|
Allen Walker Read
Allen Walker Read (June 2, 1906 – October 16, 2002) was an American etymologist and lexicographer. Born in Minnesota, he spent much of his career as a professor at Columbia University in New York. Read's work ''Classic American Graffiti'' is well regarded in the study of latrinalia and obscenity. His etymological career included his discovery of the origin of the word " OK", a longtime puzzle, and his scholarly study of the history and use of the common English vulgarity "fuck." Biography and career Read was born in Winnebago, Minnesota.''The Times'' , November 8, 2002, obituary. His one sister, Mary Jo, became a professor of geography at Eastern Illinois University. He e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Coast Today
''The Standard-Times'' (and ''Sunday Standard-Times''), based in New Bedford, Massachusetts, is the largest of three daily newspapers covering the South Coast of Massachusetts, along with ''The Herald News'' of Fall River and ''Taunton Daily Gazette'' of Taunton, Massachusetts. Like the ''Cape Cod Times'', which is the only larger newspaper in Southeastern Massachusetts, ''The Standard-Times'' is owned by Gannett. Together with the weekly newspapers of Hathaway Publishing, which also cover Fall River and several other suburban towns, ''The Standard-Times'' is part of the South Coast Media Group. Coverage ''The Standard-Times''' coverage area includes Acushnet, Dartmouth, Fairhaven, Fall River, Freetown, Lakeville, Marion, Mattapoisett, New Bedford, Rochester, Wareham, and Westport, Massachusetts. ''The Standard-Times''' main daily competitor is ''The Herald News'' of Fall River. Other rivals include ''The Boston Globe'', the ''Taunton Daily Gazette'' and the ''Providence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etymologists
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words and, by extension, the origin and evolution of their semantic meaning across time. It is a subfield of historical linguistics, and draws upon comparative semantics, morphology, semiotics, and phonetics. For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts, and texts about the language, to gather knowledge about how words were used during earlier periods, how they developed in meaning and form, or when and how they entered the language. Etymologists also apply the methods of comparative linguistics to reconstruct information about forms that are too old for any direct information to be available. By analyzing related languages with a technique known as the comparative method, linguists can make inferences about their sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1906 Births
Events January–February * January 12 – Persian Constitutional Revolution: A nationalistic coalition of merchants, religious leaders and intellectuals in Persia forces the shah Mozaffar ad-Din Shah Qajar to grant a constitution, and establish a national assembly, the Majlis. * January 16–April 7 – The Algeciras Conference convenes, to resolve the First Moroccan Crisis between France and Germany. * January 22 – The strikes a reef off Vancouver Island, Canada, killing over 100 (officially 136) in the ensuing disaster. * January 31 – The Ecuador–Colombia earthquake (8.8 on the Moment magnitude scale), and associated tsunami, cause at least 500 deaths. * February 7 – is launched, sparking a naval race between Britain and Germany. * February 11 ** Pope Pius X publishes the encyclical ''Vehementer Nos'', denouncing the 1905 French law on the Separation of the Churches and the State. ** Two British members of a poll tax collecting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
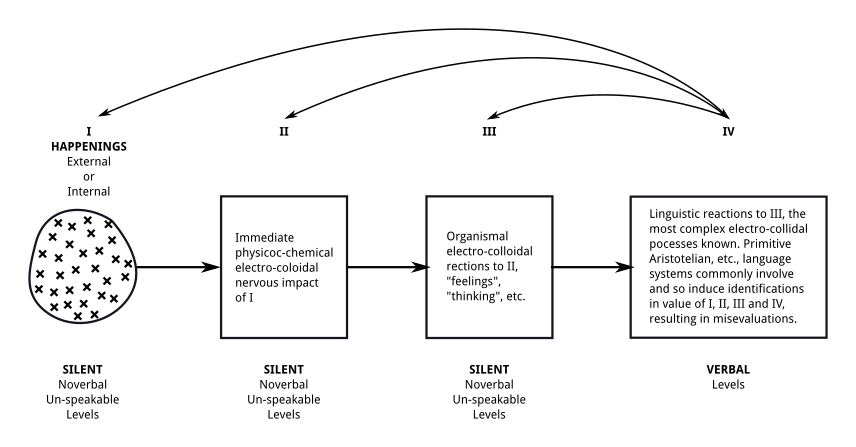
General Semantics
General semantics is concerned with how events translate to perceptions, how they are further modified by the names and labels we apply to them, and how we might gain a measure of control over our own cognitive, emotional, and behavioral responses. Proponents characterize general semantics as an antidote to certain kinds of delusional thought patterns in which incomplete and possibly warped mental constructs are projected onto the world and treated as reality itself. After partial launches under the names ''human engineering'' and ''humanology'', Polish-American originator Alfred Korzybski (1879–1950) fully launched the program as ''general semantics'' in 1933 with the publication of ''Science and Sanity: An Introduction to Non-Aristotelian Systems and General Semantics''. In ''Science and Sanity'', general semantics is presented as both a theoretical and a practical system whose adoption can reliably alter human behavior in the direction of greater sanity. In the 1947 preface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiotic Society Of America
The Semiotic Society of America is an interdisciplinary professional association serving scholars from many disciplines with common interests in semiotics, the study of signs and sign-systems. It was founded in 1975 and includes members from the United States and Canada. Its official journal is ''The American Journal of Semiotics''. The Society also publishes the proceedings of its annual conferences. Memberships in the society and publication of the journal are managed by the Philosophy Documentation Center. As its symbol, the Society uses caduceus, the staff of a messenger bearing a message, as a sign of a sign. Publications of the Semiotic Society of America * ''The American Journal of Semiotics'', 1981–present * '' Semiotics: The Proceedings of the Semiotic Society of America'', 1980–present * ''Semiotic Scene: Bulletin of the Semiotic Society of America'', 1977-1981 * ''Bulletin of Literary Semiotics'', 1975-1977 Presidents According to the society's official website, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Linguistic Association
The International Linguistic Association (ILA) was founded in 1943 as the Linguistic Circle of New York. Its founding members were academic linguists in the New York area, including many members of the École Libre des Hautes Études in exile. The model for the new organization was the Société de Linguistique de Paris. Early members included Roman Jakobson, Morris Swadesh, André Martinet, Henri F. Muller, Giuliano Bonfante, Robert Austerlitz, Robert Fowkes, Henry Lee Smith, Wolf Leslau, and Louis H. Gray. The Circle began publishing the journal WORD in 1945 under the editorship of Pauline Taylor. Both the Circle and the journal soon became known as one of the main sources of new ideas in American linguistics before the Chomsky Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American public intellectual: a linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, social critic, and political activist. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky is ... era ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doublespeak
Doublespeak is language that deliberately obscures, disguises, distorts, or reverses the meaning of words. Doublespeak may take the form of euphemisms (e.g., "downsizing" for layoffs and "servicing the target" for bombing), in which case it is primarily meant to make the truth sound more palatable. It may also refer to intentional ambiguity in language or to actual inversions of meaning. In such cases, doublespeak disguises the nature of the truth. Doublespeak is most closely associated with political language. Origins and concepts The term "doublespeak" derives from two concepts in George Orwell's novel ''Nineteen Eighty-Four'', "doublethink" and "Newspeak", though the term is not used in the book. Another variant, "doubletalk", also referring to deliberately ambiguous speech, did exist at the time Orwell wrote his book, but the usage of "doublespeak", as well as of "doubletalk", in the sense emphasizing ambiguity clearly postdates the publication of ''Nineteen Eighty- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pig Latin
Pig Latin is a language game or argot in which words in English are altered, usually by adding a fabricated suffix or by moving the onset or initial consonant or consonant cluster of a word to the end of the word and adding a vocalic syllable to create such a suffix. For example, Wikipedia would become Ikipediaway (taking the 'W' and 'ay' to create a suffix). The objective is to conceal the words from others not familiar with the rules. The reference to Latin is a deliberate misnomer; Pig Latin is simply a form of argot or jargon unrelated to Latin, and the name is used for its English connotations as a strange and foreign-sounding language. It is most often used by young children as a fun way to confuse people unfamiliar with Pig Latin. Origins and history Early mentions of pig Latin or hog Latin describe what we would today call dog Latin, a type of parody Latin. Examples of this predate even Shakespeare, whose 1598 play, ''Love's Labour's Lost'', includes a reference to do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slang
Slang is vocabulary (words, phrases, and linguistic usages) of an informal register, common in spoken conversation but avoided in formal writing. It also sometimes refers to the language generally exclusive to the members of particular in-groups in order to establish group identity, exclude outsiders, or both. The word itself came about in the 18th century and has been defined in multiple ways since its conception. Etymology of the word ''slang'' In its earliest attested use (1756), the word ''slang'' referred to the vocabulary of "low" or "disreputable" people. By the early nineteenth century, it was no longer exclusively associated with disreputable people, but continued to be applied to usages below the level of standard educated speech. In Scots dialect it meant "talk, chat, gossip", as used by Aberdeen poet William Scott in 1832: "The slang gaed on aboot their war'ly care." In northern English dialect it meant "impertinence, abusive language". The origin of the word is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |