|
Associative Sequence Learning
{{Use dmy dates, date=September 2015 Associative sequence learning (ASL) is a neuroscientific theory that attempts to explain how mirror neurons are able to match observed and performed actions, and how individuals (adults, children, animals) are able to imitate body movements. The theory was proposed by Cecilia Heyes in 2000. (For reviews see). A conceptually similar model proposed by Christian Keysers and David Perrett, based on what we know about the neural properties of mirror neurons and spike-timing-dependent plasticity is the Hebbian learning account of mirror neurons.Keysers, C., & Perrett, D.I. (2004). Demystifying social cognition: a Hebbian perspective. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8, 501–507 Its central principle is that associations between sensory and motor representations are acquired ontogenetically (i.e. acquired during development), as a result of correlated sensorimotor experience. Consider the example of an actor clenching their fist. In this situation t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the biological sciences. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches used to study the nervous system at different scales. The techniques used by neuroscientists have expanded enormously, from molecular and cellular studies of individual neurons to imaging of sensory, motor and cognitive tasks in the brain. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Classical Conditioning
Classical conditioning (also respondent conditioning and Pavlovian conditioning) is a behavioral procedure in which a biologically potent Stimulus (physiology), stimulus (e.g. food, a puff of air on the eye, a potential rival) is paired with a neutral stimulus (e.g. the sound of a Triangle (musical instrument), musical triangle). The term ''classical conditioning'' refers to the process of an automatic, conditioned response that is paired with a specific stimulus. It is essentially equivalent to a signal. The Russian physiology, physiologist Ivan Pavlov studied classical conditioning with detailed experiments with dogs, and published the experimental results in 1897. In the study of digestion, Pavlov observed that the experimental dogs salivated when fed red meat. Pavlovian conditioning is distinct from operant conditioning (instrumental conditioning), through which the strength of a voluntary behavior is modified, either by reinforcement or by Punishment (psychology), punishment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Mirror Neuron
A mirror neuron is a neuron that fires both when an animal acts and when the animal observes the same action performed by another. Thus, the neuron "mirrors" the behavior of the other, as though the observer were itself acting. Mirror neurons are not always physiologically distinct from other types of neurons in the brain; their main differentiating factor is their response patterns. By this definition, such neurons have been directly observed in humans and other primates, as well as in birds. In humans, brain activity consistent with that of mirror neurons has been found in the premotor cortex, the supplementary motor area, the primary somatosensory cortex, and the inferior parietal cortex. The function of the mirror system in humans is a subject of much speculation. Birds have been shown to have imitative resonance behaviors and neurological evidence suggests the presence of some form of mirroring system. To date, no widely accepted neural or computational models have been pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Functional Imaging
Functional imaging (or physiological imaging) is a medical imaging technique of detecting or measuring changes in metabolism, blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. As opposed to structural imaging, functional imaging centers on revealing physiological activities within a certain tissue or organ by employing medical image modalities that very often use tracers or probes to reflect spatial distribution of them within the body. These tracers are often analogous to some chemical compounds, like glucose, within the body. To achieve this, isotopes are used because they have similar chemical and biological characteristics. By appropriate proportionality, the nuclear medicine physicians can determine the real intensity of certain substances within the body to evaluate the risk or danger of developing some diseases. Modalities * Positron emission tomography (PET) ** Fludeoxyglucose for Glucose metabolism ** O-15 as a flow tracer * Single-photon emission comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive neurostimulation technique in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current in a targeted area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. A device called a stimulator generates electric pulses that are delivered to a magnetic coil placed against the scalp. The resulting magnetic field penetrates the skull and induces a secondary electric current in the underlying brain tissue, modulating neural activity. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is a safe, effective, and FDA-approved treatment for major depressive disorder (approved in 2008), chronic pain (2013), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (2018). It has strong evidence for certain neurological and psychiatric conditions—especially depression (with a large effect size), neuropathic pain, and stroke recovery—and emerging advancements like iTBS and image-guided targeting may improve its efficacy and efficiency. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Superior Temporal Sulcus
The superior temporal sulcus (STS) is the sulcus separating the superior temporal gyrus from the middle temporal gyrus, in the temporal lobe of the mammalian brain. A sulcus (plural sulci) is a deep groove that curves into the largest part of the brain, the cerebrum, and a gyrus (plural gyri) is a ridge that curves outward of the cerebrum. The STS is located under the lateral fissure, which is the fissure that separates the temporal lobe, parietal lobe, and frontal lobe. The STS has an asymmetric structure between the left and right hemisphere, with the STS being longer in the left hemisphere, but deeper in the right hemisphere. This asymmetrical structural organization between hemispheres has only been found to occur in the STS of the human brain. The STS has been shown to produce strong responses when subjects perceive stimuli in research areas that include theory of mind, biological motion, faces, voices, and language. Language processing Spoken language processing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the neuroanatomy, structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Increasingly it is also being used for quantitative research studies of brain disease and psychiatric illness. Neuroimaging is highly multidisciplinary involving neuroscience, computer science, psychology and statistics, and is not a medical specialty. Neuroimaging is sometimes confused with neuroradiology. Neuroradiology is a medical specialty that uses non-statistical brain imaging in a clinical setting, practiced by radiologists who are medical practitioners. Neuroradiology primarily focuses on recognizing brain lesions, such as vascular diseases, strokes, tumors, and inflammatory diseases. In contrast to neuroimaging, neuroradiology is qualitative (based on subjective impressions and extensive clinical training) but sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
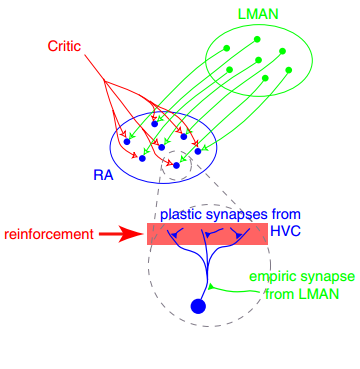 |
Synaptic Plasticity
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to Chemical synapse#Synaptic strength, strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memory, memories are postulated to be represented by vastly interconnected neural circuits in the brain, synaptic plasticity is one of the important neurochemical foundations of learning and memory (''see Hebbian theory''). Plastic change often results from the alteration of the number of neurotransmitter receptors located on a synapse. There are several underlying mechanisms that cooperate to achieve synaptic plasticity, including changes in the quantity of neurotransmitters released into a synapse and changes in how effectively cells respond to those neurotransmitters. Synaptic plasticity in both Excitatory synapse, excitatory and Inhibitory synapse, inhibitory synapses has been found to be dependent upon postsynaptic calcium release. Historical discoveries In 1973, Terje Lømo and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Serve (tennis)
A serve (or, more formally, a service) in tennis is a shot to start a point. A player will hit the ball with a racquet so it will fall into the diagonally opposite service box without being stopped by the net. Normally players begin a serve by tossing the ball into the air and hitting it (usually near the highest point of the toss). The ball can only touch the net on a return and will be considered good if it falls on the opposite side. If the ball contacts the net on the serve but then proceeds to the proper service box, it is called a ''let''; this is not a legal serve in the major tours (but see below) although it is also not a ''fault''. Players normally serve overhead; however serving underhand is allowed. The serve is the only shot a player can take their time to set up instead of having to react to an opponent's shot; however, as of 2012, there is a 25-second limit to be allowed between points. The serve is one of the most difficult shots for a novice, but once mastered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Mirror Neuron
A mirror neuron is a neuron that fires both when an animal acts and when the animal observes the same action performed by another. Thus, the neuron "mirrors" the behavior of the other, as though the observer were itself acting. Mirror neurons are not always physiologically distinct from other types of neurons in the brain; their main differentiating factor is their response patterns. By this definition, such neurons have been directly observed in humans and other primates, as well as in birds. In humans, brain activity consistent with that of mirror neurons has been found in the premotor cortex, the supplementary motor area, the primary somatosensory cortex, and the inferior parietal cortex. The function of the mirror system in humans is a subject of much speculation. Birds have been shown to have imitative resonance behaviors and neurological evidence suggests the presence of some form of mirroring system. To date, no widely accepted neural or computational models have been pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Facial Expression
Facial expression is the motion and positioning of the muscles beneath the skin of the face. These movements convey the emotional state of an individual to observers and are a form of nonverbal communication. They are a primary means of conveying social information between humans, but they also occur in most other mammals and some other animal species. Humans can adopt a facial expression voluntarily or involuntarily, and the neural mechanisms responsible for controlling the expression differ in each case. Voluntary facial expressions are often socially conditioned and follow a cortical route in the brain. Conversely, involuntary facial expressions are believed to be innate and follow a subcortical route in the brain. Facial recognition can be an emotional experience for the brain and the amygdala is highly involved in the recognition process. Beyond the accessory nature of facial expressions in spoken communication between people, they play a significant role in communication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Theory Of Cognitive Development
Piaget's theory of cognitive development, or his genetic epistemology, is a comprehensive theory about the nature and development of human intelligence. It was originated by the Swiss developmental psychologist Jean Piaget (1896–1980). The theory deals with the nature of knowledge itself and how humans gradually come to acquire, construct, and use it. Piaget's theory is mainly known as a developmental stage theory. In 1919, while working at the Alfred Binet Laboratory School in Paris, Piaget "was intrigued by the fact that children of different ages made different kinds of mistakes while solving problems". His experience and observations at the Alfred Binet Laboratory were the beginnings of his theory of cognitive development. He believed that children of different ages made different mistakes because of the "quality rather than quantity" of their intelligence. Piaget proposed four stages to describe the development process of children: sensorimotor stage, pre-operational s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |