|
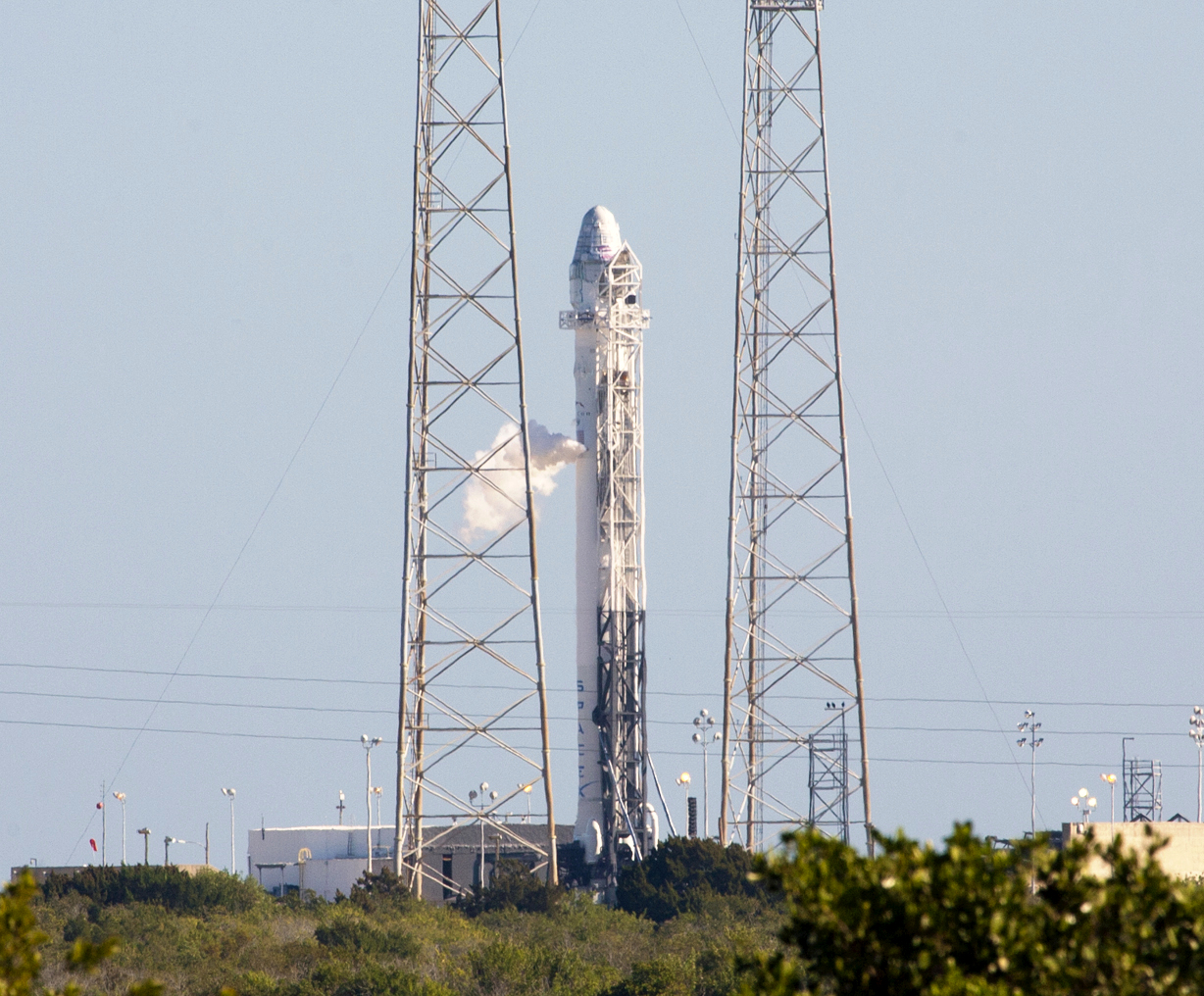
AMOS-6
AMOS-6 was an Israeli communications satellite, one of the Spacecom AMOS series, that was built by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), a defense and aerospace company. AMOS-6 was intended to be launched on flight 29 of a SpaceX Falcon 9 to geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) on 3 September 2016. On 1 September 2016, during the run-up to a static fire test, there was an anomaly on the launch pad, resulting in an explosion and the loss of the vehicle and AMOS-6. There were no injuries. Terminology AMOS stands for "Affordable Modular Optimized Satellite" and is also an allusion to the prophet Amos. This spacecraft is the second implementation of the AMOS-4000 satellite bus, the first was the AMOS-4. It is one of a AMOS series of satellites built by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI). History Spacecom, the AMOS satellites operator, announced in June 2012 that it had signed a US$195 million contract to build AMOS-6, the newest addition to the AMOS constellation, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecom
Spacecom, or Space Communication (), is an Israeli communications satellite operator in the Middle East, European Union and North America headquartered in the city of Ramat Gan, Israel. Spacecom operates two satellites at orbital position 4° West – AMOS-3 and AMOS-7, one satellite at orbital position 65° East – AMOS-4, and one satellite at orbital position 17° East – AMOS-5. History Spacecom was established in 1993 with a defined goal of marketing AMOS-1, a newly built communication satellite manufactured by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI). In 2003, Spacecom launched its second satellite, AMOS-2, owned entirely by the company. In 2008, the AMOS-3 satellite was launched to replace AMOS-1 and to increase coverage and traffic abilities. Until 2005, Spacecom was a private company controlled by four companies, including IAI and Eurocom Group. It went public on the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange in 2005. In August 2016, Spacecom shareholders agreed to sell the company fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMOS (satellite Bus)
The AMOS (Hebrew: ), an acronym for Affordable Modular Optimized Satellite, is a family of light weight satellite bus for geostationary orbit communications satellite designed and manufactured by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI) of Israel. Families Little is known regarding the different variations. But it is known of at least two built versions and a third in development. AMOS (original) The AMOS bus is a lightweight version used for satellites between , with 800 to 1700 watts of power. The satellite bus started with the AMOS-1, the smallest of all the family, and increased mass, payload successively in the AMOS-2 and AMOS-3. AMOS 4000 The AMOS 4000 platform is the second generation, a much bigger and sophisticated satellite bus. It is prepared for satellites weighing between and with power generation between 3 and 12 kW. It offers more autonomous capabilities and advanced control applications. It is composed of three modules: Bus, Repeater and Earth Facing Antenna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falcon 9 Full Thrust
Falcon 9 Full Thrust (also known as Falcon 9 v1.2, with variants Block 1 to Block 5) is a partially reusable medium-lift launch vehicle, designed and manufactured by SpaceX. Designed in 2014–2015, Falcon 9 Full Thrust began launch operations in December 2015. As of , Falcon 9 Full Thrust had performed launches without any failures. Based on the Lewis point estimate of reliability, this rocket is the most reliable orbital launch vehicle currently in operation. On April 8, 2016, the ''Full Thrust'' version of the Falcon 9 family was the first launch vehicle on an orbital trajectory to successfully vertically land a first stage. The landing followed a technology development program conducted from 2013 to 2015. Some of the required technology advances, such as landing legs, were pioneered on the Falcon 9 v1.1 version, but that version never landed intact. Starting in 2017, previously flown first-stage boosters were reused to launch new payloads into orbit. This quickly becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AsiaSat 8
AsiaSat 8 then AMOS-7 is a Hong Kong-turned- Israeli geostationary communications satellite which is operated by the Asia Satellite Telecommunications Company (Asiasat). Satellite description AsiaSat 8 was built by Space Systems/Loral, and is based on the LS-1300 satellite bus. The satellite carries twenty-four Ku-band transponders and one Ka-band payload, and was planned to be initially positioned above the equator, at a longitude of 105.5° East, providing coverage of southern and south-eastern Asia, China and the Middle East. Launch SpaceX was contracted to launch AsiaSat 8, using a Falcon 9 v1.1 launch vehicle. The launch took place from Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) on 5 August 2014 at 08:00 UTC. 4 Aug 2014, accessed 5 Aug 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of reducing space transportation costs to enable the colonization of Mars. The company manufactures the Falcon 9, Falcon Heavy, and Starship launch vehicles, several rocket engines, Cargo Dragon and Crew Dragon spacecraft, and Starlink communications satellites. SpaceX is developing a satellite internet constellation named Starlink to provide commercial internet service. In January 2020, the Starlink constellation became the largest satellite constellation ever launched, and as of December 2022 comprises over 3,300 small satellites in orbit. The company is also developing Starship, a privately funded, fully reusable, super heavy-lift launch system for interplanetary and orbital spaceflight. It is intended to become SpaceX's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMOS-4 (satellite)
AMOS-4 is an Israeli commercial communications satellite, operated by Spacecom Satellite Communications, Tel Aviv-based, part of the AMOS series of satellites. History Spacecom, the AMOS satellites operator, announced in 2007 that it has signed an agreement to build and launch AMOS-4, with Israel Aerospace Industries. IAI constructed the satellite for approximately US$365 million. Spacecom paid US$100 million for AMOS-4. The Israeli government paid Spacecom US$265 million generated from a pre-launch deal to supply it with services on AMOS-4 over the satellite's full 12 year life span. AMOS-4 was originally considered as a candidate for launch on a SpaceX Falcon-9 launch vehicle. The satellite was later assigned to a Zenit-3SLB launch vehicle and was finally launched in August 2013. Launch It lifted off on 31 August 2013, 20:05:00 UTC from Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan. The geostationary satellite provides direct-to-home television broadcasting, multimedia, broadban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel Aerospace Industries
Israel Aerospace Industries (Hebrew: התעשייה האווירית לישראל ''ha-ta'asiya ha-avirit le-yisra'el'') or IAI (תע"א) is Israel's major aerospace and aviation manufacturer, producing aerial and astronautic systems for both military and civilian usage. It has 15,000 employees as of 2018. IAI is completely state-owned by the government of Israel. IAI designs, develops, produces and maintains civil aircraft, drones, fighter aircraft, missile, avionics, and space-based systems. Although IAI's main focus is engineering, aviation and high-tech electronics, it also manufactures military systems for ground and naval forces. Many of these products are specially suited for the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) needs, while others are also marketed to foreign militaries. History Israel Aerospace Industries was founded in 1953 as Bedek Aviation Company under the initiative of Shimon Peres, then director general of the Ministry of Defense, in order to maintain Israel Defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 40
Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40), previously Launch Complex 40 (LC-40) is a launch pad for rockets located at the north end of Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. The launch pad was used by the United States Air Force for 55 Titan III and Titan IV launches between 1965 and 2005. The facility underwent multiple upgrades including the design and construction of towers with retractable and foldable platforms for vehicle assembly, instrumentation and monitoring. After 2007, the US Air Force leased the complex to SpaceX to launch the Falcon 9 rocket. As of August 2022, there have been 93 launches of the Falcon 9 from the complex. The site was heavily damaged following the September 2016 Falcon 9 flight 29 incident, due to a catastrophic failure during a static fire test. The complex was repaired and returned to operational status in December 2017 for the CRS-13 mission. Launch history Rocket launches Titan The first launch from SLC-40 (initially nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Fire
Launch vehicle system tests assess the readiness of a launch system to safely reach orbit. Launch vehicles undergo system tests before they launch. A wet dress rehearsal (WDR) and a more extensive static fire tests a fully assembled launch vehicle and its associated ground support equipment (GSE) prior to launch. The spacecraft/payload may or may not be attached to the launch vehicle during the WDR or static fire, but sufficient elements of the rocket and all relevant ground support equipment are in place to help verify that the rocket is ready for flight. Propellant load tests and static fire tests may also be done on prototype rocket stages as well, in which case no fully assembled launch vehicle is involved. Wet dress rehearsal A wet dress rehearsal is called "wet" because the liquid propellant components (such as liquid oxygen, liquid hydrogen, etc.) are loaded into the rocket during the test. In a pure wet dress rehearsal the rocket engines are not ignited. Wet dress rehear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
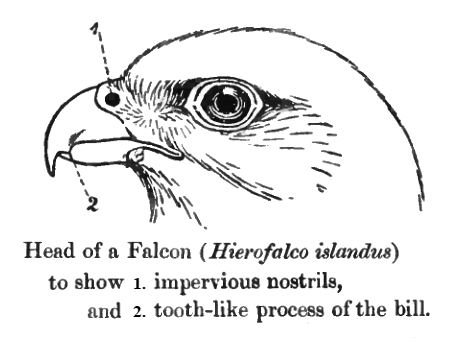
Falcon 9 Flight 29
Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene. Adult falcons have thin, tapered wings, which enable them to fly at high speed and change direction rapidly. Fledgling falcons, in their first year of flying, have longer flight feathers, which make their configuration more like that of a general-purpose bird such as a broad wing. This makes flying easier while learning the exceptional skills required to be effective hunters as adults. The falcons are the largest genus in the Falconinae subfamily of Falconidae, which itself also includes another subfamily comprising caracaras and a few other species. All these birds kill with their beaks, using a tomial "tooth" on the side of their beaks—unlike the hawks, eagles, and other birds of prey in the Accipitridae, which use their feet. The largest falcon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The high frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |