|
Alcázar De San Juan–Cádiz Railway
The Alcázar de San Juan–Cádiz railway is an important Iberian-gauge railway line in Spain. It branches from the Madrid–Valencia railway at Alcázar de San Juan and terminates in Cádiz. It was once the only line linking Madrid to Seville, but now primarily serves local commuter rail services and regional traffic since the opening of the Madrid–Seville high-speed rail line in 1992. Route The line serves major Spanish cities including Córdoba, Seville, Jerez de la Frontera and Cádiz; along with a small branch to Jaén at Linares-Baeza, and a second after Linares to Almería of around . The line also branches off at Córdoba as the Córdoba–Málaga railway. In October 2015 the section of the line between Seville and to Cádiz was upgraded to high-speed standard after 14 years of works and put in service by Alvia trains for speeds up to 200 km/h. Services The line is used by Cercanías Madrid's C-3 service, the C-1 and C-4 of Cercanías Sevilla and the C-1 of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcázar De San Juan
Alcázar de San Juan is a city and municipality of Spain located in the province of Ciudad Real, autonomous community of Castilla–La Mancha. It lies on the plain of La Mancha. From the 13th to the 19th century the history of Alcázar is strongly linked to the Grand Priory of the Order of St. John of Jerusalem. The city became a railway hub in the 19th century. Geography The municipality is part the large plain of La Mancha, standing at around 650 metres above sea level. The area is drained by two tributaries of the Guadiana: the Cigüela and the Záncara, located to the west and south of the urban centre, respectively. The municipal area also features a number of endorheic saline lagoons surrounding the city, including the Alcázar de San Juan lagoon complex (lagoons of Camino de Villafranca, Las Yeguas and La Veguilla). Name Its name is taken from an old moorish fortress (''al-qaSsr'' in Arabic language), which was afterwards garrisoned by the knights of St John (''San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerez De La Frontera
Jerez de la Frontera (), or simply Jerez (), is a Spanish city and Municipalities of Spain, municipality in the province of Cádiz in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, in southwestern Spain, located midway between the Atlantic Ocean and the Sierra de Cádiz, Cádiz Mountains. , the city, the largest in the province, had a population of 213,105. It is the fifth largest in Andalusia, and has become the transportation and communications hub of the province, surpassing even Cádiz, the provincial capital, in economic activity. Jerez de la Frontera is also, in terms of land area, the largest municipality in the province, and its sprawling outlying areas are a fertile zone for agriculture. There are also many cattle ranches and horse-breeding operations, as well as a world-renowned wine industry (Jerez de la Frontera#Wine, Xerez). Currently, Jerez, with 213,105 inhabitants, is the List of cities in Spain, 25th largest city in Spain, the 5th in Andalu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines built to handle speeds above or upgraded lines in excess of are widely considered to be high-speed. The first high-speed rail system, the Tōkaidō Shinkansen, began operations in Japan in 1964 and was widely known as the bullet train. High-speed trains mostly operate on standard gauge tracks of continuously welded rail on grade-separated rights of way with large radii. However, certain regions with wider legacy railways, including Russia and Uzbekistan, have sought to develop a high speed railway network in Russian gauge. There are no narrow gauge high-speed trains; the fastest is the Cape gauge Spirit of Queensland at . Many countries have developed, or are currently building, high-speed rail infrastructure to connect major c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercanías Cádiz
''Cercanías Cádiz'' is the commuter rail service in the cities of Cádiz and Jerez de la Frontera in Andalucia, Spain. The service consists of two lines of 14 stations over 61 km of track, serving 2.8 million passengers a year. History Suburban trains began service in Cádiz in the 1980s. In 2000, work began to place the railway line leading into Cádiz underground to enable double-tracking and create a new linear park in the city. During this work, Cádiz railway station was temporarily closed with Cortadura serving as a terminus in the meantime. In 2002 the work was completed, with the reopening of Cádiz station and new underground stations San Severiano, Segunda Aguada and Estadio; spaced apart at a distance resembling a metro. Route The service mainly uses the Alcázar de San Juan–Cádiz main line, with a branch to the University of Cádiz from Las Aletas. The section of track between Cádiz railway station and Cortadura station was doubled and put underground in 2001, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercanías Sevilla
Cercanias Sevilla is a commuter rail system operating in and around the Seville metropolitan area. Currently, it contains 5 separate lines, 251 kilometres of railway and 37 stations. Lines and stations The network consists of five lines and thirty-seven stations. The two busiest stations on the network in 2018 were Seville-Santa Justa railway station, Seville-Santa Justa and Seville-San Bernardo with 1.49 million passengers each, followed by Virgen del Rocío (751,000), Utrera (719,000) and Dos Hermanas (674,000). Line C-1 Lora del Río - Sevilla Santa Justa - Lebrija Line C-2 Sevilla-Santa Justa - Cartuja Line C-3 Sevilla-Santa Justa - Cazalla-Constantina Line C-4 Circular Line C-5 Jardines de Hércules - Sevilla-Santa Justa - Benacazón Future projects A branch line connection to Seville Airport is planned. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Cercanias Sevilla Cercanías Rail transport in Seville ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
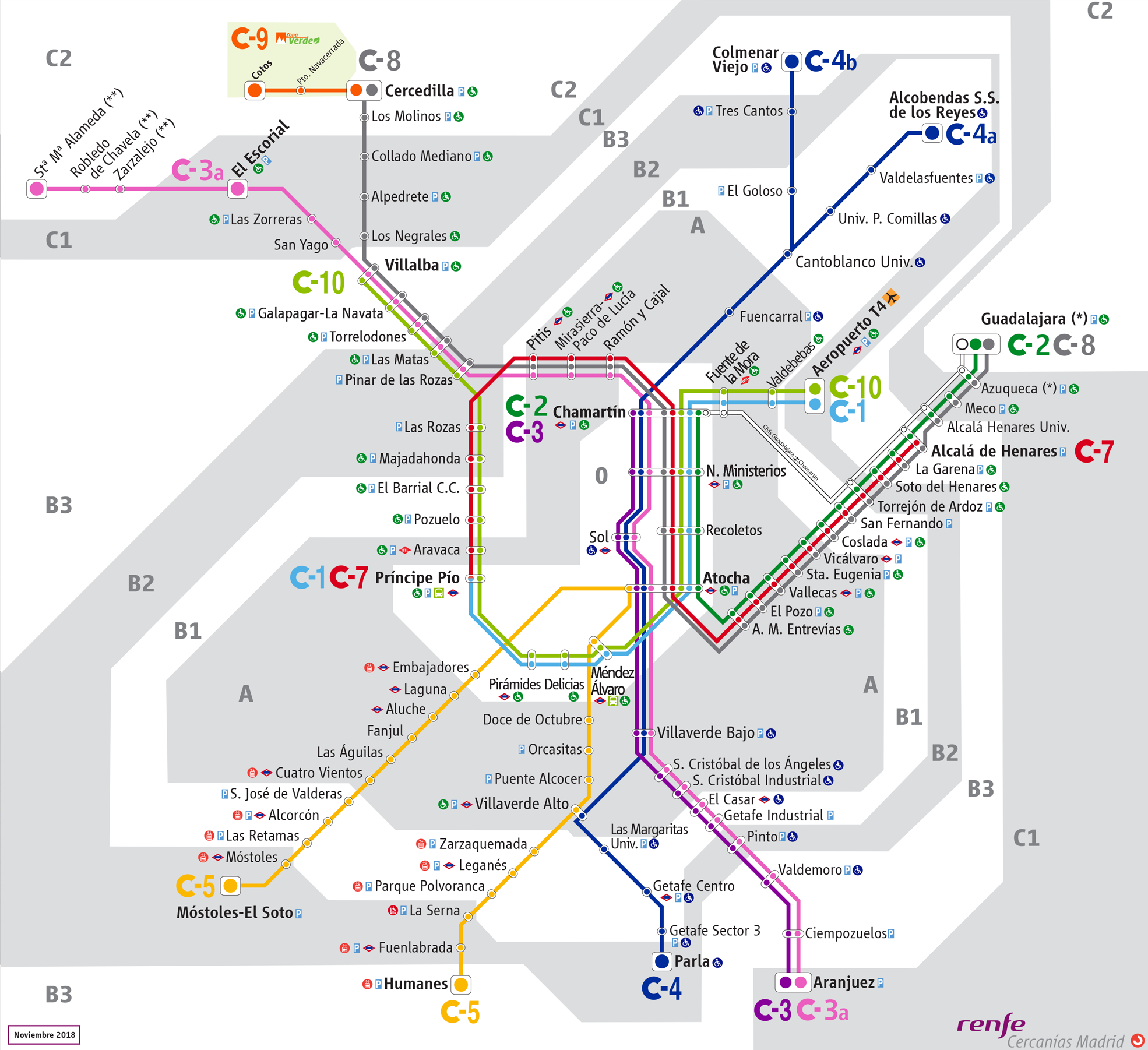
C-3 (Cercanías Madrid)
The C-3 is a line and rail service of Cercanías Madrid commuter rail network, operated by Renfe Operadora. It runs from El Escorial northwest of Madrid to Aranjuez south of Madrid. The C-3 shares tracks for half of its length with Madrid commuter rail service line while it also shares significant parts with lines , and . The line has been in operation since 1980, with its current incarnation in operation since 22 September 2011. On 5 November 2018, the C-3a service was introduced as a separation of former extended C-3 services terminating at either El Escorial or Santa María de la Alameda. The C-3a designation was formerly used for the now-closed Pinto–San Martín de la Vega branch line ( es:Línea Pinto-San Martín de la Vega) branching off from Pinto to Parque Warner Madrid and San Martín de la Vega, which operated between 2002 and 2012. List of stations The following table lists the name of each station served by line C-3 in order from northwest to south; the station's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercanías Madrid
Cercanías Madrid is the commuter rail service that serves Madrid, the capital of Spain, and its metropolitan area. It is operated by Cercanías Renfe, the commuter rail division of Renfe, the former monopoly of rail services in Spain. Its total length is 370 km. History Until 1989 The first railroad line departing from Madrid (the second in Spain and the third in the Iberian Peninsula) was built in 1851 between Madrid and Aranjuez. Soon the growing Spanish railway system was dominated by two large companies: the ''Compañía del Norte'' (Northern Company), who operated the lines between Madrid and the Atlantic North of Spain from the ''Estación del Norte'' (now Príncipe Pío),and the Madrid-Zaragoza-Alicante (MZA) who operated the lines between the capital and the Mediterranean and Andalusian cities from the Atocha station. Another station, Delicias, served the line to Lisbon. Other smaller companies operated from Madrid, mostly in narrow gauge. After the Civi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alvia
Alvia is a high-speed train service in Spain used by Renfe Operadora for long-distance service with a top speed of . The trains have the ability to use both Iberian gauge and standard gauge, which allows them to travel on the recently constructed high-speed lines for part of the journey before switching to the "classic" Iberian gauge network to complete it. Trains that run exclusively on high-speed tracks are branded AVE or Avant. Routes , RENFE Class 120 / 121, RENFE Class 130 and RENFE Class 730 trains are in service. Class 120 trains are used on the routes from Madrid to Pamplona, Logroño, Irún and Hendaye (France) (running on high-speed lines from Madrid to Burgos and changing gauge there), and between Barcelona and Irún, Bilbao (running on high-speed lines between Barcelona and Zaragoza). Class 121 trains are employed on the routes from Madrid to Huelva, Ponferrada, Gijón and Santander changing gauge at Seville, León and Venta de Baños. Class 130 trains are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Córdoba–Málaga Railway
The Córdoba–Málaga railway is an Iberian-gauge railway line in Spain. It branches from the Alcázar de San Juan–Cádiz railway at Córdoba and terminates at Málaga María Zambrano. It was once the only line linking Madrid to Málaga, but now primarily serves local commuter rail services and regional traffic since the opening of the Madrid–Málaga high-speed rail line in 2013. Services The line is used by Cercanías Málaga's C-1 service as far as Álora, and regional services from Málaga to Ronda via Bobadilla. Since 2013, due to the opening of the AVE high-speed rail line in 2007, the section between Córdoba and Bobadilla closed to passenger service and is used only by freight trains Rail freight transport is the use of railroads and trains to transport cargo as opposed to human passengers. A freight train, cargo train, or goods train is a group of freight cars (US) or goods wagons (International Union of Railways) hauled .... References {{DEFAULTSORT:C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linares Baeza–Almería Railway
The Linares Baeza–Almería railway is an Iberian-gauge railway line in Spain. It branches from the Alcázar de San Juan–Cádiz railway at Linares and terminates in Almería. It is currently the main line linking Madrid to Almería. Route The line runs through the provinces of Jaén, Granada and Almería. The route formerly contained the Hacho Bridge, which was the longest iron viaduct on the Spanish rail network.Chías Navarro, Prop and Abbot Balboa, Tomás: " Bridges of Spain ", FCC, Madrid 1994, pag. 248, Services The line is used by all trains from Almería to Madrid, with the full journey taking around six hours. To continue to Madrid from Linares, the line uses the Alcázar de San Juan–Cádiz railway as far as Alcázar de San Juan, and the Madrid–Valencia railway to Madrid Chamartín. Future In 2023, Almería railway station will be linked to the AVE high-speed rail network by the Murcia–Almería high-speed rail line The Murcia–Almería high-speed rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linares, Jaén
Linares (; ) is a city located in the Andalusian province of Jaén, Spain. It is considered the second-most important city in that province and had a population of 56,525 in the most recent census (2021). The altitude is and the total area of the municipality is . It is located on kilometer 120 on the Valencia-Córdoba highway (N-322) and is from the province capital, Jaén. Overview Location Located in the Central-Western part of the province, the city of Linares is the second-biggest city in the province after the capital, Jaén. It is also the commercial capital of Sierra Morena, as well as the referential city in the surrounding areas. Geography The city term is orientated in a NE-SW direction, giving the transition in altitude decreasing between the higher northern area of Sierra Morena; being Paño Pico (552 m) the highest area of the municipal term; and the lowest area, the Guadalimar Valley in the South-Western limit, with an altitude of (318 m). Climate The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaén Railway Station
Jaén Railway Station is a railway station serving Jaén, Spain. This station is north from the city centre, on a branch from the Alcázar de San Juan–Cádiz railway. The station is operated by RENFE and part of Adif and high-speed rail systems. Services The station is served by Renfe Media Distancia services to Madrid Chamartín and Cádiz Cádiz (, , ) is a city and port in southwestern Spain. It is the capital of the Province of Cádiz, one of eight that make up the autonomous community of Andalusia. Cádiz, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Western Europe, ..., providing travellers with frequent connections every day. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Jaen railway station Buildings and structures in Jaén, Spain Railway stations in Andalusia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Ciudad_Real_Central_Airport_&_Province%2C_Spain_(cropped).jpg)