|
Attribute-oriented Programming
Attribute-oriented programming (@OP) is a technique for embedding metadata, namely attributes, within program code. Attribute-oriented programming in various languages Java With the inclusion of Metadata Facility for Java (JSR-175) into the J2SE 5.0 release it is possible to utilize attribute-oriented programming right out of the box. XDoclet library makes it possible to use attribute-oriented programming approach in earlier versions of Java. C# The C# language has supported attributes from its very first release. These attributes was used to give run-time information and are not used by a preprocessor. Currently with source generators, you can use attributes to drive generation of additional code at compile-time. UML The Unified Modeling Language (UML) supports a kind of attribute called stereotypes In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalization, generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attribute (computing)
In computing, an attribute is a specification that defines a property of an object, element, or file. It may also refer to or set the specific value for a given instance of such. For clarity, attributes should more correctly be considered metadata. An attribute is frequently and generally a property of a property. However, in actual usage, the term attribute can and is often treated as equivalent to a property depending on the technology being discussed. An attribute of an object usually consists of a name and a value. For an element these can be a type and class name, while for a file these can be a name and an extension, respectively. Rules and typing * Rules: Each named attribute has an associated set of rules called operations: For example, one doesn't sum characters or manipulate and process an integer array the same way as an image object. Neither does one process text as if it was type of floating point ( decimal numbers). * Data types: It follows that an object d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metadata Facility For Java
The Metadata Facility for Java is a specification for Java that defines an API for annotating fields, methods, and classes as having particular attributes that indicate they should be processed in specific ways by development tools, deployment tools, or run-time libraries. The specification was developed under the Java Community Process as JSR 175, and was released as a part of J2SE 5.0 (Tiger). External links JSR 175''A Metadata Facility for the Java Programming Language'' JSR 250'' Common Annotations'' (defines common Java SE and Java EE annotations) JSR 269''Pluggable Annotation Processing API'' (defines a pluggable interface for developing build-time annotation processors) Java Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ... Java specification requests {{prog- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java Platform, Standard Edition
Java Platform, Standard Edition (Java SE) is a computing platform for development and deployment of porting, portable code for desktop computer, desktop and server (computing), server environments. Java SE was formerly known as Java 2 Platform, Standard Edition (J2SE). The platform uses the Java (programming language), Java programming language and is part of the Java (software platform), Java software-platform family. Java SE defines a range of general-purpose APIs—such as List of Java APIs, Java APIs for the Java Class Library—and also includes the Java Language Specification and the Java Virtual Machine Specification. OpenJDK is the official reference implementation since version 7. Nomenclature, standards and specifications The platform was known as ''Java 2 Platform, Standard Edition'' or ''J2SE'' from version 1.2, until the name was changed to ''Java Platform, Standard Edition'' or ''Java SE'' in version 1.5. The "SE" is used to distinguish the base platform from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XDoclet
XDoclet is an open-source code generation library that enables Attribute-oriented programming for Java via insertion of special Javadoc tags. It comes with a library of predefined tags, which simplify coding for various technologies: Java EE, Web services, Portlet Portlets are Pluggable look and feel, pluggable user interface software components that are managed and displayed in a web portal. A portlet responds to requests from a web client with and generates dynamic content. A portlet is managed by a portle ... etc. Example A typical XDoclet comment might look like this: /**** * This is the Account entity bean. It is an example of how to use the * EJBDoclet tags. * * @see Customer * * @ejb.bean * name="bank/Account" * type="CMP" * jndi-name="ejb/bank/Account" * local-jndi-name="ejb/bank/LocalAccount" * primkey-field="id" * schema = "Customers" * * @ejb.finder * signature="java.util.Collection findAll()" * uncheck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
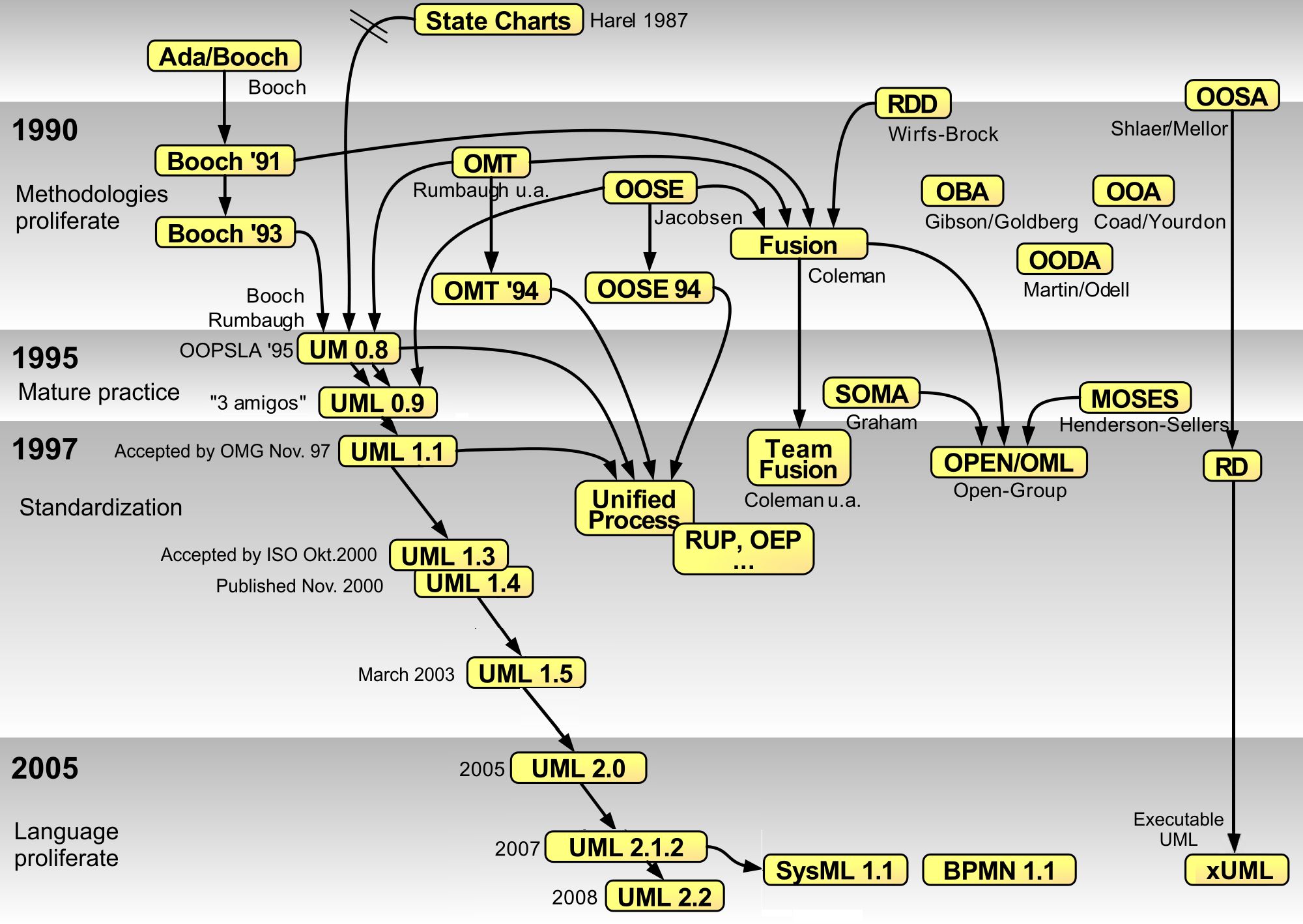
Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system. UML provides a standard notation for many types of diagrams which can be roughly divided into three main groups: behavior diagrams, interaction diagrams, and structure diagrams. The creation of UML was originally motivated by the desire to standardize the disparate notational systems and approaches to software design. It was developed at Rational Software in 1994–1995, with further development led by them through 1996. In 1997, UML was adopted as a standard by the Object Management Group (OMG) and has been managed by this organization ever since. In 2005, UML was also published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as the ISO/IEC 19501 standard. Since then the standard has been periodically revised to cover the latest revision of UML. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotype (UML)
A stereotype is one of three types of extensibility, extensibility mechanisms in the Unified Modeling Language (UML), the other two being tags and constraints. They allow designers to extend the vocabulary of UML in order to create new model elements, derived from existing ones, but that have specific properties that are suitable for a particular domain or otherwise specialized usage. The nomenclature is derived from the original meaning of Stereotype (printing), stereotype, used in printing. For example, when modeling a network, one might need to have symbols for representing routers and hubs. By using stereotyped nodes, these can be made to appear as primitive building blocks. Graphically, a stereotype is rendered as a name enclosed by guillemets (« » or, if guillemets proper are unavailable, ) and placed above the name of another element. In addition, or alternatively, it may be indicated by a specific icon. The icon image may even replace the entire UML symbol. For instance, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hack (programming Language)
Hack is a programming language for the HipHop Virtual Machine (HHVM), created by Meta Platforms, Meta (formerly Facebook) as a dialect of PHP. The language implementation is free and open-source software, licensed under an MIT License. Hack allows use of both dynamic typing and static typing. This kind of a type system is called gradual typing, which is also implemented in other programming languages such as ActionScript. Hack's type system allows types to be specified for function (programming), function argument (computer programming), arguments, function return values, and class properties; however, types of local variables are always inferred and cannot be specified. History Hack was introduced on March 20, 2014. Before the announcement of the new language, Facebook had already implemented the code and tested it on a large part of its web site. Features Hack is designed to interoperate seamlessly with PHP, which is a widely used open-source scripting language that has a fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |