|
Atomism
Atomism () is a natural philosophy proposing that the physical universe is composed of fundamental indivisible components known as atoms. References to the concept of atomism and its Atom, atoms appeared in both Ancient Greek philosophy, ancient Greek and Ancient Indian philosophy, ancient Indian philosophical traditions. Leucippus is the earliest figure whose commitment to atomism is well attested and he is usually credited with inventing atomism. He and other ancient Greek atomists theorized that nature consists of two fundamental Principle (philosophy), principles: ''atom'' and Void (philosophy), ''void''. Clusters of different shapes, arrangements, and positions give rise to the various macroscopic Substance (philosophy), substances in the world.Berryman, Sylvia, "Ancient Atomism", ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.)online/ref> Indian Buddhists, such as Dharmakirti ( 6th or 7th century) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Leucippus
Leucippus (; , ''Leúkippos''; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. He is traditionally credited as the founder of atomism, which he developed with his student Democritus. Leucippus divided the world into two entities: atoms, indivisible particles that make up all things, and the void, the nothingness that exists between the atoms. He developed his philosophy as a response to the Eleatics, who believed that all things are one and the void does not exist. Leucippus's ideas were influential in ancient and Renaissance philosophy. Leucippus was the first Western philosopher to develop the concept of atoms, but his ideas only bear a superficial resemblance to modern atomic theory. Leucippus's atoms come in infinitely many forms and exist in constant motion, creating a deterministic world in which everything is caused by the collisions of atoms. Leucippus described the beginning of the cosmos as a vortex of atoms that formed the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and other celest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mechanism (philosophy)
Mechanism is the belief that natural wholes (principally living things) are similar to complicated machines or artifacts, composed of parts lacking any intrinsic relationship to each other. The doctrine of mechanism in philosophy comes in two different varieties. They are both doctrines of metaphysics, but they are different in scope and ambitions: the first is a global doctrine about nature; the second is a local doctrine about humans and their minds, which is hotly contested. For clarity, we might distinguish these two doctrines as universal mechanism and anthropic mechanism. Mechanical philosophy Mechanical philosophy is a form of natural philosophy which compares the universe to a large-scale mechanism (i.e. a machine). Mechanical philosophy is associated with the Scientific Revolution of early modern Europe. One of the first expositions of universal mechanism is found in the opening passages of '' Leviathan'' by Thomas Hobbes, published in 1651. Some intellectual historia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Democritus
Democritus (, ; , ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, Thrace, Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomism, atomic theory of the universe. Democritus wrote extensively on a wide variety of topics. None of Democritus' original work has survived, except through second-hand references. Many of these references come from Aristotle, who viewed him as an important rival in the field of natural philosophy. He was known in antiquity as the ‘laughing philosopher’ because of his emphasis on the value of cheerfulness. Life Although many anecdotes about Democritus' life survive, their authenticity cannot be verified and modern scholars doubt their accuracy. According to Aristotle, Democritus was born in Abdera, on the coast of Thrace. He was a polymath and prolific writer, producing nearly eighty treatises on subjects such as poetry, harmon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ancient Greek Philosophy
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BC. Philosophy was used to make sense of the world using reason. It dealt with a wide variety of subjects, including astronomy, epistemology, mathematics, political philosophy, ethics, metaphysics, ontology, logic, biology, rhetoric and aesthetics. Greek philosophy continued throughout the Hellenistic period and later evolved into Roman philosophy. Greek philosophy has influenced much of Western culture since its inception, and can be found in many aspects of public education. Alfred North Whitehead once claimed: "The safest general characterization of the European philosophical tradition is that it consists of a series of footnotes to Plato". Clear, unbroken lines of influence lead from ancient Greek and Hellenistic philosophers to Roman philosophy, early Islamic philosophy, medieval scholasticism, the European Renaissance and the Age of Enlightenment. Greek philosophy was influenced to some extent by the older wisdom litera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dharmakirti
Dharmakīrti (fl. ;), was an influential Indian Buddhist philosopher who worked at Nālandā.Tom Tillemans (2011)Dharmakirti Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy He was one of the key scholars of epistemology ( pramāṇa) in Buddhist philosophy, and is associated with the Yogācāra and Sautrāntika schools. He was also one of the primary theorists of Buddhist atomism. His works influenced the scholars of Mīmāṃsā, Nyaya and Shaivism schools of Hindu philosophy as well as scholars of Jainism. Dharmakīrti's '' Pramāṇavārttika'', his largest and most important work, was very influential in India and Tibet as a central text on pramana ('valid knowledge instruments') and was widely commented on by various Indian and Tibetan scholars. His texts remain part of studies in the monasteries of Tibetan Buddhism. History Little is known for certain about the life of Dharmakirti. As per John Taber, the only reliable information that we have about his life was that he was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Eleatics
The Eleatics were a group of pre-Socratic philosophers and school of thought in the 5th century BC centered around the ancient Greek colony of Elea (), located around 80 miles south-east of Naples in southern Italy, then known as Magna Graecia. The primary philosophers who are associated with the Eleatic doctrines are Parmenides, Zeno of Elea, and Melissus of Samos, although other Italian philosophers such as Xenophanes of Colophon and Empedocles have also sometimes been classified as members of this movement. The Eleatics have traditionally been seen as advocating a strict metaphysical view of monism in response to the materialist monism advocated by their predecessors, the Ionian school. History Patricia Curd states that the chronology of pre-Socratic philosophers is one of the most contentious issues of pre-Socratic philosophy. Many of the historical details mentioned by Plato, Diogenes Laertius, or Apollodorus are generally considered by modern scholarship to be of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Natural Philosophy
Natural philosophy or philosophy of nature (from Latin ''philosophia naturalis'') is the philosophical study of physics, that is, nature and the physical universe, while ignoring any supernatural influence. It was dominant before the development of modern science. From the ancient world (at least since Aristotle) until the 19th century, ''natural philosophy'' was the common term for the study of physics (nature), a broad term that included botany, zoology, anthropology, and chemistry as well as what is now called physics. It was in the 19th century that the concept of science received its modern shape, with different subjects within science emerging, such as astronomy, biology, and physics. Institutions and communities devoted to science were founded. Isaac Newton's book '' Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica'' (1687) (English: ''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'') reflects the use of the term ''natural philosophy'' in the 17th century. Even in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kalapa (atomism)
Kalapa or rupa-kalapa (from Sanskrit '' rūpa'' "form, phenomenon" and ''kalāpa'' "bundle") is a term in Theravada Buddhist phenomenology for the smallest units of physical matter, said to be about 1/46,656th the size of a particle of dust from a wheel of chariot. Kalapas are not mentioned in the earliest Buddhists texts, such as the Tripitaka, but only in the Abhidhammattha-sangaha, an Abhidhamma commentary dated to the 11th or 12th century, and as such not part of common Theravada doctrine. According to the description found in the Abhidhammattha-sangaha, Kalapas are said to be invisible under normal circumstances but visible as a result of meditative samadhi. Kalapas are composed of eight inseparable elements of material essence in varying amounts which are: Pathavi (earth), Apo (water), Tejo (fire), Vayo ( air), Vanna (color), Gandha ( smell), Rasa (taste), and Oja (nutrition). The first four elements are called primary qualities, and are predominant in kalapas. The othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
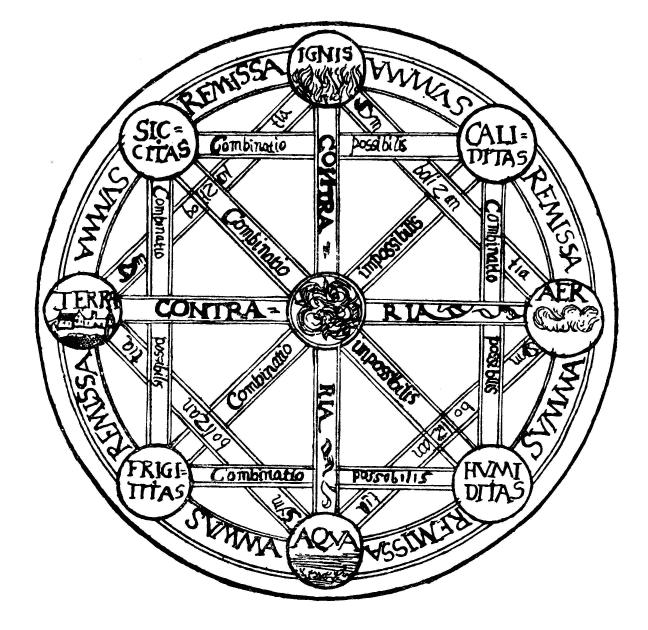
Classical Elements
The classical elements typically refer to earth, water, air, fire, and (later) aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler substances. Ancient cultures in Greece, Angola, Tibet, India, and Mali had similar lists which sometimes referred, in local languages, to "air" as "wind", and to "aether" as "space". These different cultures and even individual philosophers had widely varying explanations concerning their attributes and how they related to observable phenomena as well as cosmology. Sometimes these theories overlapped with mythology and were personified in deities. Some of these interpretations included atomism (the idea of very small, indivisible portions of matter), but other interpretations considered the elements to be divisible into infinitely small pieces without changing their nature. While the classification of the material world in ancient India, Hellenistic Egypt, and ancient Greece into air, earth, fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chemical Matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic particles. In everyday as well as scientific usage, ''matter'' generally includes atoms and anything made up of them, and any particles (or combination of particles) that act as if they have both rest mass and volume. However it does not include massless particles such as photons, or other energy phenomena or waves such as light or heat. Matter exists in various states (also known as phases). These include classical everyday phases such as solid, liquid, and gas – for example water exists as ice, liquid water, and gaseous steam – but other states are possible, including plasma, Bose–Einstein condensates, fermionic condensates, and quark–gluon plasma. Usually atoms can be imagined as a nucleus of protons and neutrons, and a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Void (philosophy)
The concept of "The Void" in philosophy encompasses the ideas of nothingness and emptiness, a notion that has been interpreted and debated across various schools of metaphysics. In ancient Greek philosophy, the Void was discussed by thinkers like Democritus, who saw it as a necessary space for atoms to move, thereby enabling the existence of matter. Contrasting this, Aristotle famously denied the existence of a true Void, arguing that nature inherently avoids a vacuum. In Eastern philosophical traditions, the Void takes on significant spiritual and metaphysical meanings. In Buddhism, ''Śūnyatā'' refers to the emptiness inherent in all things, a fundamental concept in understanding the nature of reality. In Taoism, the Void is represented by '' Wuji'', the undifferentiated state from which all existence emerges, embodying both the potential for creation and the absence of form. Throughout the history of Western thought, the Void has also been explored in the context of existen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ancient Indian Philosophy
This page lists some links to ancient philosophy, namely philosophical thought extending as far as early post-classical history (). Overview Genuine philosophical thought, depending upon original individual insights, arose in many cultures roughly contemporaneously. Karl Jaspers termed the intense period of philosophical development beginning around the 7th century BCE and concluding around the 3rd century BCE an Axial Age in human thought. In Western philosophy, the spread of Christianity in the Roman Empire marked the ending of Hellenistic philosophy and ushered in the beginnings of medieval philosophy, whereas in the Middle East, the spread of Islam through the Arab Empire marked the end of Old Iranian philosophy and ushered in the beginnings of early Islamic philosophy. Ancient Greek and Roman philosophy Philosophers Pre-Socratic philosophers * Milesian School :Thales (624 – c 546 BCE) :Anaximander (610 – 546 BCE) : Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 585 – c. 525 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |