|
Ahmed Ibn Qassim Ar-Rifa'i Ar-Ribati
Ahmed ibn Qassim ar-Rifa'i ar-Ribati () was a Moroccan calligrapher interested in the reformation and standardization of Maghrebi script. While Arabic calligraphy had undergone standardization and reform in the Mashriq under Ibn Muqla and Ibn al-Bawwab Ibn al-Bawwāb (), also known as Ali ibn-Hilal, Abu'l-Hasan, and Ibn al-Sitri, was an Arabic calligrapher and illuminator who lived in Baghdad. He is the figure most associated with the adoption of round script to transcribe the Qur'an. He most ..., it hadn't done so in the Maghreb. ar-Ribati wrote '' Stringing the Pearls of the Thread'' () in 1840, which was edited and republished by Muhammad Sabri. The book is in the form of an ''urjuza'' of 143 couplets. References Moroccan Calligraphers 19th-century calligraphers Year of birth missing Year of death missing {{Morocco-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maghrebi Script
Maghrebi script or Maghribi script () refers to a loosely related family of Arabic scripts that developed in the Maghreb (North Africa), al-Andalus (Iberia), and ''Bilad as-Sudan'' (the West African Sahel). Maghrebi script is directly derived from the Kufic script, and is traditionally written with a pointed tip (), producing a line of even thickness. The script is characterized by rounded letter forms, extended horizontal features, and final open curves below the baseline. It also differs from Mashreqi scripts in the notation of the letters ''faa'' (Maghrebi: ; Mashreqi: ) and ''qoph'' (Maghrebi: ; Mashreqi: ). For centuries, Maghrebi script was used to write Arabic manuscripts and record Andalusi and Moroccan literature, whether in Classical Arabic, Maghrebi Arabic, or Amazigh languages. History Origins Arabic script first came to the Maghreb with the Islamic conquests (643–709). The conquerors, led by Uqba ibn Nafi, used both Hijazi and Kufic scripts, as demo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Calligraphy
Arabic calligraphy is the artistic practice of handwriting and calligraphy based on the Arabic alphabet. It is known in Arabic as ''khatt'' ( ar, خط), derived from the word 'line', 'design', or 'construction'. Kufic is the oldest form of the Arabic script. From an artistic point of view, Arabic calligraphy has been known and appreciated for its diversity and great potential for development. In fact, it has been linked in the Arabic culture to various fields such as religion, art, architecture, education and craftsmanship, which in return have played an important role in its advancement. Although most Islamic calligraphy is in Arabic and most Arabic calligraphy is Islamic, the two are not identical. Coptic or other Christian manuscripts in Arabic, for example, have made use of calligraphy. Likewise, there is Islamic calligraphy in Persian or the historic Ottoman language. Arabic alphabet The Arabic alphabet is known to be used by one of the most widely used language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
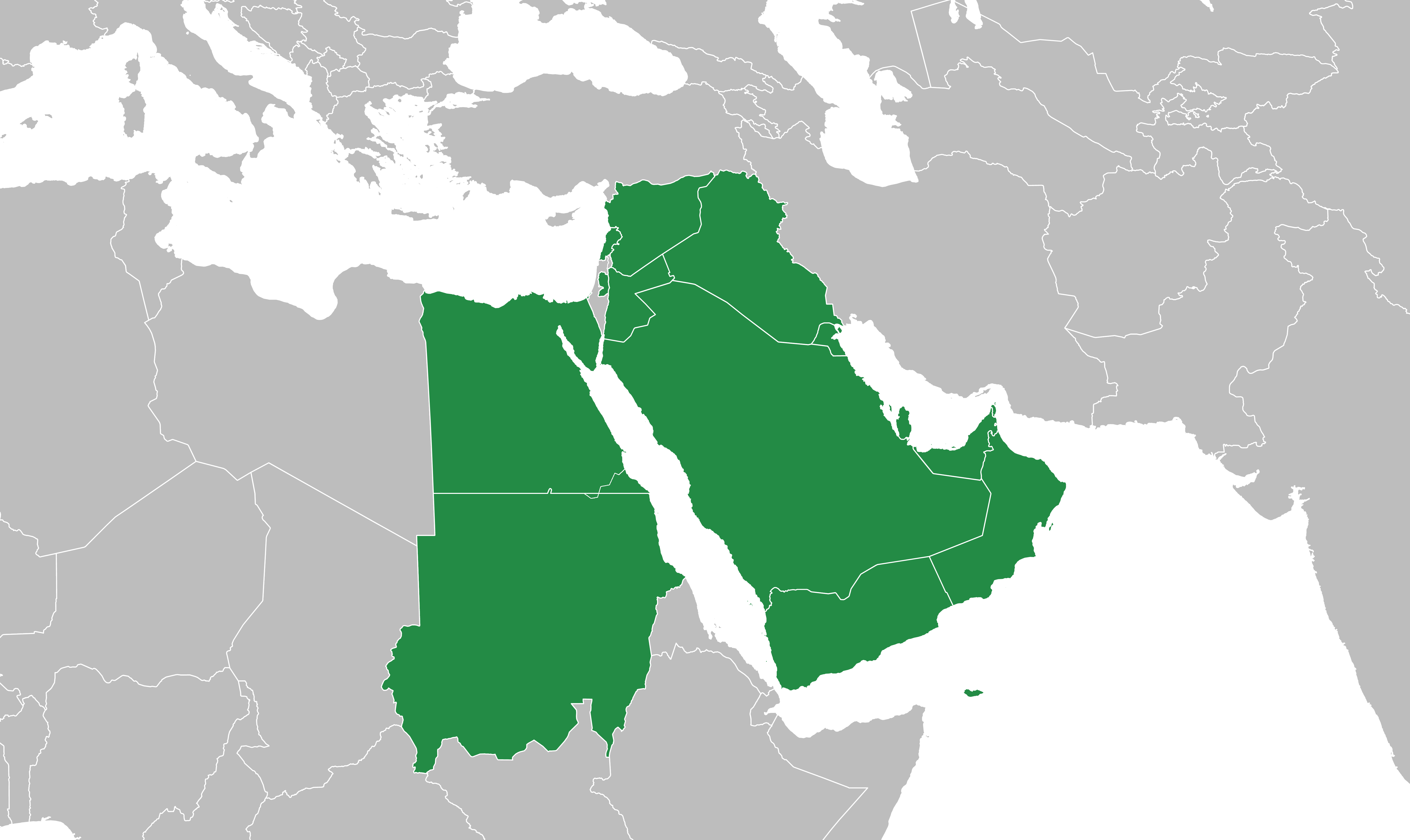
Mashriq
The Mashriq ( ar, ٱلْمَشْرِق), sometimes spelled Mashreq or Mashrek, is a term used by Arabs to refer to the eastern part of the Arab world, located in Western Asia and eastern North Africa. Poetically the "Place of Sunrise", the name is derived from the verb ''sharaqa'' ( ar, شرق, link=no "to shine, illuminate, radiate" and "to rise"), from sh-r-q root (ش-ر-ق), referring to the east, where the sun rises. The region includes the Arab states of Bahrain, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Geography As the word ''Mashriq'' refers to Arab countries located between the Mediterranean Sea and Iran, it is the companion term to '' Maghreb'' ( ar, ٱلْمَغْرِب), the western part of North Africa. Libya may be regarded as straddling the two regions, receiving influences from both the Maghreb and the Mashriq, with its eastern part ( Cyrenaica) being link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Muqla
Abu Ali Muhammad ibn Ali ibn Muqla ( ar, أبو علي محمد بن علي ابن مقلة, Abū ʿAlī Muḥammad ibn ʿAlī ibn Muqla; 885/6 – 20 July 940/1), commonly known as Ibn Muqla, was an official of the Abbasid Caliphate of Persian origin who rose to high state posts in the early 10th century. His career culminated in his own assumption of the vizierate at Baghdad thrice: in 928–930, 932–933 and 934–936. Unable to successfully challenge the growing power of regional emirs, he lost his position to the first '' amir al-umara'', Ibn Ra'iq, and died in prison. He was also a noted calligrapher, inventing ''al-khatt al-mansūb'' () and '' khatt ath-thuluth'' (). Life Early life and career Ibn Muqla was born in Baghdad, the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, in AH 272 (885/6 CE).. His career in public service began in Fars, where he served as tax collector. His rise to power in the central government came in 908, under the patronage of the powerful vizier Abu ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Al-Bawwab
Ibn al-Bawwāb (), also known as Ali ibn-Hilal, Abu'l-Hasan, and Ibn al-Sitri, was an Arabic calligrapher and illuminator who lived in Baghdad. He is the figure most associated with the adoption of round script to transcribe the Qur'an. He most likely died around 1022 CE in Baghdad. Life Ibn al-Bawwab was from a poor family. His name literally translates as the “son of the doorkeeper.” He was trained in law and theology, was very devout and is said to have been able to recite the Qur'an from memory. Detailed accounts of his life are lacking, however, it is known that he worked as a home decorator before beginning book illumination and eventually moving to calligraphy. Additionally, it is known that, upon his death in 1022 CE, he was buried in Baghdad near the tomb of Ahmad ibn-Hanbal. He was fluent in all six scripts and refined them. He achieved fame in his own lifetime and was readily recognized by his long beard. His students carried his improved style through to succe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajaz (prosody)
Rajaz (, literally 'tremor, spasm, convulsion as may occur in the behind of a camel when it wants to rise') is a metre used in classical Arabic poetry. A poem composed in this metre is an ''urjūza''. The metre accounts for about 3% of surviving ancient and classical Arabic verse. Form This form has a basic foot pattern of , ⏓ ⏓ ⏑ – , (where '–' represents a long syllable, '⏑' a short syllable, and '⏓' a syllable that can be long or short), as exemplified through the mnemonic (''Tafā'īl'') ' (). It is exceptional, but possible, for both anceps syllables to be short. Rajaz lines also have a catalectic version with the final foot , ⏓ – – , . Lines are most often of three feet (trimeter), but can also be of two feet (dimeter). Thus the possible forms are: :, ⏓ ⏓ ⏑ – , ⏓ ⏓ ⏑ – , ⏓ ⏓ ⏑ – , (trimeter) :, ⏓ ⏓ ⏑ – , ⏓ ⏓ ⏑ – , ⏓ – – , ( trimeter catalectic) :, ⏓ ⏓ ⏑ – , ⏓ ⏓ ⏑ – , (dimeter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moroccan Calligraphers
Moroccan may refer to: * Something or someone from, or related to the country of Morocco * Moroccan people * Moroccan Arabic, spoken in Morocco * Moroccan Jews See also * Morocco leather Morocco leather (also known as Levant, the French Maroquin, or German Saffian from Safi, a Moroccan town famous for leather) is a vegetable-tanned leather known for its softness, pliability, and ability to take color. It has been widely used in ... * * {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Calligraphers
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |