|
Ancient Egyptian Technology
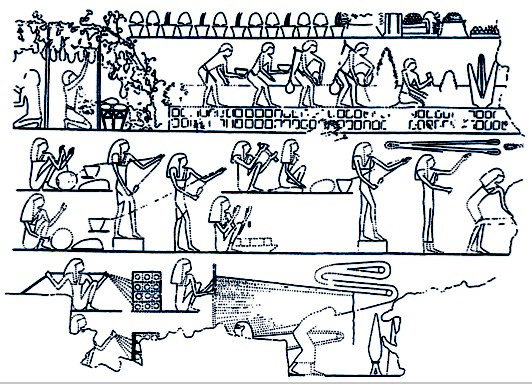
Ancient Egyptian technology describes devices and technologies invented or used in Ancient Egypt. The Egyptians invented and used many simple machines, such as the inclined plane, ramp and the lever, to aid construction processes. They used rope trusses to stiffen the beam (nautical), beam of ships. Egyptian paper, made from papyrus, and ancient Egyptian pottery, pottery were mass-produced and exported throughout the Mediterranean Basin. The wheel was used for a number of purposes, but chariots only came into use after the Second Intermediate Period. The Egyptians also played an important role in developing Mediterranean maritime history, maritime technology including ships and lighthouses. Technology in Dynastic Egypt Significant advances in ancient Egypt during the History of ancient Egypt, dynastic period include Egyptian astronomy, astronomy, Egyptian mathematics, mathematics, and Ancient Egyptian medicine, medicine. Their Egyptian geometry, geometry was a necessary outgrowth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lens (optics), lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways. Lighthouses mark dangerous coastlines, hazardous shoals, reefs, rocks, and safe entries to harbors; they also assist in aerial navigation. Once widely used, the number of operational lighthouses has declined due to the expense of maintenance and the advent of much cheaper, more sophisticated, and more effective electronic navigational systems. History Ancient lighthouses Before the development of clearly defined ports, mariners were guided by fires built on hilltops. Since elevating the fire would improve visibility, placing the fire on a platform became a practice that led to the development of the lighthouse. In antiquity, the lighthouse functioned more as an entrance marker to ports than as a warning signal for reefs and promontory, prom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writing Material
A writing material, also called a writing medium, is a surface that can be written on with suitable instruments, or used for symbolic or representational drawings. Building materials on which writings or drawings are produced are not included. The gross characterization of writing materials is by the material constituting the writing surface (for example, paper) and the number, size, usage, and storage configuration of multiple surfaces (for example, paper sheets) into a single object. Early media Because drawing preceded writing, the first remains of writing materials are the stone walls of the caves on which cave paintings were drawn. Another precursor was tally sticks used to record the count of objects. Writing seems to have become more widespread with the invention of papyrus in Egypt. Parchment, using sheepskins left after the wool was removed for cloth, was sometimes cheaper than papyrus, which had to be imported from outside of Egypt. To save money on expensive papy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of The Dead Of Hunefer Sheet 3
A book is a structured presentation of recorded information, primarily verbal and graphical, through a medium. Originally physical, electronic books and audiobooks are now existent. Physical books are objects that contain printed material, mostly of writing and images. Modern books are typically composed of many pages bound together and protected by a cover, what is known as the ''codex'' format; older formats include the scroll and the tablet. As a conceptual object, a ''book'' often refers to a written work of substantial length by one or more authors, which may also be distributed digitally as an electronic book (ebook). These kinds of works can be broadly classified into fiction (containing invented content, often narratives) and non-fiction (containing content intended as factual truth). But a physical book may not contain a written work: for example, it may contain ''only'' drawings, engravings, photographs, sheet music, puzzles, or removable content like paper dolls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchemy
Alchemy (from the Arabic word , ) is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practised in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first attested in a number of pseudepigraphical texts written in Greco-Roman Egypt during the first few centuries AD.. Greek-speaking alchemists often referred to their craft as "the Art" (τέχνη) or "Knowledge" (ἐπιστήμη), and it was often characterised as mystic (μυστική), sacred (ἱɛρά), or divine (θɛíα). Alchemists attempted to purify, mature, and perfect certain materials. Common aims were chrysopoeia, the transmutation of " base metals" (e.g., lead) into "noble metals" (particularly gold); the creation of an elixir of immortality; and the creation of panaceas able to cure any disease. The perfection of the human body and soul was thought to result from the alchemical ''magnum opus'' ("Great Work"). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Triangle
A right triangle or right-angled triangle, sometimes called an orthogonal triangle or rectangular triangle, is a triangle in which two sides are perpendicular, forming a right angle ( turn or 90 degrees). The side opposite to the right angle is called the '' hypotenuse'' (side c in the figure). The sides adjacent to the right angle are called ''legs'' (or ''catheti'', singular: '' cathetus''). Side a may be identified as the side ''adjacent'' to angle B and ''opposite'' (or ''opposed to'') angle A, while side b is the side adjacent to angle A and opposite angle B. Every right triangle is half of a rectangle which has been divided along its diagonal. When the rectangle is a square, its right-triangular half is isosceles, with two congruent sides and two congruent angles. When the rectangle is not a square, its right-triangular half is scalene. Every triangle whose base is the diameter of a circle and whose apex lies on the circle is a right triangle, with the right angle at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile River
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists Say Of the world's major rivers, the Nile has one of the lowest average annual flow rates. About long, its covers eleven countries: the |
Surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the land, terrestrial Plane (mathematics), two-dimensional or Three-dimensional space#In Euclidean geometry, three-dimensional positions of Point (geometry), points and the Euclidean distance, distances and angles between them. These points are usually on the surface of the Earth, and they are often used to establish maps and boundaries for ownership, locations, such as the designated positions of structural components for construction or the surface location of subsurface features, or other purposes required by government or civil law, such as property sales. A professional in land surveying is called a land surveyor. Surveyors work with elements of geodesy, geometry, trigonometry, regression analysis, physics, engineering, metrology, programming languages, and the law. They use equipment, such as total stations, robotic total stations, theodolites, Satellite navigation, GNSS receivers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Geometry
Egyptian geometry refers to geometry as it was developed and used in Ancient Egypt. Their geometry was a necessary outgrowth of surveying to preserve the layout and ownership of farmland, which was flooded annually by the Nile river. We only have a limited number of problems from ancient Egypt that concern geometry. Geometric problems appear in both the Moscow Mathematical Papyrus (MMP) and in the Rhind Mathematical Papyrus (RMP). The examples demonstrate that the ancient Egyptians knew how to compute areas of several geometric shapes and the volumes of cylinders and pyramids. Area The ancient Egyptians wrote out their problems in multiple parts. They gave the title and the data for the given problem, in some of the texts they would show how to solve the problem, and as the last step they verified that the problem was correct. The scribes did not use any variables and the problems were written in prose form. The solutions were written out in steps, outlining the process. Egyptia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Medicine
The medicine of the ancient Egyptians is some of the oldest documented. From the beginnings of the civilization in the late fourth millennium BC until the Achaemenid Empire, Persian invasion of 525 BC, Egyptian medical practice went largely unchanged and included simple non-invasive surgery, setting of bones, dentistry, and an extensive set of pharmacopoeia. Egyptian medical thought influenced later traditions, including the Greek medicine, Greeks. History Sources of information Until the 19th century, the main sources of information about ancient Egyptian medicine were writings from later in antiquity. The Greek historian Herodotus visited Egypt around 440 BC and wrote extensively of his observations of their medicinal practice. Pliny the Elder also wrote favorably of them in historical review. Hippocrates (the "father of medicine"), Herophilos, Erasistratus and later Galen studied at the temple of Amenhotep, and acknowledged the contribution of ancient Egyptian medicine to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Mathematics
Ancient Egyptian mathematics is the mathematics that was developed and used in Ancient Egypt 3000 to c. , from the Old Kingdom of Egypt until roughly the beginning of Hellenistic Egypt. The ancient Egyptians utilized a numeral system for counting and solving written mathematical problems, often involving multiplication and fractions. Evidence for Egyptian mathematics is limited to a scarce amount of surviving sources written on papyrus. From these texts it is known that ancient Egyptians understood concepts of geometry, such as determining the surface area and volume of three-dimensional shapes useful for architectural engineering, and algebra, such as the false position method and quadratic equations. Overview Written evidence of the use of mathematics dates back to at least 3200 BC with the ivory labels found in Tomb U-j at Abydos. These labels appear to have been used as tags for grave goods and some are inscribed with numbers. Further evidence of the use of the base 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
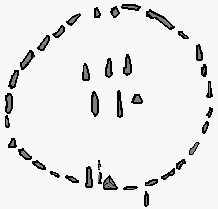
Egyptian Astronomy
Egyptian astronomy started in prehistory, prehistoric times, in the Prehistoric Egypt, Predynastic Period. In the 5th millennium BCE, the stone circles at Nabta Playa may have made use of astronomical alignments. By the time the historical Ancient Egypt, Dynastic Period began in the 3rd millennium BCE, the 365 day period of the Egyptian calendar was already in use, and the observation of stars was important in determining the annual flooding of the Nile. The Egyptian pyramids were carefully aligned towards the pole star, and the temple of Amun, Amun-Re at Karnak was aligned on the rising of the winter solstice, midwinter Sun. Astronomy played a considerable part in fixing the dates of religious festivals and determining the hours of night, and temple astrology, astrologers were especially adept at watching the stars and observing the conjunction (astronomy), conjunctions and risings of the Sun, Moon, and planets, as well as the lunar phases. In Ptolemaic Kingdom, Ptolemaic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |