|
Battle Of Krithia
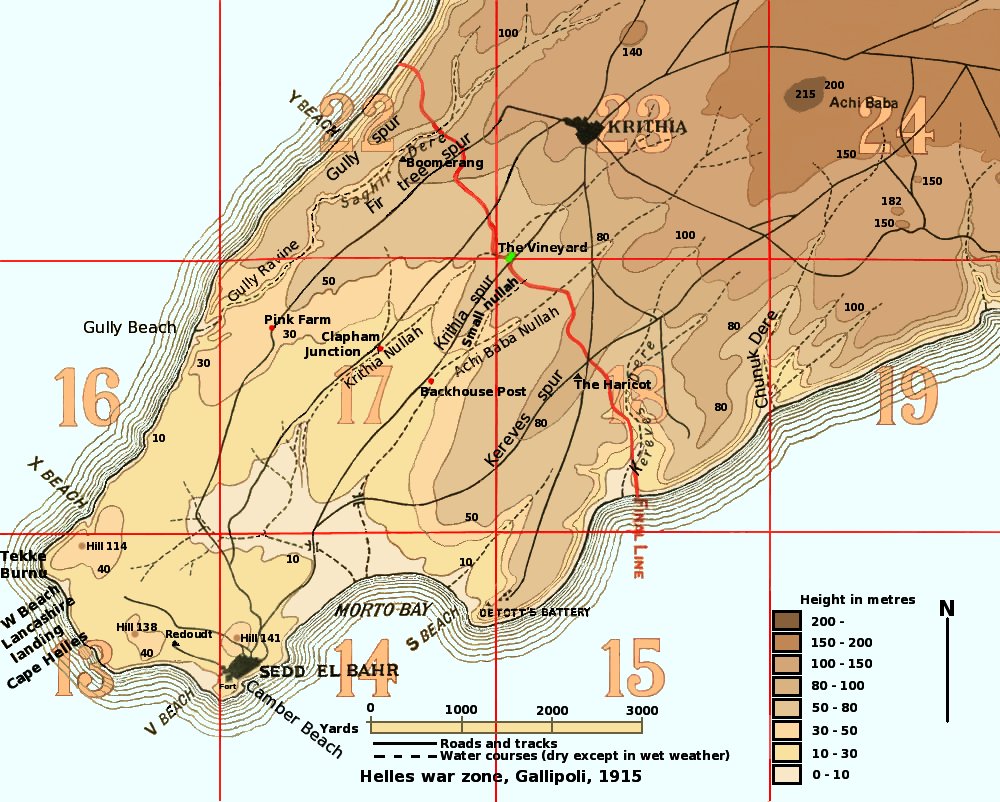
During the Gallipoli campaign in 1915, several battles were fought near the village of Krithia, today Alçıtepe. The village was an objective of the first day of the landing, 25 April 1915. Over the following months, invading British Empire (including the 89th Punjabis of the British Indian Army The Indian Army was the force of British Raj, British India, until Indian Independence Act 1947, national independence in 1947. Formed in 1895 by uniting the three Presidency armies, it was responsible for the defence of both British India and ...) and French troops, who had landed near Cape Helles at the end of the peninsula, made several attempts to capture the village. It was never reached; the Ottoman defenders successfully repulsed every assault. The attacks came to be known as: * The First Battle of Krithia - 28 April * The Second Battle of Krithia - 6 May - 8 May * The Third Battle of Krithia - 4 June * The Battle of Krithia Vineyard - 6 August – 13 August Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the English overseas possessions, overseas possessions and trading posts established by Kingdom of England, England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries, and colonisation attempts by Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland during the 17th century. At its height in the 19th and early 20th centuries, it became the List of largest empires, largest empire in history and, for a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, Westminster system, its constitutional, Common law, legal, English language, linguistic, and Culture of the United Kingdom, cultural legacy is widespread. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
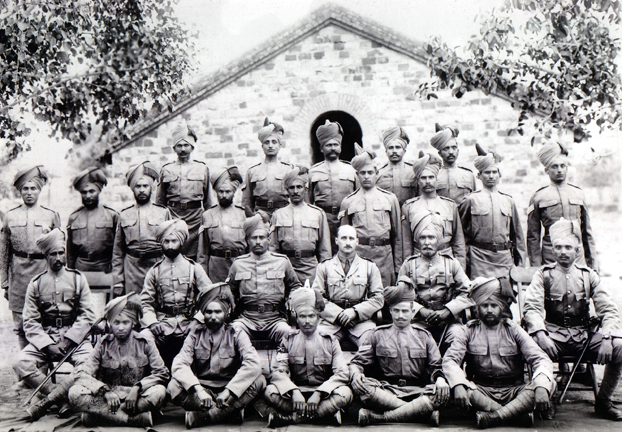
89th Punjabis
The 89th Punjabis was an infantry regiment of the British Indian Army raised in 1798 as a battalion of Madras Native Infantry. It was designated as the 89th Punjabis in 1903 and became 1st Battalion 8th Punjab Regiment in 1922. In 1947, it was allocated to Pakistan Army, where it continues to exist as 1st Battalion, The Baloch Regiment.Ahmad, Lt Col Rifat Nadeem. (2012). ''The Gallant One: War Services of First Battalion The Baloch Regiment''. Rawalpindi: The Battalion. History Formation and early service The regiment was raised on 9 November 1798 at Masulipatam as the 3rd Extra Battalion of Madras Native Infantry by Captain Alexander MacLeod and was known as ''MacLeod ki Paltan'' (MacLeod's Battalion). In 1800, it was designated as the 1st Battalion 15th Regiment, and in 1824, as the 29th Regiment of Madras Native Infantry. The battalion was composed mostly of Muslims, Tamils and Telugus of South India. In 1818, it was dispatched to Ceylon to suppress a rebellion of the Sinhalese. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Indian Army
The Indian Army was the force of British Raj, British India, until Indian Independence Act 1947, national independence in 1947. Formed in 1895 by uniting the three Presidency armies, it was responsible for the defence of both British India and the princely states, which could also have their own Imperial Service Troops, armies. As stated in the ''Imperial Gazetteer of India'', the "British Government has undertaken to protect the dominions of the Native princes from invasion and even from rebellion within: its army is organized for the defence not merely of British India, but of all possessions under the suzerainty of the Emperor of India, King-Emperor." The Indian Army was a vital part of the British Empire's military forces, especially in World War I and World War II. The Indian Presidencies and provinces of British India, Presidency armies were originally under East India Company command, and comprised the Bengal Army, Madras Army, and Bombay Army. After the Indian Rebellion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (, , ), is the principal Army, land warfare force of France, and the largest component of the French Armed Forces; it is responsible to the Government of France, alongside the French Navy, French Air and Space Force, and the National Gendarmerie. The Army is commanded by the Chief of Staff of the French Army (CEMAT), who is subordinate of the Chief of the Defence Staff (France), Chief of the Defence Staff (CEMA), who commands active service Army units and in turn is responsible to the President of France. CEMAT is also directly responsible to the Ministry of Armed Forces (France), Ministry of the Armed Forces for administration, preparation, and equipment. The French Army, following the French Revolution, has generally been composed of a mixed force of conscripts and professional volunteers. It is now considered a professional force, since the French Parliament suspended the Conscription in France, conscription of soldiers. Acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Helles
Cape Helles is the rocky headland at the southwesternmost tip of the Gallipoli peninsula, Turkey. It was the scene of heavy fighting between Ottoman Turkish and British troops during the landing at Cape Helles at the beginning of the Gallipoli campaign in 1915. The name derives from the Greek Helle; Helles means "Helle's" in Greek (see also Hellespont). The Helles Memorial is a British and Commonwealth battle memorial for the whole Gallipoli campaign. It lists all units that served on the peninsula during the campaign including the Australian and New Zealand units that served in the Anzac sector and all units that served in the Suvla Bay sector. The Helles Memorial also commemorates the names of all United Kingdom and Indian forces who died anywhere on the peninsula and have no known grave. Australians who died in the Helles sector are commemorated on the Helles Memorial and are not commemorated on the Lone Prine Memorial. Over 20,000 names are commemorated on the Helles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of Krithia
The First Battle of Krithia () was the first Allied attempt to advance in the Battle of Gallipoli during the First World War. Starting on 28 April, three days after the Landing at Cape Helles, the defensive power of the Ottoman forces quickly overwhelmed the attack, which suffered from poor leadership and planning, lack of communications, and exhaustion & demoralisation of the troops. Prelude On the morning of 25 April 1915, the 29th Division ( Major General Aylmer Hunter-Weston), landed on five beaches around Cape Helles at the southern tip of the Gallipoli peninsula in the Ottoman Empire. The main landings at 'V' and 'W' Beaches were hotly contested and the British suffered heavy casualties. A supporting landing made at 'Y' Beach on the Aegean coast to the north was made without opposition but the troops were without instructions and made no attempt to either advance or dig in. The first-day objectives of the village of Krithia and the nearby hill of Achi Baba were virtual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Krithia
The Second Battle of Krithia () continued the Allies' attempts to advance on the Helles battlefield during the Battle of Gallipoli of the First World War. The village of Krithia and neighbouring hill of Achi Baba had to be captured in order for the British to advance up the Gallipoli peninsula to the forts that controlled passage of the Dardanelles straits. A small amount of ground was captured after two days of costly fighting, but the objectives remained out of reach. Prelude Forces Following the failure of the First Battle of Krithia, the exhausted soldiers of the British 29th Division halted to consolidate their positions. They had to endure a number of Ottoman counter-attacks on 1 and 4 May. Similar counter-attacks were repulsed at the Anzac landing on 2 May so that General William Birdwood, commander of the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps deemed his front sufficiently secure to enable two brigades to be moved to Helles for the next assault on Krithia. These were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Battle Of Krithia
The Third Battle of Krithia ( Turkish: ''Üçüncü Kirte Muharebesi''), fought on the Gallipoli peninsula during World War I, was the last in a series of Allied attacks against the Ottoman defences aimed at achieving the original objectives of 25 April 1915. The previous failures in the first and second battles resulted in a less ambitious plan being developed for the attack, but the outcome was another costly failure for the Allies. The allied aim was, as always, to facilitate the capture of ''Alçı Tepe'' ( Achi Baba) which commanded most of the peninsula. Prelude By late May, the British contingent on the Cape Helles front at Gallipoli had been expanded to three division and a brigade: the 29th Division (which had made the original landing), the Royal Naval Division (now reinforced to 12 battalions), the 42nd (East Lancashire) Division and the 29th Indian Brigade. On 24 May, the commander of the 29th Division, Major General Aylmer Hunter-Weston, was promoted to lie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Krithia Vineyard
The Battle of Krithia Vineyard (6–13 August 1915) was fought during the Gallipoli Campaign during the First World War. It was originally intended as a minor British action at Helles on the Gallipoli peninsula to divert attention from the imminent launch of the August Offensive, but instead, the British commander, Brigadier General H.E. Street, mounted a futile and bloody series of attacks that in the end gained a small patch of ground known as "The Vineyard". Prelude The original commander of the British VIII Corps at Helles, Lieutenant General Aylmer Hunter-Weston, had departed the peninsula in July, following the last Helles offensive—the Battle of Gully Ravine. His replacement, Lieutenant General Francis Davies, arrived in early August but had not yet assumed command of the corps when a series of diversions were due to be launched from Anzac and Helles to divert Ottoman attention from the planned landing at Suvla and the break out from Anzac. Consequently, the Hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |