|
Band Bending
In solid-state physics, band bending refers to the process in which the electronic band structure in a material curves up or down near a junction or interface. It does not involve any physical (spatial) bending. When the electrochemical potential of the free charge carriers around an interface of a semiconductor is dissimilar, charge carriers are transferred between the two materials until an equilibrium state is reached whereby the potential difference vanishes. The band bending concept was first developed in 1938 when Nevill Francis Mott, Mott, Alexander Davydov (physicist), Davydov and Walter H. Schottky, Schottky all published theories of the rectifying effect of Metal–semiconductor junction, metal-semiconductor contacts. The use of semiconductor junctions sparked the computer revolution in the second half of the 20th century. Devices such as the diode, the transistor, the Photoelectric sensor, photocell and many more play crucial roles in technology. Qualitative description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-state Physics
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as solid-state chemistry, quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state physics studies how the large-scale properties of solid materials result from their atomic-scale properties. Thus, solid-state physics forms a theoretical basis of materials science. Along with solid-state chemistry, it also has direct applications in the technology of transistors and semiconductors. Background Solid materials are formed from densely packed atoms, which interact intensely. These interactions produce the mechanical (e.g. hardness and Elasticity (physics), elasticity), Heat conduction, thermal, Electrical conduction, electrical, Magnetism, magnetic and Crystal optics, optical properties of solids. Depending on the material involved and the conditions in which it was formed, the atoms may be arranged in a regular, geometric patt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
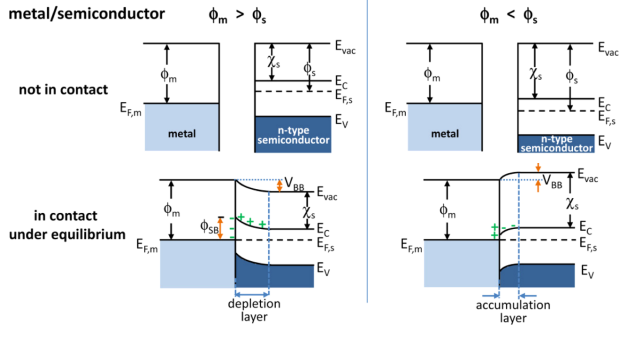
Band Diagram
In solid-state physics of semiconductors, a band diagram is a diagram plotting various key electron energy levels (Fermi level and nearby energy band edges) as a function of some spatial dimension, which is often denoted ''x''. These diagrams help to explain the operation of many kinds of semiconductor devices and to visualize how bands change with position (band bending). The bands may be coloured to distinguish Fermi–Dirac statistics, level filling. A band diagram should not be confused with a band structure plot. In both a band diagram and a band structure plot, the vertical axis corresponds to the energy of an electron. The difference is that in a band structure plot the horizontal axis represents the wave vector of an electron in an infinitely large, homogeneous material (usually a crystal), whereas in a band diagram the horizontal axis represents position in space, usually passing through multiple materials. Because a band diagram shows the ''changes'' in the band st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface States
Surface states are electronic states found at the Surface (topology), surface of materials. They are formed due to the sharp transition from solid material that ends with a surface and are found only at the atom layers closest to the surface. The termination of a material with a surface leads to a change of the electronic band structure from the bulk material to the vacuum. In the weakened potential at the surface, new electronic states can be formed, so called surface states. Origin at condensed matter interfaces As stated by Bloch wave, Bloch's theorem, eigenstates of the single-electron Schrödinger equation with a perfectly periodic potential, a crystal, are Bloch waves : \begin \Psi_ &=\mathrm^u_(\boldsymbol). \end Here u_(\boldsymbol) is a function with the same periodicity as the crystal, ''n'' is the band index and k is the wave number. The allowed wave numbers for a given potential are found by applying the usual Born–von Karman cyclic boundary conditions. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Bending 2
Band or BAND may refer to: Places *Bánd, a village in Hungary * Band, Iran, a village in Urmia County, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran * Band, Mureș, a commune in Romania * Band-e Majid Khan, a village in Bukan County, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran People * Band (surname), various people with the surname Arts, entertainment, and media Music *Musical ensemble, a group of people who perform instrumental or vocal music **Band (rock and pop), a small ensemble that plays rock or pop **Concert band, an ensemble of woodwind, brass, and percussion instruments **Dansband, band playing popular music for a partner-dancing audience **Jazz band, a musical ensemble that plays jazz music **Marching band, a group of instrumental musicians who generally perform outdoors **School band, a group of student musicians who rehearse and perform instrumental music *The Band, a Canadian-American rock and roll group ** ''The Band'' (album), The Band's eponymous 1969 album * "Bands" (song), by American r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accumulation Layer
Accumulation may refer to: Finance * Accumulation function, a mathematical function defined in terms of the ratio future value to present value * Capital accumulation, the gathering of objects of value Science and engineering * Accumulate (higher-order function), a family of functions to analyze a recursive data structure in computer science * Bioaccumulation, of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals in an organism * Glacier ice accumulation, an element in the glacier mass balance formula * Metabolic trapping, a localization mechanism of the synthesized radiocompounds in human body * Tree accumulation, in computer science, the process of accumulating data placed in tree nodes according to their tree structure * Accumulation point, another name for a limit point * Cumulative sum, for example cumulative distribution function In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Potential Energy
Electric potential energy is a potential energy (measured in joules) that results from conservative Coulomb forces and is associated with the configuration of a particular set of point charges within a defined system. An ''object'' may be said to have electric potential energy by virtue of either its own electric charge or its relative position to other electrically charged ''objects''. The term "electric potential energy" is used to describe the potential energy in systems with time-variant electric fields, while the term "electrostatic potential energy" is used to describe the potential energy in systems with time-invariant electric fields. Definition The electric potential energy of a system of point charges is defined as the work required to assemble this system of charges by bringing them close together, as in the system from an infinite distance. Alternatively, the electric potential energy of any given charge or system of charges is termed as the total work done by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depletion Region
In semiconductor physics, the depletion region, also called depletion layer, depletion zone, junction region, space charge region, or space charge layer, is an insulating region within a conductive, doped semiconductor material where the mobile charge carriers dissipate, or been forced away by an electric field. The only elements left in the depletion region are ionized donor or acceptor impurities. This region of uncovered positive and negative ions is called the depletion region due to the depletion of carriers in this region, leaving none to carry a current. Understanding the depletion region is key to explaining modern semiconductor electronics: diodes, bipolar junction transistors, field-effect transistors, and variable capacitance diodes all rely on depletion region phenomena. Formation in a p–n junction A depletion region forms instantaneously across a p–n junction. It is most easily described when the junction is in thermal equilibrium or in a steady stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) describes their capacity to exert attractive or repulsive forces on another charged object. Charged particles exert attractive forces on each other when the sign of their charges are opposite, one being positive while the other is negative, and repel each other when the signs of the charges are the same. Because these forces are exerted mutually, two charges must be present for the forces to take place. These forces are described by Coulomb's law, which says that the greater the magnitude of the charges, the greater the force, and the greater the distance between them, the weaker the force. Informally, the greater the charge of an object, the stronger its electric field. Similarly, an electric field is stronger nearer charged objects and weaker f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatic Induction
Electrostatic induction, also known as "electrostatic influence" or simply "influence" in Europe and Latin America, is a redistribution of electric charge in an object that is caused by the influence of nearby charges. In the presence of a charged body, an insulated conductor develops a positive charge on one end and a negative charge on the other end. Induction was discovered by British scientist John Canton in 1753 and Swedish professor Johan Carl Wilcke in 1762. Electrostatic generators, such as the Wimshurst machine, the Van de Graaff generator and the electrophorus, use this principle. See also Stephen Gray (scientist), Stephen Gray in this context. Due to induction, the electrostatic potential (voltage) is constant at any point throughout a conductor. Electrostatic induction is also responsible for the attraction of light nonconductive objects, such as balloons, paper or styrofoam scraps, to static electric charges. Electrostatic induction laws apply in dynamic situations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Layer (surface Science)
Double layer may refer to: * Double layer (biospecific), the surface where two different phases of matter are in contact * Double layer (plasma physics), a structure in a plasma and consists of two parallel layers with opposite electrical charge * Double layer (surface science), a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is placed into a liquid * Double layer forces, which occur between charged objects across liquids * Double layer potential, a solution of Laplace's equation * Double layer suturing, two layers of sutures, first in a deep level of a tissue and then at a more superficial level * DVD+R DL or Double layer, a DVD format {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up quark, up and down quark, down quarks. Electrons are extremely lightweight particles that orbit the positively charged atomic nucleus, nucleus of atoms. Their negative charge is balanced by the positive charge of protons in the nucleus, giving atoms their overall electric charge#Charge neutrality, neutral charge. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, each consisting of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a number of orbiting electrons equal to the number of protons. The configuration and energy levels of these orbiting electrons determine the chemical properties of an atom. Electrons are bound to the nucleus to different degrees. The outermost or valence electron, valence electrons are the least tightly bound and are responsible for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge Carriers
In solid state physics, a charge carrier is a particle or quasiparticle that is free to move, carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric charges in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons, ions and holes. In a conducting medium, an electric field can exert force on these free particles, causing a net motion of the particles through the medium; this is what constitutes an electric current. The electron and the proton are the elementary charge carriers, each carrying one elementary charge (''e''), of the same magnitude and opposite sign. In conductors In conducting mediums, particles serve to carry charge. In many metals, the charge carriers are electrons. One or two of the valence electrons from each atom are able to move about freely within the crystal structure of the metal. The free electrons are referred to as conduction electrons, and the cloud of free electrons is called a Fermi gas. Many metals have electron and hole bands. In som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |