|
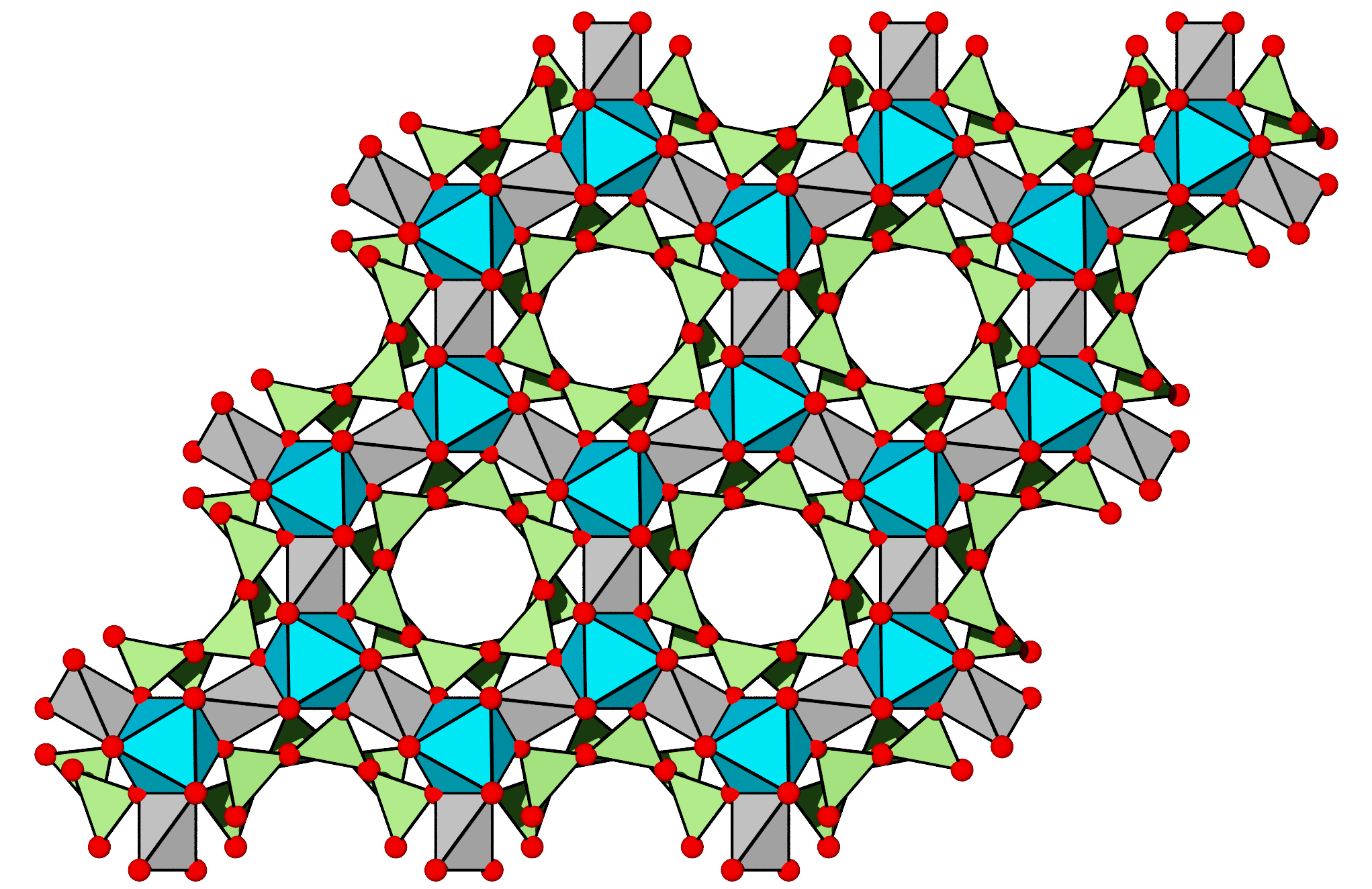
Beryl
Beryl ( ) is a mineral composed of beryllium aluminium Silicate minerals#Cyclosilicates, silicate with the chemical formula Be3Al2(SiO3)6. Well-known varieties of beryl include emerald and Aquamarine (gem), aquamarine. Naturally occurring Hexagonal crystal system, hexagonal crystals of beryl can be up to several meters in size, but double terminated crystal, terminated crystals are relatively rare. Pure beryl is colorless, but it is frequently tinted by impurities; possible colors are green, blue, yellow, pink, and red (the rarest). It is an ore source of beryllium. Etymology The word ''beryl'' – – is borrowed, via and , from Ancient Greek βήρυλλος ''bḗryllos'', which referred to various blue-green stones, from Prakrit ''veruḷiya'', ''veḷuriya'' 'beryl' which is ultimately of Dravidian languages, Dravidian origin, maybe from the name of Belur, Karnataka, Belur or ''Velur'', a town in Karnataka, southern India. The term was later adopted for the mineral ber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, hard, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form minerals. Gemstones high in beryllium include beryl (Aquamarine (gemstone), aquamarine, emerald, red beryl) and chrysoberyl. It is a Abundance of the chemical elements#Universe, relatively rare element in the universe, usually occurring as a product of the spallation of larger atomic nuclei that have collided with cosmic rays. Within the cores of stars, beryllium is depleted as it is fused into heavier elements. Beryllium constitutes about 0.0004 percent by mass of Earth's crust. The world's annual beryllium production of 220 tons is usually manufactured by extraction from the mineral beryl, a difficult process because beryllium bonds strongly to oxygen. In structural applications, the combination of high flexural ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
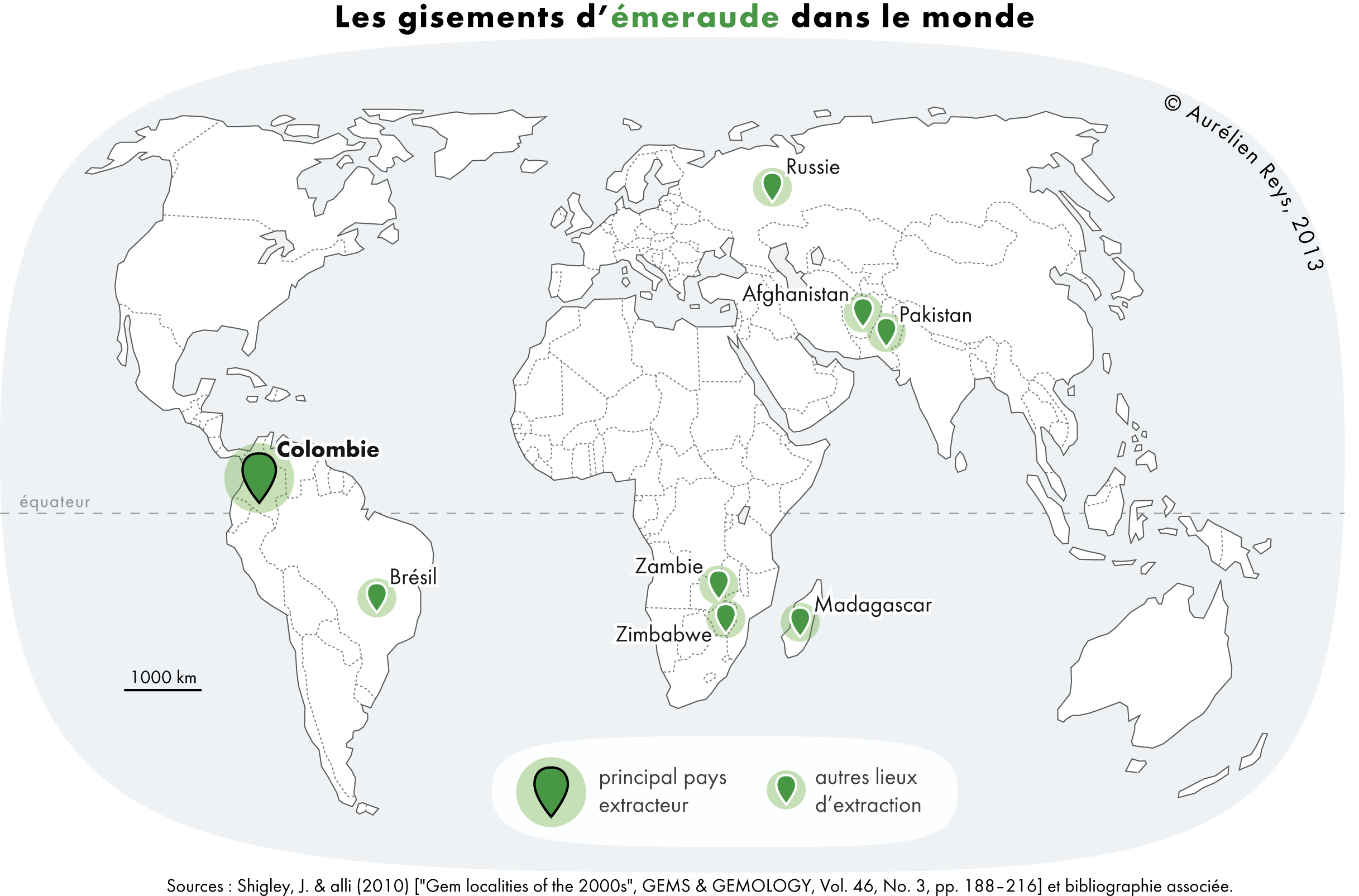
Emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr., and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991). ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 203, . Beryl has a hardness of 7.5–8 on the Mohs scale. Most emeralds have many inclusions, so their toughness (resistance to breakage) is classified as generally poor. Emerald is a cyclosilicate. Etymology The word "emerald" is derived (via and ), from Vulgar Latin: ''esmaralda/esmaraldus'', a variant of Latin ''smaragdus'', which was via (smáragdos; "green gem"). The Greek word may have a Semitic, Sanskrit or Persian origin. According to ''Webster's Dictionary'' the term emerald was first used in the 14th century. Properties determining value Emeralds, like all colored gemstones, are graded using four basic parameters known as "the four ''C''s": ''color'', ''clarity,'' ''cut'' and ''carat weight''. Normally, in grading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicate Minerals
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust. In mineralogy, the crystalline forms of silica (silicon dioxide, ) are usually considered to be tectosilicates, and they are classified as such in the Dana system (75.1). However, the Nickel-Strunz system classifies them as oxide minerals (4.DA). Silica is found in nature as the mineral quartz, and its polymorphs. On Earth, a wide variety of silicate minerals occur in an even wider range of combinations as a result of the processes that have been forming and re-working the crust for billions of years. These processes include partial melting, crystallization, fractionation, metamorphism, weathering, and diagenesis. Living organisms also contribute to this geologic cycle. For example, a type of plankton known as diatoms construct their exoskeletons ("frustules") from silica extracted from s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cymophane
The mineral or gemstone chrysoberyl is an aluminate of beryllium with the formula Be Al2 O4. The name chrysoberyl is derived from the Greek words χρυσός ''chrysos'' and βήρυλλος ''beryllos'', meaning "a gold-white spar". Despite the similarity of their names, chrysoberyl and beryl are two completely different gemstones, although they both contain beryllium. Chrysoberyl is the third-hardest frequently encountered natural gemstone and lies at 8.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, between corundum (9) and topaz (8). An interesting feature of its crystals are the cyclic twins called ''trillings''. These twinned crystals have a hexagonal appearance, but are the result of a triplet of twins with each "twin" oriented at 120° to its neighbors and taking up 120° of the cyclic trilling. If only two of the three possible twin orientations are present, a V-shaped twin results. Ordinary chrysoberyl is yellowish-green and transparent to translucent. When the mineral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morganite (gem)
Morganite is an orange or pink variety of beryl and is also a gemstone. Morganite is mined in Brazil, Afghanistan, Mozambique, Namibia, the United States, and Madagascar. Morganite has grown in popularity since 2010. '' Brides'' and CNN have listed it as a possible alternative to diamond for engagement rings. Name Following the discovery of a new locality for rose beryl in Madagascar in 1910, George Kunz proposed the name morganite at a meeting of the New York Academy of Sciences on 5 December 1910 to honour his friend and customer J.P. Morgan for his financial support for the arts and sciences, and his important gifts of gems to the American Museum of Natural History in New York and to the Museum of Natural History in Paris. Morgan was one of the most important gem collectors in the early 1900s – his collection was partly assembled by Tiffany and Company and their chief gemmologist, Kunz. Morganite is also known as pink beryl, rose beryl, pink emerald, and "cesian (or ''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclosilicate
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust. In mineralogy, the crystalline forms of silica (silicon dioxide, ) are usually considered to be Silicate mineral#Tectosilicates, tectosilicates, and they are classified as such in the Dana system (75.1). However, the Nickel-Strunz system classifies them as oxide minerals (4.DA). Silica is found in nature as the mineral quartz, and its polymorphism (materials science), polymorphs. On Earth, a wide variety of silicate minerals occur in an even wider range of combinations as a result of the processes that have been forming and re-working the crust for billions of years. These processes include partial melting, crystallization, fractionation, metamorphism, weathering, and diagenesis. Living organisms also contribute to this carbonate–silicate cycle, geologic cycle. For example, a type of plankton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquamarine (gem)
Aquamarine is a pale-blue to light-green variety of the beryl family, with its name relating to water and sea. The color of aquamarine can be changed by heat, with a goal to enhance its physical appearance (though this practice is frowned upon by collectors and jewelers). It is the birth stone of March. Aquamarine is a fairly common gemstone, rendering it more accessible for purchase, compared to other gems in the beryl family. Overall, its value is determined by weight, color, cut, and clarity. It is transparent to translucent and possesses a hexagonal crystal system. Aquamarine mainly forms in granite pegmatites and hydrothermal veins, and it is a very lengthy process that can take millions of years to form. Aquamarine occurs in many countries over the world, and is most commonly used for jewelry, decoration and its properties. Aquamarine is mainly extracted through open-pit mining, however underground mining is also a possibility to access aquamarine reserves. Aquamarine i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemstone
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, semiprecious stone, or simply gem) is a piece of mineral crystal which, when cut or polished, is used to make jewellery, jewelry or other adornments. Certain Rock (geology), rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, and obsidian) and occasionally organic chemistry, organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, Jet (gemstone), jet, and pearl) may also be used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some softer minerals such as brazilianite may be used in jewelry because of their color or Lustre (mineralogy), luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. However, generally speaking, soft minerals are not typically used as gemstones by virtue of their brittleness and lack of durability. Found all over the world, the industry of coloured gemstones (i.e. anything other than diamonds) is currently estimated at US$1.55billion and is projected to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquamarine (gem)
Aquamarine is a pale-blue to light-green variety of the beryl family, with its name relating to water and sea. The color of aquamarine can be changed by heat, with a goal to enhance its physical appearance (though this practice is frowned upon by collectors and jewelers). It is the birth stone of March. Aquamarine is a fairly common gemstone, rendering it more accessible for purchase, compared to other gems in the beryl family. Overall, its value is determined by weight, color, cut, and clarity. It is transparent to translucent and possesses a hexagonal crystal system. Aquamarine mainly forms in granite pegmatites and hydrothermal veins, and it is a very lengthy process that can take millions of years to form. Aquamarine occurs in many countries over the world, and is most commonly used for jewelry, decoration and its properties. Aquamarine is mainly extracted through open-pit mining, however underground mining is also a possibility to access aquamarine reserves. Aquamarine i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitreous Lustre
Lustre (Commonwealth English) or luster (American English; see spelling differences) is the way light interacts with the surface of a crystal, rock, or mineral. The word traces its origins back to the Latin ''lux'', meaning "light", and generally implies radiance, gloss, or brilliance. A range of terms are used to describe lustre, such as ''earthy'', ''metallic'', ''greasy'', and ''silky''. Similarly, the term ''vitreous'' (derived from the Latin for glass, ''vitrum'') refers to a glassy lustre. A list of these terms is given below. Lustre varies over a wide continuum, and so there are no rigid boundaries between the different types of lustre. (For this reason, different sources can often describe the same mineral differently. This ambiguity is further complicated by lustre's ability to vary widely within a particular mineral species). The terms are frequently combined to describe intermediate types of lustre (for example, a "vitreous greasy" lustre). Some minerals exhib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexagonal Crystal System
In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal family is one of the six crystal family, crystal families, which includes two crystal systems (hexagonal and trigonal) and two lattice systems (hexagonal and rhombohedral). While commonly confused, the trigonal crystal system and the rhombohedral lattice system are not equivalent (see section hexagonal crystal family#Crystal systems, crystal systems below). In particular, there are crystals that have trigonal symmetry but belong to the hexagonal lattice (such as α-quartz). The hexagonal crystal family consists of the 12 point groups such that at least one of their space groups has the hexagonal lattice as underlying lattice, and is the union of the hexagonal crystal system and the trigonal crystal system. There are 52 space groups associated with it, which are exactly those whose Bravais lattice is either hexagonal or rhombohedral. __TOC__ Lattice systems The hexagonal crystal family consists of two lattice systems: hexagonal and rhom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexagonal Crystal Family
In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal family is one of the six crystal families, which includes two crystal systems (hexagonal and trigonal) and two lattice systems (hexagonal and rhombohedral). While commonly confused, the trigonal crystal system and the rhombohedral lattice system are not equivalent (see section crystal systems below). In particular, there are crystals that have trigonal symmetry but belong to the hexagonal lattice (such as α-quartz). The hexagonal crystal family consists of the 12 point groups such that at least one of their space groups has the hexagonal lattice as underlying lattice, and is the union of the hexagonal crystal system and the trigonal crystal system. There are 52 space groups associated with it, which are exactly those whose Bravais lattice is either hexagonal or rhombohedral. __TOC__ Lattice systems The hexagonal crystal family consists of two lattice systems: hexagonal and rhombohedral. Each lattice system consists of one Bravais ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |