Vitebsk. He received his education at the University of Dorpat (1813–14) as a student of Karl Friedrich von Ledebour, with whom he later embarked on a scientific journey to the Crimean Peninsula, Crimea (1818). In 1826, with Ledebour and Alexander G. von Bunge, he took part in an expedition to the Altay Mountains and the Kirghiz Steppe (Kazakhstan). Plants collected on the trip formed the basis of "Flora Altaica" (four volumes issued between 1829 and 1833).JSTOR Global Plants JSTOR Global Plants] (biography) In 1835 he began work as a botanist for the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, Academy of Sciences in St. Petersburg, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta (plant)
''Beta'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Amaranthaceae. The best known member is the common beet, ''Beta vulgaris'', but several other species are recognised. Almost all have common names containing the word "beet". Wild ''Beta'' species can be found throughout the Atlantic coast of Europe, the Mediterranean coastline, the Near East, and parts of Asia including India. Description This genus consists of annual, biennial, or perennial species, often with fleshy, thickened roots. The stems grow erect or procumbent. The alternate leaves are petiolate or sessile, with ovate-cordate to rhombic-cuneate leaf blades, their margins mostly entire, with obtuse apex. The inflorescences are long spikelike cymes or glomerules. Bracts can be leaflike (''Beta macrorhiza'') or very small, the upper half of the inflorescence often without bracts. The bisexual flowers consist of (3–) 5 basally connate perianth segments (either greenish, dorsally ridged and with hooded tips, or p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
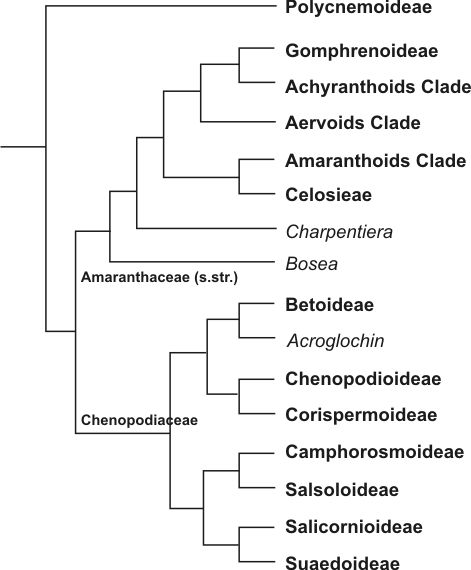
Amaranthaceae
Amaranthaceae ( ) is a family of flowering plants commonly known as the amaranth family, in reference to its type genus '' Amaranthus''. It includes the former goosefoot family Chenopodiaceae and contains about 165 genera and 2,040 species, making it the most species-rich lineage within its parent order, Caryophyllales. Description Most species in the Amaranthaceae are annual or perennial herbs or subshrubs; others are shrubs; very few species are vines or trees. Some species are succulent. Many species have stems with thickened nodes. The wood of the perennial stem has a typical "anomalous" secondary growth; only in subfamily Polycnemoideae is secondary growth normal. The leaves are simple and mostly alternate, sometimes opposite. They never possess stipules. They are flat or terete, and their shape is extremely variable, with entire or toothed margins. In some species, the leaves are reduced to minute scales. In most cases, neither basal nor terminal aggregations of leav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcaucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, Georgia, and Azerbaijan, which are sometimes collectively known as the Caucasian States. The total area of these countries measures about . The South Caucasus and the North Caucasus together comprise the larger Caucasus geographical region that divides Eurasia. The South Caucasus is a dynamic and complex region where the three countries have pursued distinct geopolitical pathways. Geography The South Caucasus spans the southern portion of the Caucasus Mountains and their lowlands, straddling the border between the continents of Europe and Asia, and extending southwards from the southern part of the Main Caucasian Range of southwestern Russia to the Turkish and Armenian borders, and from the Black Sea in the west to the Caspian Sea coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair—the form in which chromosomes naturally exist. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar Beet
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose and that is grown commercially for sugar production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris''). Together with other beet cultivars, such as beetroot and chard, it belongs to the subspecies ''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'' but classified as ''var. saccharifera''. Its closest wild relative is the sea beet (''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''maritima''). Sugar beets are grown in climates that are too cold for sugarcane. In 2020, Russia, the United States, Germany, France and Turkey were the world's five largest sugar beet producers. In 2010–2011, Europe, and North America except Arctic territories failed to supply the overall domestic demand for sugar and were all net importers of sugar. The US harvested of sugar beets in 2008. In 2009, sugar beets accounted for 20% of the world's sugar production and nearly 30% by 2013. Sugarcane accounts for most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Cyprus
The wildlife of Cyprus includes its flora and fauna and their natural habitats. Cyprus has a rich flora and a diverse fauna albeit with relatively few mammals. Like most modern countries, the natural habitats in Cyprus have been steadily disappearing, currently retaining only 20% of its original habitat due to rapid urbanization, usage of forests for commercial purposes, tourism and various other reasons. One of the features of Cyprus' habitats is the wild and sharp differences in elevations and habitats on the island as well as climate, all of which supply a diverse habitat for an array of fauna and flora. Terra Cypria was established as a trust in 1992 to conserve the Cypriot environment and its biodiversity. Fauna Amphibians The fauna of Cyprus has four amphibians. Birds Cyprus also has over 380 species of bird due to being on migration routes between Africa, Europe and western Asia including Eleonora's falcon (''Falco eleonorae''), flamingo and the imperial eagle (''Aq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Turkey
The flora of Turkey consists of almost 10,000 species of plants, as well as a number of fungi and algae. Around 32% of Turkey's plants are found only in the country. One reason for the high proportion of endemics is that Anatolia is both mountainous and quite fragmented. The country is divided into three main floristic areas: the Mediterranean, Euro-Siberian, and Irano-Tranian area. The flora of the European part of Turkey is similar to that of adjoining Greece. The ecoregions here include Balkan mixed forests dominated by Oak, oaks, and Aegean and Western Turkey sclerophyllous and mixed forests where some of the main species are oaks, Arbutus unedo, strawberry tree, ''Arbutus andrachne, Greek strawberry tree'', Spartium junceum, Spanish broom and Laurus nobilis, laurel. The country is at a meeting point of three Phytogeography, phytogeographical regions Mediterranean basin, Mediterranean, Euro-Siberian region, Euro-Siberian, and Irano-Turanian Region, Irano-Turonian. The regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of The Transcaucasus
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring ( indigenous) native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora as in the terms ''gut flora'' or ''skin flora'' for purposes of specificity. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Iran
The wildlife of Iran include the fauna and flora of Iran. One of the most famous animals of Iran is the critically endangered Asiatic cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus venaticus''), which today survives only in Iran. Another notable species is the Iranian ground jay (''Podoces pleskei''), the only bird endemic to Iran. History The animals of Iran were described by Hamdallah Mustawfi in the 14th century. In the 18th and 19th centuries, Samuel Gottlieb Gmelin and Édouard Ménétries explored the Caspian Sea area and the Talysh Mountains to document Caspian fauna. Several naturalists followed in the 19th century, including Filippo de Filippi, William Thomas Blanford, and Nikolai Zarudny who documented mammal, bird, reptile, amphibian and fish species. The Complete Fauna of Iran by Eskandar Firouz, documents a wide range of species across the country’s ecosystems Flora More than one-tenth of the country is forested. The most extensive forest is found on the mountain slopes rising from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |