|
August Friedrich Ferdinand Von Der Goltz
August Friedrich Ferdinand Graf von der Goltz (July 20, 1765 – January 17, 1832) was Minister for Foreign Affairs of Prussia between 1808 and 1814, the first person to hold that title. Biography Born into the Von der Goltz noble family, August was the son of Count Carl Friedrich von der Goltz (1727-1805) and his wife, Anna Maria Karolina von Rummel (1735–1809). He entered the diplomatic service of Prussia in 1787. He help posts in the Prussian Legations at Copenhagen, Mainz, Stockholm, and St Petersburg. In 1807 at the Peace of Tilsit when Napoleon refused to negotiate with Karl August von Hardenberg and demanded his retirement, Goltz signed the treaty in place of Hardenberg and the next year became Minister of Foreign Affairs. Goltz represented Prussia at the Congress of Erfurt in 1808. He was head of the Corporate Governance in Berlin and after the Paris Peace of 1814 he became '' Oberhofmarschal'' to the Prussian court, in 1816 the courts representative to the Bundest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hofmarschall
The ''Hofmarschall'' (plural: Hofmarschälle) was the administrative official in charge of a princely German court, supervising all its economic affairs. Historically, every civil service was regarded as court service (e.g. the Russian nobility is even now called the ''Dvoryanstvo'', i.e. courtiers), though today high officials in the royal courts that still exist frequently use titles like ''marshal'', ''chancellor'' or ''minister'', which in other countries are now only used by the civil administration or the military. A ''Hofmarschall'' always belonged to the nobility or was a retired high-ranking military officers of major general rank or above. A ''Hofmarschall''s duties included organizing the king and the queen's receptions, foreign trips and state visits and supervising the royal household. He organized the whole court household, maintenance of the royal castles, and the provision of food and drink for the princely table, kitchens and wine-cellars. In larger courts the offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politicians From Dresden
A politician is a person active in party politics, or a person holding or seeking an elected office in government. Politicians propose, support, reject and create laws that govern the land and by an extension of its people. Broadly speaking, a politician can be anyone who seeks to achieve political power in a government. Identity Politicians are people who are politically active, especially in party politics. Political positions range from local governments to state governments to federal governments to international governments. All ''government leaders'' are considered politicians. Media and rhetoric Politicians are known for their rhetoric, as in speeches or campaign advertisements. They are especially known for using common themes that allow them to develop their political positions in terms familiar to the voters. Politicians of necessity become expert users of the media. Politicians in the 19th century made heavy use of newspapers, magazines, and pamphlets, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian Politicians
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a Germans, German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by Preußenschlag, an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by Abolition of Prussia, an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, History of Berlin, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. In 1871, Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck unification of Germany, united most German principalities into the German Empire under his leadership, although this was considered to be a "Lesser Germany" because Austrian Empire, Austria and Switzerland were not included. In N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian Diplomats
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. In 1871, Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck united most German principalities into the German Empire under his leadership, although this was considered to be a "Lesser Germany" because Austria and Switzerland were not included. In November 1918, the monarchies were abolished and the nobility lost its political power during the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counts Of Germany
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: Barnes & Noble, 1992. p. 73. . The etymologically related English term "county" denoted the territories associated with the countship. Definition The word ''count'' came into English from the French ''comte'', itself from Latin ''comes''—in its accusative ''comitem''—meaning “companion”, and later “companion of the emperor, delegate of the emperor”. The adjective form of the word is "comital". The British and Irish equivalent is an earl (whose wife is a "countess", for lack of an English term). In the late Roman Empire, the Latin title ''comes'' denoted the high rank of various courtiers and provincial officials, either military or administrative: before Anthemius became emperor in the West in 467, he was a military ''comes' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1832 Deaths
Year 183 ( CLXXXIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Victorinus (or, less frequently, year 936 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 183 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * An assassination attempt on Emperor Commodus by members of the Senate fails. Births * January 26 – Lady Zhen, wife of the Cao Wei state Emperor Cao Pi (d. 221) * Hu Zong, Chinese general, official and poet of the Eastern Wu state (d. 242) * Liu Zan (Zhengming), Chinese general of the Eastern Wu state (d. 255) * Lu Xun, Chinese general and politician of the Eastern Wu state (d. 245 __NOTOC__ Year 245 ( CCXLV) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calenda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1765 Births
Events January–March * January 23 – Prince Joseph of Austria marries Princess Maria Josepha of Bavaria in Vienna. * January 29 – One week before his death, Mir Jafar, who had been enthroned as the Nawab of Bengal and ruler of the Bengali people with the support and protection of the British East India Company, abdicates in favor of his 18-year-old son, Najmuddin Ali Khan. * February 8 – ** Frederick the Great, the King of Prussia, issues a decree abolishing the historic punishments against unmarried women in Germany for "sex crimes", particularly the ''Hurenstrafen'' (literally "whore shaming") practices of public humiliation. **Isaac Barré, a member of the British House of Commons for Wycombe and a veteran of the French and Indian War in the British American colonies, coins the term "Sons of Liberty" in a rebuttal to Charles Townshend's derisive description of the American colonists during the introduction of the proposed Stamp Act. MP Barr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meyers Konversations-Lexikon
' or ' was a major encyclopedia in the German language that existed in various editions, and by several titles, from 1839 to 1984, when it merged with the '. Joseph Meyer (1796–1856), who had founded the publishing house in 1826, intended to issue a universal encyclopaedia meant for a broad public: people having a general knowledge as well as businessmen, technicians and scholars, considering contemporary works like those of and to be superficial or obsolete. First edition The first part of ' ("Great encyclopaedia for the educated classes") appeared in October 1839. In contrast to its contemporaries, it contained maps and illustrations with the text. There is no indication of the planned number of volumes or a time limit for this project, but little headway had been made by the otherwise dynamic . After six years, 14 volumes had appeared, covering only one fifth of the alphabet. Another six years passed before the last (46th) volume was published. Six supplementary vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
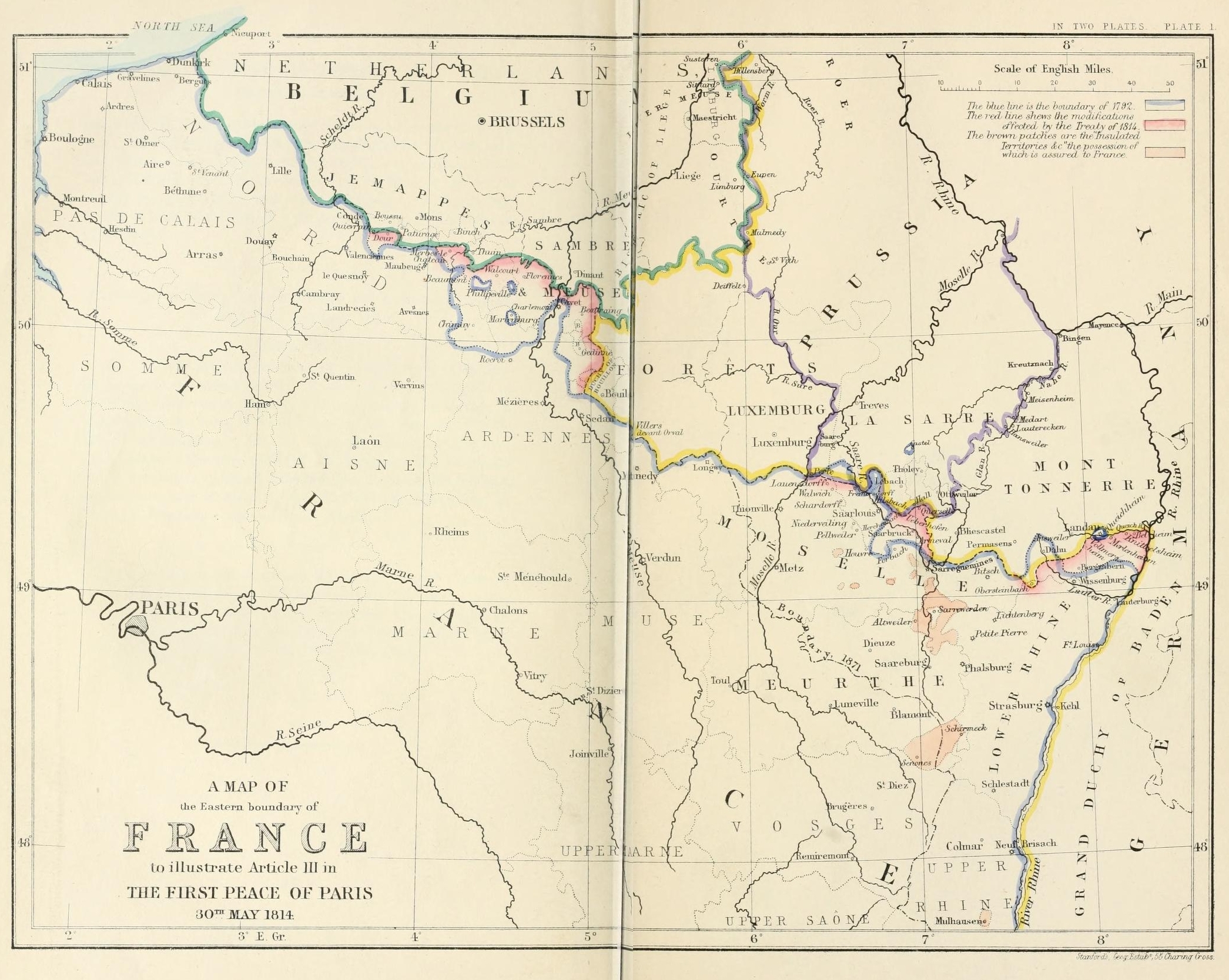
Treaty Of Paris (1814)
The Treaty of Paris, signed on 30 May 1814, ended the war between France and the Sixth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars, following an armistice signed on 23 April between Charles, Count of Artois, and the allies. The treaty set the borders for France under the House of Bourbon and restored territories to other nations. It is sometimes called the First Peace of Paris, as another one followed in 1815. Parties to the treaty This treaty was signed on 30 May 1814, following an armistice signed on 23 April 1814 between Charles, Count of Artois, and the allies. Napoleon had abdicated as Emperor on 6 April, as a result of negotiations at Fontainebleau. Peace talks had started on 9 May between Talleyrand, who negotiated with the allies of Chaumont on behalf of the exiled Bourbon king Louis XVIII of France, and the allies. The Treaty of Paris established peace between France and Great Britain, Russia, Austria, and Prussia, who in March had defined their common war aim in Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Minister Of Prussia
This article lists Foreign Ministers of Prussia. After the creation of the German Empire in 1871, the Imperial Chancellor was normally also Foreign Minister of Prussia. However, during the chancellorship of Prince Hohenlohe (1894–1900), the position was held by the State Secretaries for Foreign Affairs. Prussian Ministers of Foreign Affairs, 1768–1918 * Ewald Friedrich von Hertzberg 1768–1791 * Count August Friedrich Ferdinand von der Goltz 1808–1814 * Prince Karl August von Hardenberg 1814–1818 * Count Christian Günther Bernstorff 1818–1832 *Friedrich Ancillon 1832–1837 * Baron Heinrich Wilhelm Werther 1837–1841 * Count Mortimer Maltzan 1841–1842 * Baron Heinrich von Bülow 1842–1845 * Baron Karl Ernst Wilhelm von Canitz und Dallwitz 1845–1848 * Count Adolf Heinrich Arnim-Boitzenburg 19 – 21 March 1848 * Baron Heinrich Alexander von Arnim 21 March – 20 June 1848 *Baron Alexander von Schleinitz 20 – 27 June 1848 * Rudolf von Auerswald 27 June – 7 S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Of Erfurt
The Congress of Erfurt was the meeting between Napoleon, Emperor of the French, and Alexander I, Emperor of All Russia, from Tuesday 27 September to Friday 14 October 1808 intended to reaffirm the alliance concluded the previous year with the Treaties of Tilsit which followed the end of the War of the Fourth Coalition.Steffen Raßloff (2012). ''Geschichte der Stadt Erfurt''. Erfurt: Sutton Verlag. Background At Tilsit, Napoleon had made an admirer of Alexander, but by the time of the meeting at Erfurt anti-French sentiment at the Russian court was beginning to threaten the newly forged alliance. Napoleon and his foreign minister Jean-Baptiste Nompère de Champagny sought to strengthen the alliance once more in order to settle affairs in Spain and prepare for the expected war with Austria. Working at cross-purposes to Napoleon was Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord who had by this time come to the conclusion that Napoleon was leading France to destruction, and who secre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |