|
Analytical Technique
Analytical technique is a method used to determine a chemical or physical property of a chemical substance, chemical element, or mixture. There is a wide variety of techniques used for analysis, from simple weighing to advanced techniques using highly specialized instrumentation. Classical methods of analysis Classical analysis methods involve basic analytical methods widely used in laboratories. Gravimetric analysis measures the weight of the sample. Titrimetry is a technique used to determine the concentration of the analyte. Spectrochemical analysis Spectrometer can determine chemical composition through its measure of spectrums. The common spectrometer used in analytical chemistry is Mass spectrometry. In a mass spectrometer, a small amount of sample is ionized and converted to gaseous ions, where they are separated and analyzed according to their mass-to-charge ratios. Electroanalytical analysis Electroanalytical methods utilize the potential or current of a electrochem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Substance
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances (substances consisting of a single chemical element), chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical substances are often called 'pure' to set them apart from mixtures. A common example of a chemical substance is pure water; it has the same properties and the same ratio of hydrogen to oxygen whether it is isolated from a river or made in a laboratory. Other chemical substances commonly encountered in pure form are diamond (carbon), gold, table salt ( sodium chloride) and refined sugar ( sucrose). However, in practice, no substance is entirely pure, and chemical purity is specified according to the intended use of the chemical. Chemical substances exist as so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin-layer Chromatography
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) is a chromatography technique used to separate non-volatile mixtures. Thin-layer chromatography is performed on a sheet of an inert substrate such as glass, plastic, or aluminium foil, which is coated with a thin layer of adsorbent material, usually silica gel, aluminium oxide (alumina), or cellulose. This layer of adsorbent is known as the stationary phase. After the sample has been applied on the plate, a solvent or solvent mixture (known as the mobile phase) is drawn up the plate via capillary action. Because different analytes ascend the TLC plate at different rates, separation is achieved. It may be performed on the analytical scale as a means of monitoring the progress of a reaction, or on the preparative scale to purify small amounts of a compound. TLC is an analytical tool widely used because of its simplicity, relative low cost, high sensitivity, and speed of separation. TLC functions on the same principle as all chromatography: a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioanalytical Chemistry
Radioanalytical chemistry focuses on the analysis of sample for their radionuclide content. Various methods are employed to purify and identify the radioelement of interest through chemical methods and sample measurement techniques. History The field of radioanalytical chemistry was originally developed by Marie Curie with contributions by Ernest Rutherford and Frederick Soddy. They developed chemical separation and radiation measurement techniques on terrestrial radioactive substances. During the twenty years that followed 1897 the concepts of radionuclides was born. Since Curie's time, applications of radioanalytical chemistry have proliferated. Modern advances in nuclear and radiochemistry research have allowed practitioners to apply chemistry and nuclear procedures to elucidate nuclear properties and reactions, used radioactive substances as tracers, and measure radionuclides in many different types of samples. The importance of radioanalytical chemistry spans many fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Reaction Analysis
*
*
{{Di ...
Nuclear may refer to: Physics Relating to the nucleus of the atom: * Nuclear engineering *Nuclear physics *Nuclear power *Nuclear reactor *Nuclear weapon *Nuclear medicine *Radiation therapy *Nuclear warfare Mathematics *Nuclear space *Nuclear operator *Nuclear congruence *Nuclear C*-algebra Biology Relating to the nucleus of the cell: * Nuclear DNA Society * Nuclear family, a family consisting of a pair of adults and their children Music * "Nuclear" (band), group music. * "Nuclear" (Ryan Adams song), 2002 *"Nuclear", a song by Mike Oldfield from his ''Man on the Rocks'' album * ''Nu.Clear'' (EP) by South Korean girl group CLC See also *Nucleus (other) *Nucleolus * Nucleation * Nucleic acid *Nucular ''Nucular'' is a common, proscribed pronunciation of the word "nuclear". It is a rough phonetic spelling of . The ''Oxford English Dictionary''s entry dates the word's first published appearance to 1943. Dictionary notes This is one of two con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
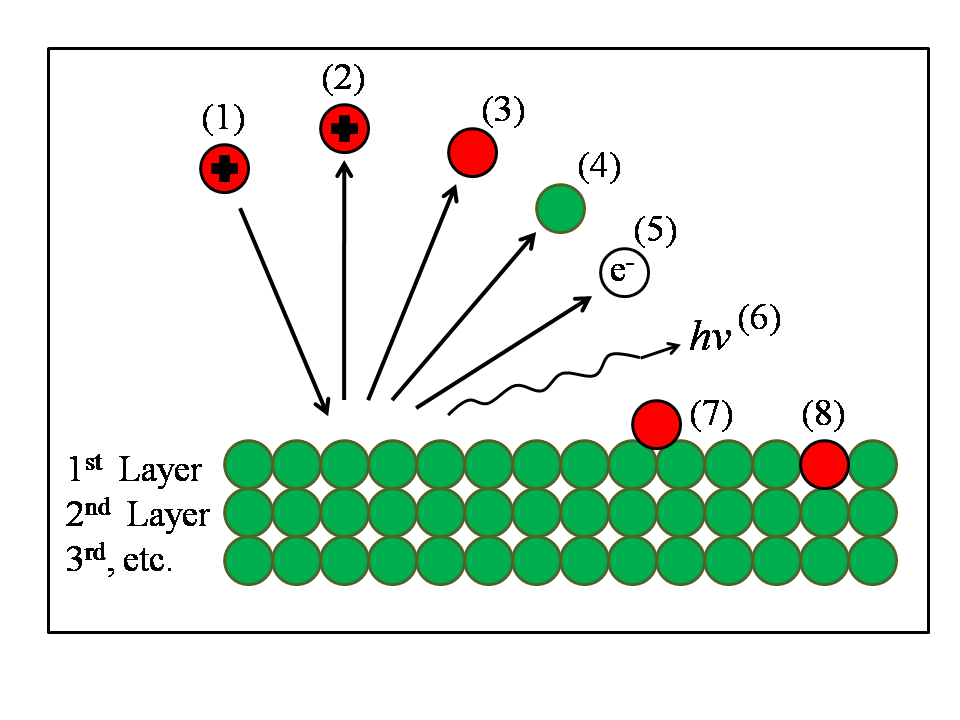
Rutherford Backscattering Spectroscopy
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample. Geiger–Marsden experiment Rutherford backscattering spectrometry is named after Lord Rutherford, a physicist sometimes referred to as the father of nuclear physics. Rutherford supervised a series of experiments carried out by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden between 1909 and 1914 studying the scattering of alpha particles through metal foils. While attempting to eliminate "stray particles" they believed to be caused by an imperfection in their alpha source, Rutherford suggested that Marsden attempt to measure backscattering from a gold foil sample. According to the then-dominant plum-pudding model of the atom, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Beam Analysis
Ion beam analysis ("IBA") is an important family of modern analytical techniques involving the use of MeV ion beams to probe the composition and obtain elemental depth profiles in the near-surface layer of solids. All IBA methods are highly sensitive and allow the detection of elements in the sub-monolayer range. The depth resolution is typically in the range of a few nanometers to a few ten nanometers. Atomic depth resolution can be achieved, but requires special equipment. The analyzed depth ranges from a few ten nanometers to a few ten micrometers. IBA methods are always quantitative with an accuracy of a few percent. Channeling allows to determine the depth profile of damage in single crystals. *RBS: Rutherford backscattering is sensitive to heavy elements in a light matrix *EBS: ''Elastic (non-Rutherford) backscattering spectrometry'' can be sensitive even to light elements in a heavy matrix. The term ''EBS'' is used when the incident particle is going so fast that it exceeds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microanalysis
Microanalysis is the chemical identification and quantitative analysis of very small amounts of chemical substances (generally less than 10 mg or 1 ml) or very small surfaces of material (generally less than 1 cm2). One of the pioneers in the microanalysis of chemical elements was the Austrian Nobel Prize winner Fritz Pregl.http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/1923/index.html ''The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1923''. Nobelprize.org. Retrieved 2014-08-06 Methods The most known methods used in microanalysis include: * Most of the spectroscopy methods: ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray fluorescence, Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, Wavelength-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry * Most of the chromatography methods : high-performance liquid chromatography, Gel permeation chromatography; * Some thermal analysis methods: differential scanning calorimetry, thermogravimetric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Materials Analysis Methods
This is a list of analysis methods used in materials science. Analysis methods are listed by their acronym, if one exists. Symbols * μSR – see muon spin spectroscopy * χ – see magnetic susceptibility A * AAS – Atomic absorption spectroscopy * AED – Auger electron diffraction * AES – Auger electron spectroscopy * AFM – Atomic force microscopy * AFS – Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy * Analytical ultracentrifugation * APFIM – Atom probe field ion microscopy * APS – Appearance potential spectroscopy * ARPES – Angle resolved photoemission spectroscopy * ARUPS – Angle resolved ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy * ATR – Attenuated total reflectance B * BET – BET surface area measurement (BET from Brunauer, Emmett, Teller) * BiFC – Bimolecular fluorescence complementation * BKD – Backscatter Kikuchi diffraction, see EBSD * BRET – Bioluminescence resonance energy transfer * BSED – Back scattered electron diffraction, see EBSD C * CAI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chemical Analysis Methods
A list of chemical analysis methods with acronyms. {{Compact ToC, name=no, center=no, top=yes, seealso=yes A * Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) * Atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) * Atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (AFS) * Alpha particle X-ray spectrometer (APXS) C * Capillary electrophoresis (CE) * Chromatography * Colorimetry * Computed tomography * Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) D * Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) E * Electrodialysis * Electrolysis * Electron microscopy * Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) also called Electron spin resonance (ESR) * Electrophoresis * Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS/EDX) F * Field flow fractionation (FFF) * Flow injection analysis (FIA) * Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) G * Gas chromatography (GC) * Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) * Gas chromatography-IR spectroscopy (GC-IR) * Gel permeation chromatography-IR spectroscopy (GPC-IR) H * High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) * High p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-performance Liquid Chromatography
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify each component in a mixture. It relies on pumps to pass a pressurized liquid solvent containing the sample mixture through a column filled with a solid adsorbent material. Each component in the sample interacts slightly differently with the adsorbent material, causing different flow rates for the different components and leading to the separation of the components as they flow out of the column. HPLC has been used for manufacturing (''e.g.'', during the production process of pharmaceutical and biological products), legal (''e.g.'', detecting performance enhancement drugs in urine), research (''e.g.'', separating the components of a complex biological sample, or of similar synthetic chemicals from each other), and medical (''e.g.'', detecting vitamin D levels in blood serum) purposes. Chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Chromatography
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture. In preparative chromatography, GC can be used to prepare pure compounds from a mixture. Gas chromatography is also sometimes known as vapor-phase chromatography (VPC), or gas–liquid partition chromatography (GLPC). These alternative names, as well as their respective abbreviations, are frequently used in scientific literature. Gas chromatography is the process of separating compounds in a mixture by injecting a gaseous or liquid sample into a mobile phase, typically called the carrier gas, and passing the gas through a stationary phase. The mobile phase is usually an inert gas or an unreactive gas such as helium, argon, nitrogen or hydrogen. The stationary phase is a microscopic l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be preparative or analytical. The purpose of preparati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |