|
Be X-ray Binaries
Be/X-ray binaries (BeXRBs or BeXBs) are a class of high-mass X-ray binaries that consist of a Be star and a neutron star. The neutron star is usually in a wide highly elliptical orbit around the Be star. The Be stellar wind forms a disk confined to a plane often different from the orbital plane of the neutron star. When the neutron star passes through the Be disk, it accretes a large mass of hot gas in a short time. As the gas falls onto the neutron star, a bright flare in hard X-rays is seen. Definition and classification Be/X-ray binaries belong to the high-mass X-ray binary category. The optical companion is a non-supergiant, fast-rotating Be type star with emission lines indicating luminosity class III-V. Most BeXRBs have eccentric orbits and contain a neutron star, confirmed through X-ray pulsations. BeXRBs are classified as either transient or persistent. Transient BeXRBs show two outburst types: type I outbursts are regular, periodic events occurring near periastron (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-mass X-ray Binaries
X-ray binaries are a class of binary stars that are luminous in X-rays. The X-rays are produced by matter falling from one component, called the ''donor'' (usually a relatively common main sequence star), to the other component, called the ''accretor'', which can be a white dwarf, neutron star or black hole. The infalling matter releases gravitational energy, gravitational potential energy, up to 30 percent of its rest mass, as X-rays. (Hydrogen nuclear fusion, fusion releases only about 0.7 percent of rest mass.) The lifetime and the mass-transfer rate in an X-ray binary depends on the evolutionary status of the donor star, the mass ratio between the stellar components, and their orbital separation. An estimated 1041 positrons escape per second from a typical X-ray binary#Low-mass X-ray binary, low-mass X-ray binary. Classification X-ray binaries are further subdivided into several (sometimes overlapping) subclasses, that perhaps reflect the underlying physics better. Not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
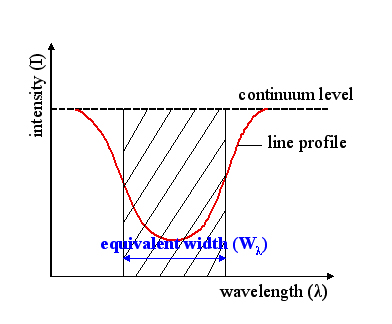
Equivalent Width
The equivalent width of a spectral line is a measure of the area of the line on a plot of intensity versus wavelength in relation to underlying continuum level. It is found by forming a rectangle with a height equal to that of continuum emission, and finding the width such that the area of the rectangle is equal to the area in the spectral line. It is a measure of the strength of spectral features that is primarily used in astronomy. Definition Formally, the equivalent width is given by the equation W_\lambda = \int d\lambda = \int (1 - F_s / F_c) d\lambda. Here, F_c(\lambda) represents the underlying continuum intensity, while F_s(\lambda) represents the intensity of the actual spectrum (the line and continuum). Then W_\lambda represents the width of a hypothetical line which drops to an intensity of zero and has the "same integrated flux deficit from the continuum as the true one." This equation can be applied to either emission or absorption, but when applied to emission, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Persei
X Persei is a high-mass X-ray binary system located in the constellation Perseus (constellation), Perseus, approximately 950 parsecs away. It is catalogued as 4U 0352+309 in the final Uhuru (satellite), Uhuru catalog of X-ray objects. The conventional star component of X Persei has been classified either as an O-type giant or a B-type main sequence star. It is a Be star, rotating rapidly, and at times surrounded by a disk of expelled material. This qualifies it as a Gamma Cassiopeiae variable, and the visual range is magnitude 6 - 7. In 1989 and 1990, the spectrum of X Persei changed from a Be star to a normal B class star while it faded significantly. This appears to have been caused by the loss of the excretion disk. The disk has since reformed and shows strong emission lines. The system also contains a neutron star which is a pulsar with an unusually long period of 837 seconds. The pulsar has shown period changes that are associated with mass transfer from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Hole
A black hole is a massive, compact astronomical object so dense that its gravity prevents anything from escaping, even light. Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will form a black hole. The boundary (topology), boundary of no escape is called the event horizon. A black hole has a great effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, but has no locally detectable features according to general relativity. In many ways, a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light. Quantum field theory in curved spacetime predicts that event horizons emit Hawking radiation, with thermal radiation, the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass. This temperature is of the Orders of magnitude (temperature), order of billionths of a kelvin for stellar black holes, making it essentially impossible to observe directly. Objects whose gravitational fields are too strong for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsar
A pulsar (''pulsating star, on the model of quasar'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its Poles of astronomical bodies#Magnetic poles, magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Earth (similar to the way a lighthouse can be seen only when the light is pointed in the direction of an observer), and is responsible for the pulsed appearance of emission. Neutron stars are very density, dense and have short, regular rotational Period (physics), periods. This produces a very precise interval between pulses that ranges from milliseconds to seconds for an individual pulsar. Pulsars are one of the candidates for the source of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays (see also centrifugal mechanism of acceleration). Pulsars’ highly regular pulses make them very useful tools for astronomers. For example, observations of a pulsar in a PSR B1913+16, binary neutron star system were use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
γ Cassiopeiae Variable
Gamma (; uppercase , lowercase ; ) is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop . In Modern Greek, this letter normally represents a voiced velar fricative , except before either of the two front vowels (/e/, /i/), where it represents a voiced palatal fricative ; while /g/ in foreign words is instead commonly transcribed as γκ). In the International Phonetic Alphabet and other modern Latin-alphabet based phonetic notations, it represents the voiced velar fricative. History The Greek letter Gamma Γ is a grapheme derived from the Phoenician letter (''gīml'') which was rotated from the right-to-left script of Canaanite to accommodate the Greek language's writing system of left-to-right. The Canaanite grapheme represented the /g/ phoneme in the Canaanite language, and as such is cognate with ''gimel'' ג of the Hebrew alphabet. Based on its name, the lett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure and electronic structure of matter to be investigated at the atomic, molecular and macro scale, and over astronomical distances. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Current applications of spectroscopy include biomedical spectroscopy in the areas of tissue analysis and medical imaging. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Formation
Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space—sometimes referred to as "stellar nurseries" or "star-forming regions"—Jeans instability, collapse and form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function. Most stars do not form in isolation but as part of a group of stars referred as star clusters or stellar associations. First stars Star formation is divided into three groups called "Populations". Population III stars formed from primordial hydrogen after the Big Bang. These stars are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallicity
In astronomy, metallicity is the Abundance of the chemical elements, abundance of Chemical element, elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal currently detectable (i.e. non-Dark matter, dark) matter in the universe is either hydrogen or helium, and astronomers use the word ''metals'' as convenient shorthand for ''all elements except hydrogen and helium''. This word-use is distinct from the conventional chemical or physical definition of a metal as an electrically conducting element. Stars and nebulae with relatively high abundances of heavier elements are called ''metal-rich'' when discussing metallicity, even though many of those elements are called ''Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetals'' in chemistry. Metals in early spectroscopy In 1802, William Hyde WollastonMelvyn C. UsselmanWilliam Hyde WollastonEncyclopædia Britannica, retrieved 31 March 2013 noted the appearance of a number of dark features in the solar spectrum. In 1814, Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Magellanic Cloud
The Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC) is a dwarf galaxy near the Milky Way. Classified as a dwarf irregular galaxy, the SMC has a D25 isophotal diameter of about , and contains several hundred million stars. It has a total mass of approximately 7 billion solar masses. At a distance of about 200,000 light-years, the SMC is among the nearest intergalactic neighbors of the Milky Way and is one of the most distant objects visible to the naked eye. The SMC is visible from the entire Southern Hemisphere and can be fully glimpsed low above the southern horizon from tropics, latitudes south of about 15th parallel north, 15° north. The galaxy is located across the constellation of Tucana and part of Hydrus, appearing as a faint, hazy patch resembling a detached piece of the Milky Way. The SMC has an average apparent diameter of about 4.2° (8 times the Moon's) and thus covers an area of about 14 square degrees (70 times the Moon's). Since its surface brightness is very low, this deep-sky objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magellanic Clouds
The Magellanic Clouds (''Magellanic system'' or ''Nubeculae Magellani'') are two irregular dwarf galaxies in the southern celestial hemisphere. Orbiting the Milky Way galaxy, these satellite galaxies are members of the Local Group. Because both show signs of a bar structure, they are often reclassified as Magellanic spiral galaxies. The two galaxies are the following: * Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), about away * Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), about away The Magellanic Clouds are visible to the unaided eye from the Southern Hemisphere, but cannot be observed from the most northern latitudes. History They may be the objects mentioned by the polymath Ibn Qutaybah (d. 889 CE), in his book on ''Al-Anwā̵’'' (the stations of the Moon in pre-Islamic Arabian culture): وأسفل من سهيل قدما سهيل . وفى مجرى قدمى سهيل، من خلفهما كواكب زهر كبار، لا ترى بالعراق، يسميها أهل تهامة الأعبار And be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |