|
Automaticity
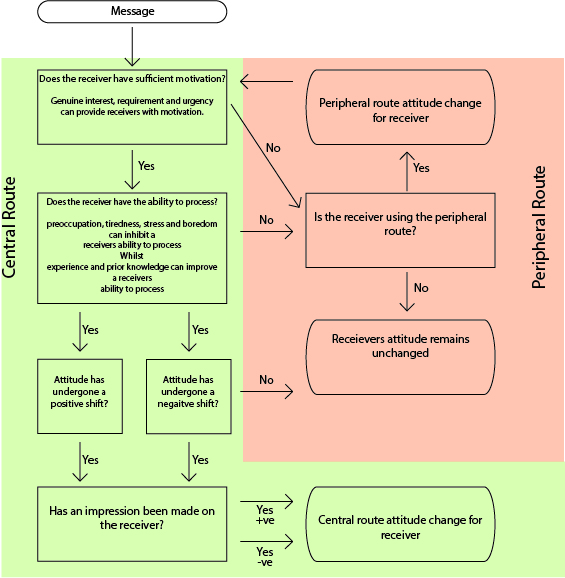
In the field of psychology, automaticity is the ability to do things without occupying the mind with the low-level details required, allowing it to become an automatic response pattern or habit. It is usually the result of learning, repetition, and practice. Examples of tasks carried out by ' muscle memory' often involve some degree of automaticity. Examples of automaticity are common activities such as walking, speaking, bicycle-riding, assembly-line work, and driving a car (the last of these sometimes being termed " highway hypnosis"). After an activity is sufficiently practiced, it is possible to focus the mind on other activities or thoughts while undertaking an automatized activity (for example, holding a conversation or planning a speech while driving a car). Characteristics John Bargh (1994), based on over a decade of research, suggested that four characteristics usually accompany automatic behavior: ;Awareness :A person may be unaware of the mental process that is oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bargh
John A. Bargh (; born 1955) is a social psychologist currently working at Yale University, where he has formed the Automaticity in Cognition, Motivation, and Evaluation (ACME) Laboratory. Bargh's work focuses on automaticity and unconscious processing as a method to better understand social behavior, as well as philosophical topics such as free will. Much of Bargh's work investigates whether behaviors thought to be under volitional control may result from automatic interpretations of and reactions to external stimuli, such as words. Bargh is particularly famous for his research on priming and its effects on behavior. In one of his most well-known studies, Bargh and colleagues reported that participants who were exposed to words related to the elderly stereotype (e.g., "Florida", "Bingo") subsequently walked more slowly when exiting the laboratory, compared to participants who were exposed to neutral words.J. A. Bargh, M. Chen and L. Burrows. (1996). Automaticity of social behavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habit (psychology)
A habit (or wont, as a humorous and formal term) is a routine of behavior that is repeated regularly and tends to occur subconsciously. A 1903 paper in the '' American Journal of Psychology'' defined a "habit, from the standpoint of psychology, sa more or less fixed way of thinking, willing, or feeling acquired through previous repetition of a mental experience." Habitual behavior often goes unnoticed by persons exhibiting it, because a person does not need to engage in self-analysis when undertaking routine tasks. Habits are sometimes compulsory. A 2002 daily experience study by habit researcher Wendy Wood and her colleagues found that approximately 43% of daily behaviors are performed out of habit. New behaviours can become automatic through the process of habit formation. Old habits are hard to break and new habits are hard to form because the behavioural patterns that humans repeat become imprinted in neural pathways, but it is possible to form new habits through repetit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feelings, and motivation, motives. Psychology is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the Natural science, natural and social sciences. Biological psychologists seek an understanding of the Emergence, emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as Behavioural sciences, behavioral or Cognitive science, cognitive scientists. Some psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Psychology
Social psychology is the methodical study of how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others. Although studying many of the same substantive topics as its counterpart in the field of sociology, psychological social psychology places more emphasis on the individual, rather than society; the influence of social structure and culture on individual outcomes, such as personality, behavior, and one's position in social hierarchies. Social psychologists typically explain human behavior as a result of the relationship between mental states and social situations, studying the social conditions under which thoughts, feelings, and behaviors occur, and how these variables influence social interactions. History 19th century In the 19th century, social psychology began to emerge from the larger field of psychology. At the time, many psychologists were concerned with developing concrete explanations for the different aspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotype
In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalization, generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example, an expectation about the group's personality, preferences, appearance or ability. Stereotypes make information processing easier by allowing the perceiver to rely on previously stored knowledge in place of incoming information. Stereotypes are often faulty generalization, faulty, inaccurate, and Belief perseverance, resistant to new information. Although stereotypes generally have negative implications, they aren't necessarily negative. They may be positive, neutral, or negative. They can be broken down into two categories: explicit stereotypes, which are conscious, and implicit stereotypes, which are subconscious. Explicit stereotypes An explicit stereotype is a belief about a group that a person is consciously aware of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centipede's Dilemma
"The Centipede's Dilemma" is a short poem that has lent its name to a psychological effect called the centipede effect or centipede syndrome. The centipede effect occurs when a normally automatic or unconscious activity is disrupted by consciousness of it or reflection on it. For example, a golfer thinking too closely about their swing or someone thinking too much about how they knot their tie may find their performance of the task impaired. The effect is also known as hyperreflection or Humphrey's law after English psychologist George Humphrey (1889–1966), who propounded it in 1923. As he wrote of the poem, "This is a most psychological rhyme. It contains a profound truth which is illustrated daily in the lives of all of us". The effect is the reverse of a ''solvitur ambulando''. Poem The short poem is usually attributed to Katherine Craster (1841–1874) in ''Pinafore Poems'', 1871. By 1881, it had begun appearing in journals such as ''The Spectator'' and '' Littell's Living Ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highway Hypnosis
Highway hypnosis, also known as white line fever, is an altered mental state in which an automobile driver can drive lengthy distances and respond adequately to external events with no recollection of consciously having done so. It appears that in this state, the driver's conscious attention is fully focused elsewhere, yet their brain is still able to process a significant amount of information related to the road and vehicle control on a subconscious level. Highway hypnosis is a manifestation of the common process of automaticity, meaning actions are performed without awareness. In some cases, the trance state in a driver can be so deep that auditory and visual distortions occur. History The idea of a hypnotic trance while driving was first described in a 1921 article that mentioned the phenomenon of "road hypnotism": driving in a trance-like state while gazing at a fixed point. A 1929 study, ''Sleeping with the Eyes Open'' by Walter Miles, also addressed the subject, suggest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attention
Attention or focus, is the concentration of awareness on some phenomenon to the exclusion of other stimuli. It is the selective concentration on discrete information, either subjectively or objectively. William James (1890) wrote that "Attention is the taking possession by the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously possible objects or trains of thought. Focalization, concentration, of consciousness are of its essence." Attention has also been described as the allocation of limited cognitive processing resources. Attention is manifested by an attentional bottleneck, in terms of the amount of data the brain can process each second; for example, in human vision, less than 1% of the visual input data stream of 1MByte/sec can enter the bottleneck, leading to inattentional blindness. Attention remains a crucial area of investigation within education, psychology, neuroscience, cognitive neuroscience, and neuropsychology. Areas of activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerox
Xerox Holdings Corporation (, ) is an American corporation that sells print and electronic document, digital document products and services in more than 160 countries. Xerox was the pioneer of the photocopier market, beginning with the introduction of the Xerox 914 in 1959, so much so that the word ''xerox'' is commonly used as a synonym for ''photocopy''. Xerox is headquartered in Norwalk, Connecticut, though it is incorporated in New York (state), New York with its largest group of employees based around Rochester, New York, the area in which the company was founded. As a large developed company, it is consistently placed in the list of Fortune 500 companies. The company purchased Affiliated Computer Services for $6.4 billion in early 2010. On December 31, 2016, Xerox separated its business process service operations, essentially those operations acquired with the purchase of Affiliated Computer Services, into a new publicly traded company, Conduent. Xerox focuses on its docu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habituation
Habituation is a form of non-associative learning in which an organism’s non-reinforced response to an inconsequential stimulus decreases after repeated or prolonged presentations of that stimulus. For example, organisms may habituate to repeated sudden loud noises when they learn that these have no consequences. Habituation can occur in responses that habituate include those that involve an entire organism or specific biological component systems of an organism. The broad ubiquity of habituation across all forms of life has led to it being called "the simplest, most universal form of learning...as fundamental a characteristic of life as DNA." Functionally, habituation is thought to free up cognitive resources for other stimuli that are associated with biologically important events by diminishing the response to inconsequential stimuli. A progressive decline of a behavior in a habituation procedure may also reflect nonspecific effects such as fatigue, which must be ruled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |