|
Apology (Plato)
The ''Apology of Socrates'' ( grc-gre, Ἀπολογία Σωκράτους, ''Apología Sokrátous''; la, Apologia Socratis), written by Plato, is a Socratic dialogue of the speech of legal self-defence which Socrates (469–399 BC) spoke at his trial for impiety and corruption in 399 BC. Specifically, the ''Apology of Socrates'' is a defence against the charges of "corrupting the youth" and "not believing in the gods in whom the city believes, but in other '' daimonia'' that are novel" to Athens (24b). Among the primary sources about the trial and death of the philosopher Socrates, the ''Apology of Socrates'' is the dialogue that depicts the trial, and is one of four Socratic dialogues, along with ''Euthyphro'', ''Phaedo'', and ''Crito'', through which Plato details the final days of the philosopher Socrates. The text of apology The ''Apology of Socrates'', by the philosopher Plato (429–347 BC), was one of many explanatory ''apologia'' about Socrates's legal defense ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
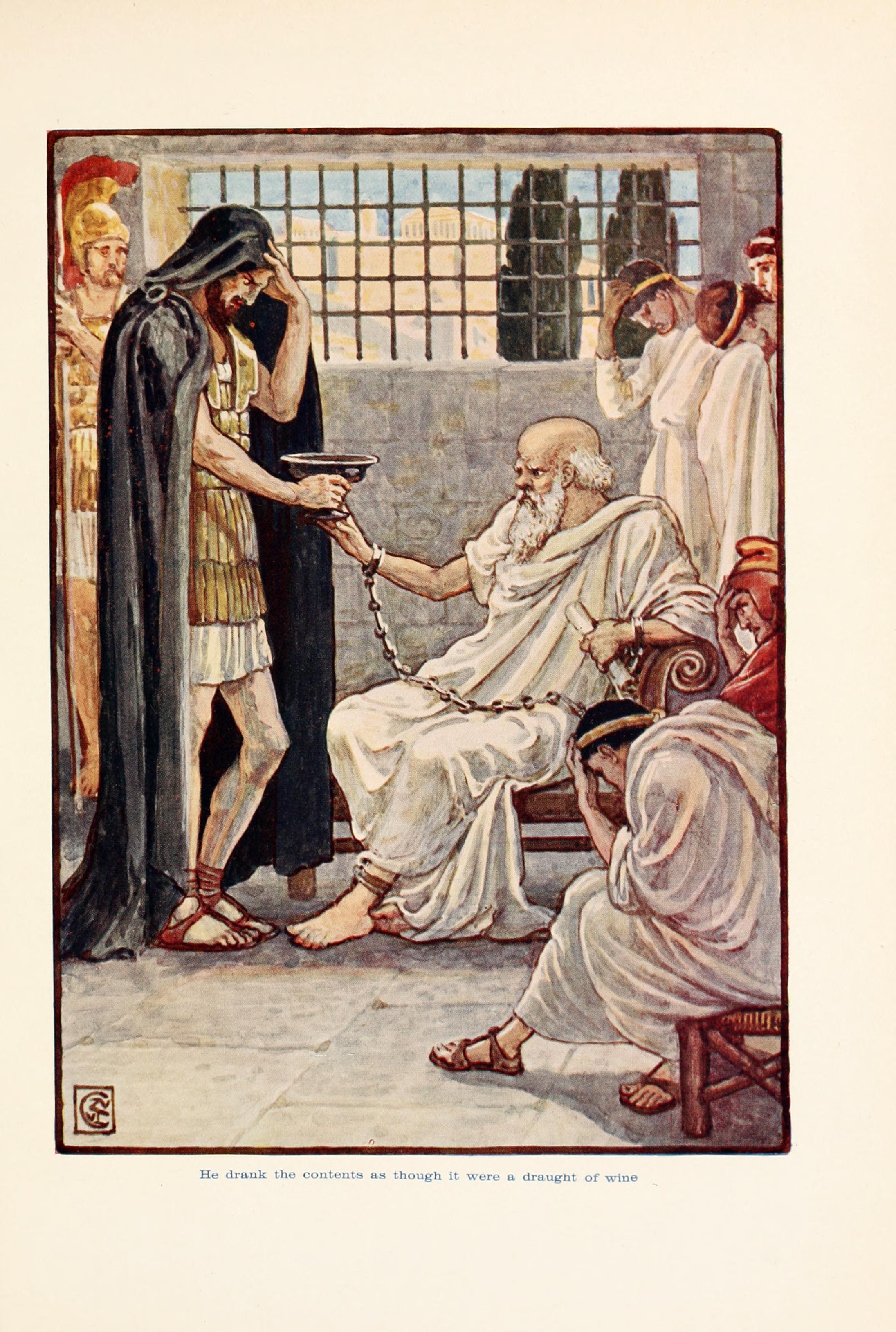
Trial Of Socrates
The trial of Socrates (399 BC) was held to determine the philosopher's guilt of two charges: ''asebeia'' (impiety) against the pantheon of Athens, and corruption of the youth of the city-state; the accusers cited two impious acts by Socrates: "failing to acknowledge the gods that the city acknowledges" and "introducing new deities". The death sentence of Socrates was the legal consequence of asking politico-philosophic questions of his students, which resulted in the two accusations of moral corruption and impiety. At trial, the majority of the ''dikasts'' (male-citizen jurors chosen by lot) voted to convict him of the two charges; then, consistent with common legal practice voted to determine his punishment and agreed to a sentence of death to be executed by Socrates's drinking a poisonous beverage of hemlock. Primary-source accounts of the trial and execution of Socrates are the '' Apology of Socrates'' by Plato and the '' Apology of Socrates to the Jury'' by Xenophon of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, wikt:Ξενοφῶν, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Ancient Greek mercenaries, Greek mercenary armies of the Achaemenid Empire, the Ten Thousand, that marched on and came close to capturing Babylon in 401 BC. As the military historian Theodore Ayrault Dodge wrote, "the centuries since have devised nothing to surpass the genius of this warrior". Xenophon established precedents for many logistical operations, and was among the first to describe strategic flanking maneuvers and feints in combat. Xenophon's ''Anabasis (Xenophon), Anabasis'' recounts his adventures with the Ten Thousand while in the service of Cyrus the Younger, Cyrus's failed campaign to claim the Persian throne from Artaxerxes II of Persia, and the return of Greek mercenaries after Cyrus's death in the Battle of Cunaxa. ''Anabasis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wisdom
Wisdom, sapience, or sagacity is the ability to contemplate and act using knowledge, experience, understanding, common sense and insight. Wisdom is associated with attributes such as unbiased judgment, compassion, experiential self-knowledge, self-transcendence and non-attachment, and virtues such as ethics and benevolence. Wisdom has been defined in many different ways, including several distinct approaches to assess the characteristics attributed to wisdom. Definitions The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' defines wisdom as "Capacity of judging rightly in matters relating to life and conduct; soundness of judgment in the choice of means and ends; sometimes, less strictly, sound sense, esp. in practical affairs: opp. to folly;" also "Knowledge (esp. of a high or abstruse kind); enlightenment, learning, erudition." Charles Haddon Spurgeon defined wisdom as "the right use of knowledge". Robert I. Sutton and Andrew Hargadon defined the "attitude of wisdom" as "acting with knowle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meno
''Meno'' (; grc-gre, Μένων, ''Ménōn'') is a Socratic dialogue by Plato. Meno begins the dialogue by asking Socrates whether virtue is taught, acquired by practice, or comes by nature. In order to determine whether virtue is teachable or not, Socrates tells Meno that they first need to determine what virtue is. When the characters speak of virtue, or rather ''arete'', they refer to virtue in general, rather than particular virtues, such as justice or temperance. The first part of the work showcases Socratic dialectical style; Meno, unable to adequately define virtue, is reduced to confusion or aporia. Socrates suggests that they seek an adequate definition for virtue together. In response, Meno suggests that it is impossible to seek what one does not know, because one will be unable to determine whether one has found it. Socrates challenges Meno's argument, often called "Meno's Paradox" or the "Learner's Paradox", by introducing the theory of knowledge as recollectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophists
A sophist ( el, σοφιστής, sophistes) was a teacher in ancient Greece in the fifth and fourth centuries BC. Sophists specialized in one or more subject areas, such as philosophy, rhetoric, music, athletics, and mathematics. They taught ''arete'' – "virtue" or "excellence" – predominantly to young statesmen and nobility. In the present day, however, a sophist refers to someone who deliberately argues using fallacious arguments or reasoning, in order to mislead; see the section below. Etymology The Greek word el, σοφός, sophos, a wise man, label=none is related to the noun el, σοφία, sophia, wisdom, label=none. Since the times of Homer it commonly referred to an expert in his profession or craft. Charioteers, sculptors, or military experts could be referred to as in their occupations. The word has gradually come to connote general wisdom and especially wisdom in human affairs such as politics, ethics, and household management. This was the meaning ascr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_drawing_29.gif)
