|
Abel's Uniform Convergence Test
In mathematics, Abel's test (also known as Abel's criterion) is a method of testing for the convergence of an infinite series. The test is named after mathematician Niels Henrik Abel. There are two slightly different versions of Abel's test – one is used with series of real numbers, and the other is used with power series in complex analysis. Abel's uniform convergence test is a criterion for the uniform convergence of a series of functions dependent on parameters. Abel's test in real analysis Suppose the following statements are true: # \sum a_n is a convergent series, # is a monotone sequence, and # is bounded. Then \sum a_nb_n is also convergent. It is important to understand that this test is mainly pertinent and useful in the context of non absolutely convergent series \sum a_n. For absolutely convergent series, this theorem, albeit true, is almost self evident. This theorem can be proved directly using summation by parts. Abel's test in complex analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius Of Convergence
In mathematics, the radius of convergence of a power series is the radius of the largest disk at the center of the series in which the series converges. It is either a non-negative real number or \infty. When it is positive, the power series converges absolutely and uniformly on compact sets inside the open disk of radius equal to the radius of convergence, and it is the Taylor series of the analytic function to which it converges. In case of multiple singularities of a function (singularities are those values of the argument for which the function is not defined), the radius of convergence is the shortest or minimum of all the respective distances (which are all non-negative numbers) calculated from the center of the disk of convergence to the respective singularities of the function. Definition For a power series ''f'' defined as: :f(z) = \sum_^\infty c_n (z-a)^n, where *''a'' is a complex constant, the center of the disk of convergence, *''c''''n'' is the ''n''-th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addison-Wesley
Addison-Wesley is an American publisher of textbooks and computer literature. It is an imprint of Pearson PLC, a global publishing and education company. In addition to publishing books, Addison-Wesley also distributes its technical titles through the O'Reilly Online Learning e-reference service. Addison-Wesley's majority of sales derive from the United States (55%) and Europe (22%). The Addison-Wesley Professional Imprint produces content including books, eBooks, and video for the professional IT worker including developers, programmers, managers, system administrators. Classic titles include ''The Art of Computer Programming'', ''The C++ Programming Language'', ''The Mythical Man-Month'', and ''Design Patterns''. History Lew Addison Cummings and Melbourne Wesley Cummings founded Addison-Wesley in 1942, with the first book published by Addison-Wesley being Massachusetts Institute of Technology professor Francis Weston Sears' ''Mechanics''. Its first computer book was ''Prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Function
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function such that a continuous variation (that is a change without jump) of the argument induces a continuous variation of the value of the function. This means that there are no abrupt changes in value, known as '' discontinuities''. More precisely, a function is continuous if arbitrarily small changes in its value can be assured by restricting to sufficiently small changes of its argument. A discontinuous function is a function that is . Up until the 19th century, mathematicians largely relied on intuitive notions of continuity, and considered only continuous functions. The epsilon–delta definition of a limit was introduced to formalize the definition of continuity. Continuity is one of the core concepts of calculus and mathematical analysis, where arguments and values of functions are real and complex numbers. The concept has been generalized to functions between metric spaces and between topological spaces. The latter are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniformly Bounded
In mathematics, a uniformly bounded family of functions is a family of bounded functions that can all be bounded by the same constant. This constant is larger than or equal to the absolute value of any value of any of the functions in the family. Definition Real line and complex plane Let :\mathcal F=\ be a family of functions indexed by I, where X is an arbitrary set and K is the set of real or complex numbers. We call \mathcal F uniformly bounded if there exists a real number M such that :, f_i(x), \le M \qquad \forall i \in I \quad \forall x \in X. Metric space In general let Y be a metric space with metric d, then the set :\mathcal F=\ is called uniformly bounded if there exists an element a from Y and a real number M such that :d(f_i(x), a) \leq M \qquad \forall i \in I \quad \forall x \in X. Examples * Every uniformly convergent sequence of bounded functions is uniformly bounded. * The family of functions f_n(x)=\sin nx defined for real x with n traveling thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
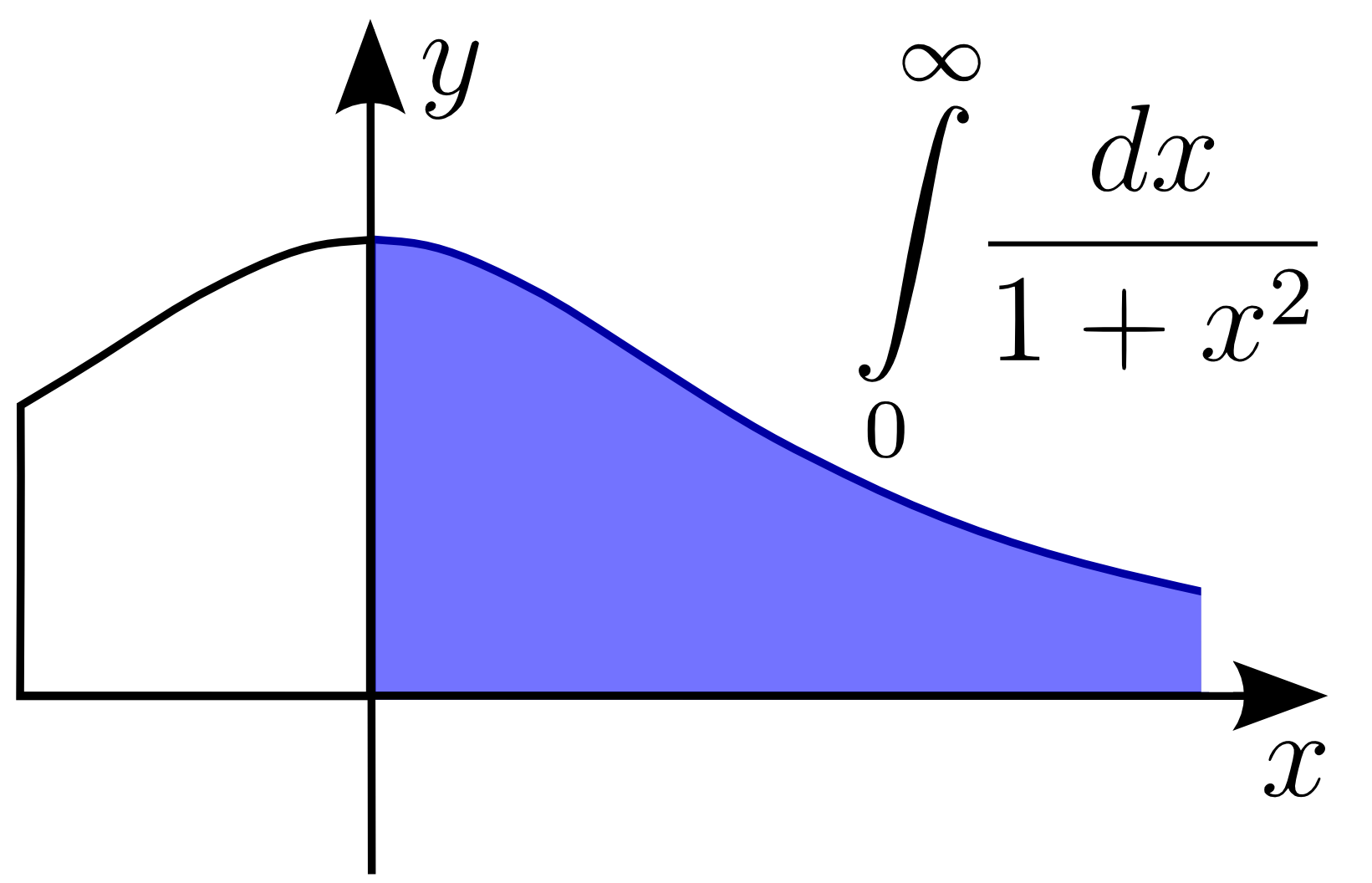
Improper Integral
In mathematical analysis, an improper integral is the limit of a definite integral as an endpoint of the interval(s) of integration approaches either a specified real number or positive or negative infinity; or in some instances as both endpoints approach limits. Such an integral is often written symbolically just like a standard definite integral, in some cases with ''infinity'' as a limit of integration. Specifically, an improper integral is a limit of the form: :\lim_ \int_a^bf(x)\, dx, \quad \lim_ \int_a^bf(x)\, dx or :\lim_ \int_a^cf(x)\ dx,\quad \lim_ \int_c^bf(x)\ dx in which one takes a limit in one or the other (or sometimes both) endpoints . By abuse of notation, improper integrals are often written symbolically just like standard definite integrals, perhaps with ''infinity'' among the limits of integration. When the definite integral exists (in the sense of either the Riemann integral or the more powerful Lebesgue integral), this ambiguity is resolved as both the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirichlet's Test
In mathematics, Dirichlet's test is a method of testing for the convergence of a series. It is named after its author Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet, and was published posthumously in the ''Journal de Mathématiques Pures et Appliquées'' in 1862. Statement The test states that if \ is a sequence of real numbers and \ a sequence of complex numbers satisfying * \ is monotonically decreasing heorem 1: Let an ≥ 0 be a decreasing sequence * * for every positive integer ''N'' where ''M'' is some constant, then the series converges. Proof Let and . From[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Series Test
In mathematical analysis, the alternating series test is the method used to show that an alternating series is convergent when its terms (1) decrease in absolute value, and (2) approach zero in the limit. The test was used by Gottfried Leibniz and is sometimes known as Leibniz's test, Leibniz's rule, or the Leibniz criterion. The test is only sufficient, not necessary, so some convergent alternating series may fail the first part of the test. Formal Statement Alternating series test A series of the form : \sum_^\infty (-1)^ a_n = a_0-a_1 + a_2 - a_3 + \cdots \! where either all ''a''''n'' are positive or all ''a''''n'' are negative, is called an alternating series. The alternating series test guarantees that an alternating series converges if the following two conditions are met: # , a_n, decreases monotonically, i.e., , a_, \leq, a_n, , and # \lim_ a_n = 0 Alternating series estimation theorem Moreover, let ''L'' denote the sum of the series, then the partial s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Circle
In mathematics, a unit circle is a circle of unit radius—that is, a radius of 1. Frequently, especially in trigonometry, the unit circle is the circle of radius 1 centered at the origin (0, 0) in the Cartesian coordinate system in the Euclidean plane. In topology, it is often denoted as because it is a one-dimensional unit -sphere. If is a point on the unit circle's circumference, then and are the lengths of the legs of a right triangle whose hypotenuse has length 1. Thus, by the Pythagorean theorem, and satisfy the equation x^2 + y^2 = 1. Since for all , and since the reflection of any point on the unit circle about the - or -axis is also on the unit circle, the above equation holds for all points on the unit circle, not only those in the first quadrant. The interior of the unit circle is called the open unit disk, while the interior of the unit circle combined with the unit circle itself is called the closed unit disk. One may also use other notions of "dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summation By Parts
In mathematics, summation by parts transforms the summation of products of sequences into other summations, often simplifying the computation or (especially) estimation of certain types of sums. It is also called Abel's lemma or Abel transformation, named after Niels Henrik Abel who introduced it in 1826. Statement Suppose \ and \ are two sequences. Then, :\sum_^n f_k(g_-g_k) = \left(f_g_ - f_m g_m\right) - \sum_^n g_(f_- f_). Using the forward difference operator \Delta, it can be stated more succinctly as :\sum_^n f_k\Delta g_k = \left(f_ g_ - f_m g_m\right) - \sum_^ g_\Delta f_k, Summation by parts is an analogue to integration by parts: :\int f\,dg = f g - \int g\,df, or to Abel's summation formula: :\sum_^n f(k)(g_-g_)= \left(f(n)g_ - f(m) g_m\right) - \int_^n g_ f'(t) dt. An alternative statement is :f_n g_n - f_m g_m = \sum_^ f_k\Delta g_k + \sum_^ g_k\Delta f_k + \sum_^ \Delta f_k \Delta g_k which is analogous to the integration by parts formula for semimartingal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Series
In mathematics, a series is the sum of the terms of an infinite sequence of numbers. More precisely, an infinite sequence (a_0, a_1, a_2, \ldots) defines a series that is denoted :S=a_0 +a_1+ a_2 + \cdots=\sum_^\infty a_k. The th partial sum is the sum of the first terms of the sequence; that is, :S_n = \sum_^n a_k. A series is convergent (or converges) if the sequence (S_1, S_2, S_3, \dots) of its partial sums tends to a limit; that means that, when adding one a_k after the other ''in the order given by the indices'', one gets partial sums that become closer and closer to a given number. More precisely, a series converges, if there exists a number \ell such that for every arbitrarily small positive number \varepsilon, there is a (sufficiently large) integer N such that for all n \ge N, :\left , S_n - \ell \right , 1 produce a convergent series: *: ++++++\cdots = . * Alternating the signs of reciprocals of powers of 2 also produces a convergent series: *: -+-+-+\cdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parameter
A parameter (), generally, is any characteristic that can help in defining or classifying a particular system (meaning an event, project, object, situation, etc.). That is, a parameter is an element of a system that is useful, or critical, when identifying the system, or when evaluating its performance, status, condition, etc. ''Parameter'' has more specific meanings within various disciplines, including mathematics, computer programming, engineering, statistics, logic, linguistics, and electronic musical composition. In addition to its technical uses, there are also extended uses, especially in non-scientific contexts, where it is used to mean defining characteristics or boundaries, as in the phrases 'test parameters' or 'game play parameters'. Modelization When a system is modeled by equations, the values that describe the system are called ''parameters''. For example, in mechanics, the masses, the dimensions and shapes (for solid bodies), the densities and the visco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |