|
Australia (continent)
The continent of Australia, sometimes known in technical contexts by the names Sahul (), Australia-New Guinea, Australinea, Meganesia, or Papualand to distinguish it from the Australia, country of Australia, is located within the Southern Hemisphere, Southern and Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern hemispheres. The name "Sahul" takes its name from the Sahul Shelf, which is a part of the continental shelf of the Australian continent. The continent includes mainland Australia, Tasmania, the island of New Guinea (Papua New Guinea and Indonesian Western New Guinea), the Aru Islands Regency, Aru Islands, the Ashmore and Cartier Islands, most of the Coral Sea Islands, and some other list of islands of Australia, nearby islands. Situated in the geographical region of Oceania, Australia is the Continent#Area and population, smallest of the seven traditional continents. The continent includes a continental shelf overlain by shallow seas which divide it into several landmasses—the Arafura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia-New Guinea (orthographic Projection)
The continent of Australia, sometimes known in technical contexts by the names Sahul (), Australia-New Guinea, Australinea, Meganesia, or Papualand to distinguish it from the country of Australia, is located within the Southern and Eastern hemispheres. The name " Sahul" takes its name from the Sahul Shelf, which is a part of the continental shelf of the Australian continent. The continent includes mainland Australia, Tasmania, the island of New Guinea (Papua New Guinea and Indonesian Western New Guinea), the Aru Islands, the Ashmore and Cartier Islands, most of the Coral Sea Islands, and some other nearby islands. Situated in the geographical region of Oceania, Australia is the smallest of the seven traditional continents. The continent includes a continental shelf overlain by shallow seas which divide it into several landmasses—the Arafura Sea and Torres Strait between mainland Australia and New Guinea, and Bass Strait between mainland Australia and Tasmania. When s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
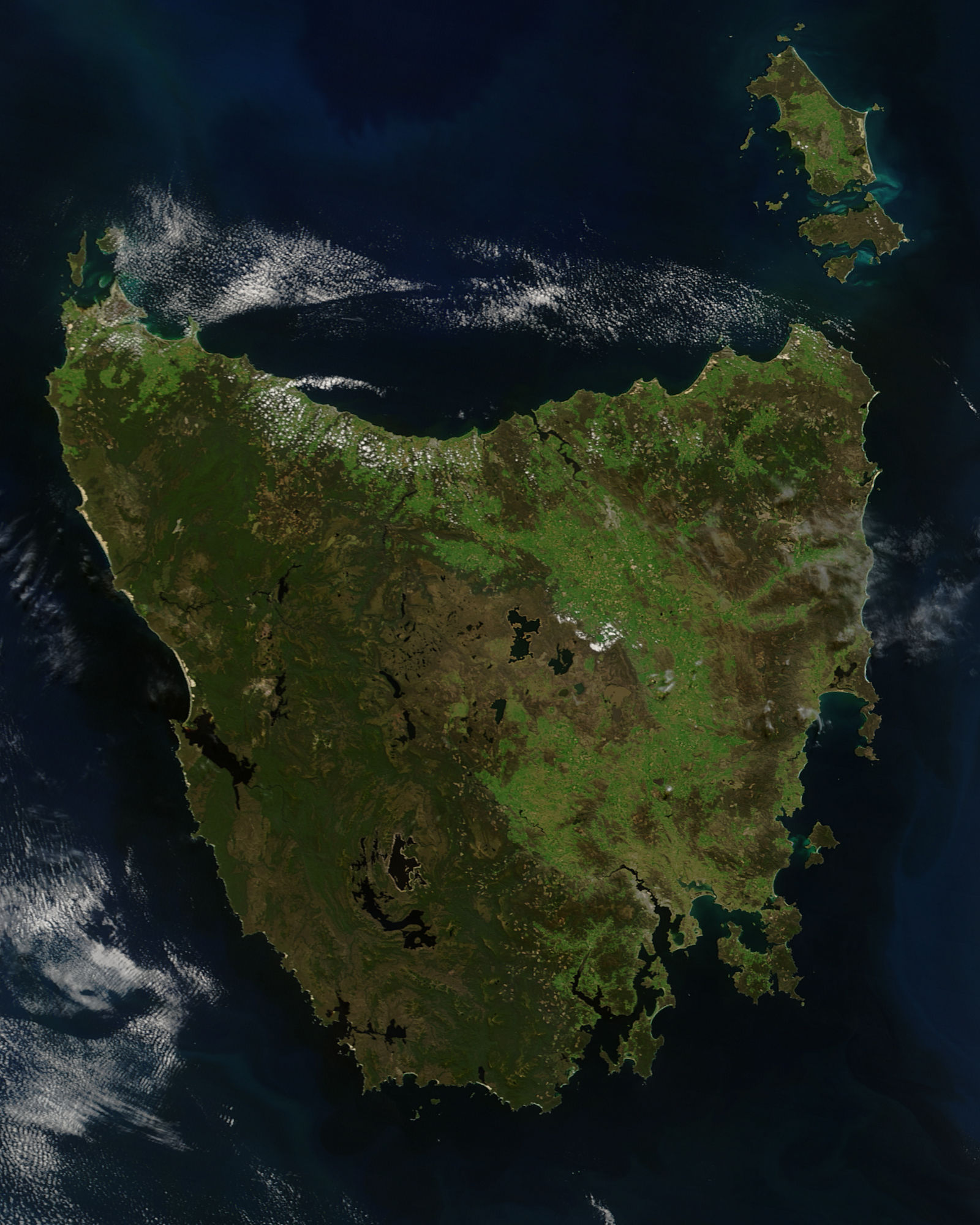
Tasmania
) , nickname = , image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Tasmania , established_title2 = Federation , established_date2 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Abel Tasman , demonym = , capital = Hobart , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 29 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papuan Languages
The Papuan languages are the non- Austronesian and non- Australian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, as well as neighbouring islands, by around 4 million people. It is a strictly geographical grouping, and does not imply a genetic relationship. The concept of Papuan (non-Austronesian) speaking Melanesians as distinct from Austronesian-speaking Melanesians was first suggested and named by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1892. New Guinea is the most linguistically diverse region in the world. Besides the Austronesian languages, there are some (arguably) 800 languages divided into perhaps sixty small language families, with unclear relationships to each other or to any other languages, plus many language isolates. The majority of the Papuan languages are spoken on the island of New Guinea, with a number spoken in the Bismarck Archipelago, Bougainville Island and the Solomon Islands to the east, and in Halmahera, Timor and the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiri Motu Language
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea). It is a simplified version of Motu, from the Austronesian language family. Although it is strictly neither a pidgin nor a creole, it possesses some features from both language types. Phonological and grammatical differences make Hiri Motu not mutually intelligible with Motu. The languages are lexically very similar, and retain a common, albeit simplified, Austronesian syntactical basis. It has also been influenced to some degree by Tok Pisin. Even in the areas where it was once well established as a '' lingua franca'', the use of Hiri Motu has been declining in favour of Tok Pisin and English for many years. The language has some statutory recognition. Origin of Hiri Motu The term '' hiri'' is the name for the traditional trade voyages that created a culture and style of living for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tok Pisin
Tok Pisin (,Laurie Bauer, 2007, ''The Linguistics Student’s Handbook'', Edinburgh ; Tok Pisin ), often referred to by English speakers as "New Guinea Pidgin" or simply Pidgin, is a creole language spoken throughout Papua New Guinea. It is an official language of Papua New Guinea and the most widely used language in the country. However, in parts of the southern provinces of Western, Gulf, Central, Oro, and Milne Bay, the use of Tok Pisin has a shorter history and is less universal, especially among older people. Between five and six million people use Tok Pisin to some degree, although not all speak it fluently. Many now learn it as a first language, in particular the children of parents or grandparents who originally spoke different languages (for example, a mother from Madang and a father from Rabaul). Urban families in particular, and those of police and defence force members, often communicate among themselves in Tok Pisin, either never gaining fluency in a local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesian Language
Indonesian ( ) is the official and national language of Indonesia. It is a standardized variety of Malay, an Austronesian language that has been used as a lingua franca in the multilingual Indonesian archipelago for centuries. Indonesia is the fourth most populous nation in the world, with over 270 million inhabitants—of which the majority speak Indonesian, which makes it one of the most widely spoken languages in the world. James Neil Sneddon. ''The Indonesian Language: Its History and Role in Modern Society''. UNSW Press, 2004. Most Indonesians, aside from speaking the national language, are fluent in at least one of the more than 700 indigenous local languages; examples include Javanese and Sundanese, which are commonly used at home and within the local community. However, most formal education and nearly all national mass media, governance, administration, and judiciary and other forms of communication are conducted in Indonesian. Under Indonesian rule from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian English
Australian English (AusE, AusEng, AuE, AuEng, en-AU) is the set of varieties of the English language native to Australia. It is the country's common language and ''de facto'' national language; while Australia has no official language, English is the first language of the majority of the population, and has been entrenched as the ''de facto'' national language since European settlement, being the only language spoken in the home for 72% of Australians. It is also the main language used in compulsory education, as well as federal, state and territorial legislatures and courts. Australian English began to diverge from British and Irish English after the First Fleet established the Colony of New South Wales in 1788. Australian English arose from a dialectal 'melting pot' created by the intermingling of early settlers who were from a variety of dialectal regions of Great Britain and Ireland, though its most significant influences were the dialects of Southeast England. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Administrative Divisions By Country
The table below indicates the types and, where known, numbers of administrative divisions used by countries and their major dependent territories. It is ordered alphabetically by country name in English. Administrative divisions by country Member and observer states of the United Nations Other states See also * Country subdivision * ISO 3166-2, codes for country subdivisions * Associated state * Asymmetric federation * Capital districts and territories * Condominium, joint sovereignty over an area shared by two or more states. * Dependent territory * Federacy * Federation * Federated state * List of terms for country subdivisions * List of national capitals serving as administrative divisions * List of autonomous areas by country * List of ISO 3166 country codes * List of sovereign states * Matrix of country subdivisions * List of political and geographic subdivisions by total area, comparing continents, countries, and first-level administrative country subdivisions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cato Trough
The Cato Trough or the Chesterfield Trough is an oceanic trough in the Coral Sea of the South Pacific Ocean. It separates the continental crust of Australia and Zealandia to within and has a depth of . The trough is underlain by oceanic crust, having formed as a result of seafloor spreading Seafloor spreading or Seafloor spread is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. History of study Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener a ... from about 63 to 50 million years ago. References External links Marine Gazetteer Placedetails Coral Sea Oceanic trenches of the Pacific Ocean {{marine-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middleton Reef
Middleton Reef is a coral reef in the Coral Sea. It is separated by a deep oceanic pass some 47 km wide from nearby Elizabeth Reef, forming part of the Lord Howe Rise underwater plateau. It is around 230 km from Lord Howe Island and 555 km from the coast of New South Wales. In 1997 thEnvironment, Sport and Territories Legislation Amendment Bill 1996included the reef in Australia's Coral Sea Islands Territory. It is among the southernmost platform reefs in the world. Despite its relatively high latitude, there is a wide variety of flora and fauna on the reef and in the surrounding waters, due to converging tropical and temperate ocean currents. It is about 8.9 km long by 6.3 km wide. At low tide most of the reef flat is exposed, at high tide only one cay is visible, The Sound, 100 m by 70 m and one metre above sea level. The reefs form thElizabeth and Middleton Reefs Marine National Park Reservemanaged by the Government of Australia under the Natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral Sea Islands
The Coral Sea Islands Territory is an external territory of Australia which comprises a group of small and mostly uninhabited tropical islands and reefs in the Coral Sea, northeast of Queensland, Australia. The only inhabited island is Willis Island. The territory covers , most of which is ocean, extending east and south from the outer edge of the Great Barrier Reef and includes Heralds Beacon Island, Osprey Reef, the Willis Group and fifteen other reef/island groups. Cato Island is the highest point in the Territory.Geoscience AustraliaCoral Sea Islands History and status The Coral Sea Islands were first charted in 1803. In the 1870s and 1880s the islands were mined for guano but the absence of a reliable supply of fresh water prevented long-term habitation. The Coral Sea Islands became an Australian external territory in 1969 by the ''Coral Sea Islands Act'' (prior to that, the area was considered a part of Queensland) and extended in 1997 to include Elizabeth Reef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Reef
Elizabeth Reef, located at is a coral reef in the Coral Sea. The reef is separated by a deep oceanic pass, some 47 km wide, from nearby Middleton Reef, both of which are part of the underwater plateau known as the Lord Howe Rise. It is around 150 km from Lord Howe Island and 600 km from the New South Wales coast of Australia. ThEnvironment, Sport and Territories Legislation Amendment Act 1997included Elizabeth Reef in Australia's Coral Sea Islands Territory. It is the southernmost coral atoll in the world and one of the southernmost platform reefs in the world. It measures 10.5 km by 6.1 km. Despite the relatively high latitude, a wide variety of flora and fauna exists on the reef and in the surrounding waters due to their location where tropical and temperate ocean currents converge. At low tide most of the reef flat is exposed; at high tide, both a cay and a sand spit are visible. Elizabeth Island, with a diameter of about 50 m, is one me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(20323954256).jpg)

_(20163567039).jpg)