|
Abrskil
Abrskil or Abrskila was the hero of Abkhazian national epos, Abrskil. He was a role model of the Greek Prometheus and hence was also known as Abkhaz Prometheus. The Abrskil Cave, a notable landmark near the village of Otapi, is named after this legend. Legend According to the popular folk legend of Abkhazian, Abraskil is the name of the legendary boy born out of wedlock to a lovely girl called Abkhazia. He grew up in wild and wayward ways. He was unlike other boys and grew up into a very strong, handsome person with huge ambitions. He could ride on a horse and hurl large stones while riding on it. His favourite horse was called Arasch. His bravery and daring was a kind of Robin Hood image for his friends and compatriots. He challenged God that he was as good as Him and that he could perform any act which God could do. He moved between the mountains and the sea with great aplomb and abandon; he was kind of invincible in his movements on his magic horse Arasch. He had a following of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abrskil Cave
Abrskil Cave or Abrskila ( ka, აბრსკილის მღვიმე) is a stalactite cave near Otapi village in Abkhazia, Georgia. It is named after the national hero of Abrskil — a parallel folk hero of the Greek Prometheus and Georgian Amiran — known as Abkhaz Prometheus. It is also called the Otap cave. Abrskila is more than 2 km in length out of which about 1.5 to 1.7 km is accessible for viewing. Its beauty and fame is compared favourably with another cave known as the New Athos Cave. Geography Abrskil Cave is located in the picturesque southern slopes of the Panavi ridge near the port of Ochamchire, in karstic limestone. The cave is about 2 km long (3 km length including passages has also been reported), out of which 1.5 to 1.7 km has been made accessible. The cave has a winding gallery from where Achkitzgo River is seen to emerge. This gallery has six chambers, out of which the main hall is studded with naturally devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
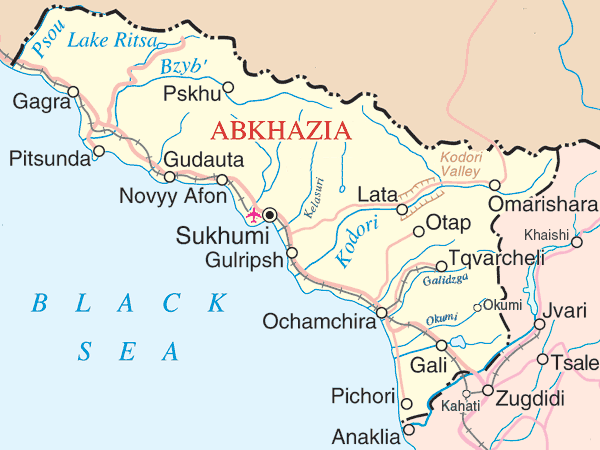
Otapi
, ka, ოტაფი , other_name = , settlement_type = Village and municipality , image_skyline = , imagesize = , image_caption = , image_map = Otap.PNG , map_caption = Municipal location within Ochamchira District (shaded orange) , pushpin_map = Georgia Abkhazia#Georgia (country) , pushpin_label_position = right , pushpin_map_caption = Location of Otapi , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Partially recognized independent country , subdivision_name1 = , subdivision_type2 = District , subdivision_name2 = Ochamchira , leader_title = District head (as of 2010) , leader_name = Murman Dzhopua , established_title = , established_date = , area_total_km2 = , population_as_of = 2010 , population_footnotes = , population_total = Approx. 150 , population_density_km2 = , tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and other territories. Most of these regions were officially unified only once, for 13 years, under Alexander the Great's empire from 336 to 323 BC (though this excludes a number of Greek city-states free from Alexander's jurisdiction in the western Mediterranean, around the Black Sea, Cyprus, and Cyrenaica). In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Roughly three centuries after the Late Bronze Age collapse of Mycenaean Greece, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus (; , , possibly meaning "forethought")Smith"Prometheus". is a Titan god of fire. Prometheus is best known for defying the gods by stealing fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of technology, knowledge, and more generally, civilization. In some versions of the myth, he is also credited with the creation of humanity from clay. Prometheus is known for his intelligence and for being a champion of humankind, and is also generally seen as the author of the human arts and sciences. He is sometimes presented as the father of Deucalion, the hero of the flood story. The punishment of Prometheus as a consequence of the theft of fire and giving it to humans is a popular subject of both ancient and modern culture. Zeus, king of the Olympian gods, sentenced Prometheus to eternal torment for his transgression. Prometheus was bound to a rock, and an eagle—the emblem of Zeus—was sent to eat his liver (in ancient Greece, the liver was thoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robin Hood
Robin Hood is a legendary heroic outlaw originally depicted in English folklore and subsequently featured in literature and film. According to legend, he was a highly skilled archer and swordsman. In some versions of the legend, he is depicted as being of noble birth, and in modern retellings he is sometimes depicted as having fought in the Crusades before returning to England to find his lands taken by the Sheriff. In the oldest known versions he is instead a member of the yeoman class. Traditionally depicted dressed in Lincoln green, he is said to have robbed from the rich and given to the poor. Through retellings, additions, and variations, a body of familiar characters associated with Robin Hood has been created. These include his lover, Maid Marian, his band of outlaws, the Merry Men, and his chief opponent, the Sheriff of Nottingham. The Sheriff is often depicted as assisting Prince John in usurping the rightful but absent King Richard, to whom Robin Hood remains loy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarzan
Tarzan (John Clayton II, Viscount Greystoke) is a fictional character, an archetypal feral child raised in the African jungle by the Mangani great apes; he later experiences civilization, only to reject it and return to the wild as a heroic adventurer. Created by Edgar Rice Burroughs, Tarzan first appeared in the novel ''Tarzan of the Apes'' (magazine publication 1912, book publication 1914), and subsequently in 23 sequels, several books by Burroughs and other authors, and innumerable works in other media, both authorized and unauthorized. Character biography Tarzan is the son of a British lord and lady who were marooned on the coast of Africa by mutineers. When Tarzan was an infant, his mother died, and his father was killed by Kerchak, leader of the ape tribe by whom Tarzan was adopted. Soon after his parents' death, Tarzan became a feral child, and his tribe of apes is known as the Mangani, great apes of a species unknown to science. Kala is his ape mother. Burroughs adde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. The Black Sea is supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper, and Don. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe. The Black Sea covers (not including the Sea of Azov), has a maximum depth of , and a volume of . Most of its coasts ascend rapidly. These rises are the Pontic Mountains to the south, bar the southwest-facing peninsulas, the Caucasus Mountains to the east, and the Crimean Mountains to the mid-north. In the west, the coast is generally small floodplains below foothills such as the Strandzha; Cape Emine, a dwindling of the east end of the Balkan Mountains; and the Dobruja Plateau considerably farth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant rocks, such as quartzite, given the right conditions. Subterranean drainage may limit surface water, with few to no rivers or lakes. However, in regions where the dissolved bedrock is covered (perhaps by debris) or confined by one or more superimposed non-soluble rock strata, distinctive karst features may occur only at subsurface levels and can be totally missing above ground. The study of ''paleokarst'' (buried karst in the stratigraphic column) is important in petroleum geology because as much as 50% of the world's hydrocarbon reserves are hosted in carbonate rock, and much of this is found in porous karst systems. Etymology The English word ''karst'' was borrowed from German in the late 19th century, which entered German much earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
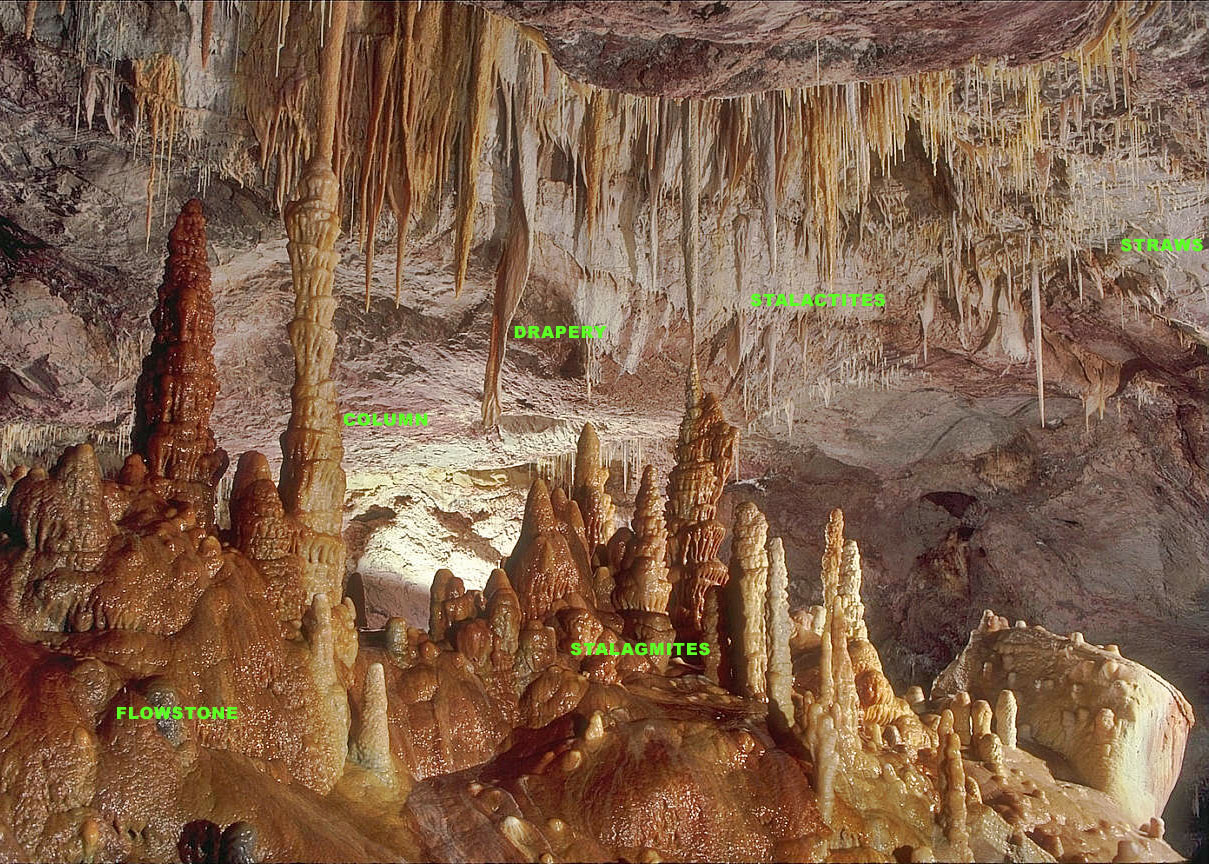
Stalactite
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via ''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension, or is capable of being melted, may form a stalactite. Stalactites may be composed of lava, minerals, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). A stalactite is not necessarily a speleothem, though speleothems are the most common form of stalactite because of the abundance of limestone caves. The corresponding formation on the floor of the cave is known as a stalagmite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground". Another example is that ''stalactites'' "hang on ''T''ight" and ''stalagmites'' "''M''ight grow up" � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalagmite
A stalagmite (, ; from the Greek , from , "dropping, trickling") is a type of rock formation that rises from the floor of a cave due to the accumulation of material deposited on the floor from ceiling drippings. Stalagmites are typically composed of calcium carbonate, but may consist of lava, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). The corresponding formation hanging down from the ceiling of a cave is a stalactite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground", another is that, as with ants in the pants, the mites go up and the tights (tites) come down. Formation and type Limestone stalagmites The most common stalagmites are speleothems, which usually form in limestone caves. Stalagmite formation occurs only under certain pH conditions within the cavern. They form through deposition of calcium carbonate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Abkhazia
Abkhazia ( ab, Аҧсны ''Apsny,'' ''Apkhazeti'' or ''Abkhazeti, '' ''Abkhazia'') is a ''de facto'' independent, partially recognised country lying on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, its southern border. It is bordered by Russia to the north, and Georgia to the east recognised by Russia, Nicaragua, Venezuela, and the ''de facto'' independent republics of South Ossetia and Transnistria, in which context it is referred to as the Republic of Abkhazia with Sukhumi as its capital. Religion The population (including all ethnic groups) of Abkhazia are majority Orthodox Christians and Sunni Muslims. Most of the ethnic Armenians living in Abkhazia belong to the Armenian Apostolic Church. However, most of the people who declare themselves Christian or Muslim do not attend religious services. There is also a very small number of Jews, Jehovah's Witnesses and the followers of new religions. The Jehovah's Witnesses organization has officially been banned since 1995, though the decree is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.jpg)