|
Asemonea Clara
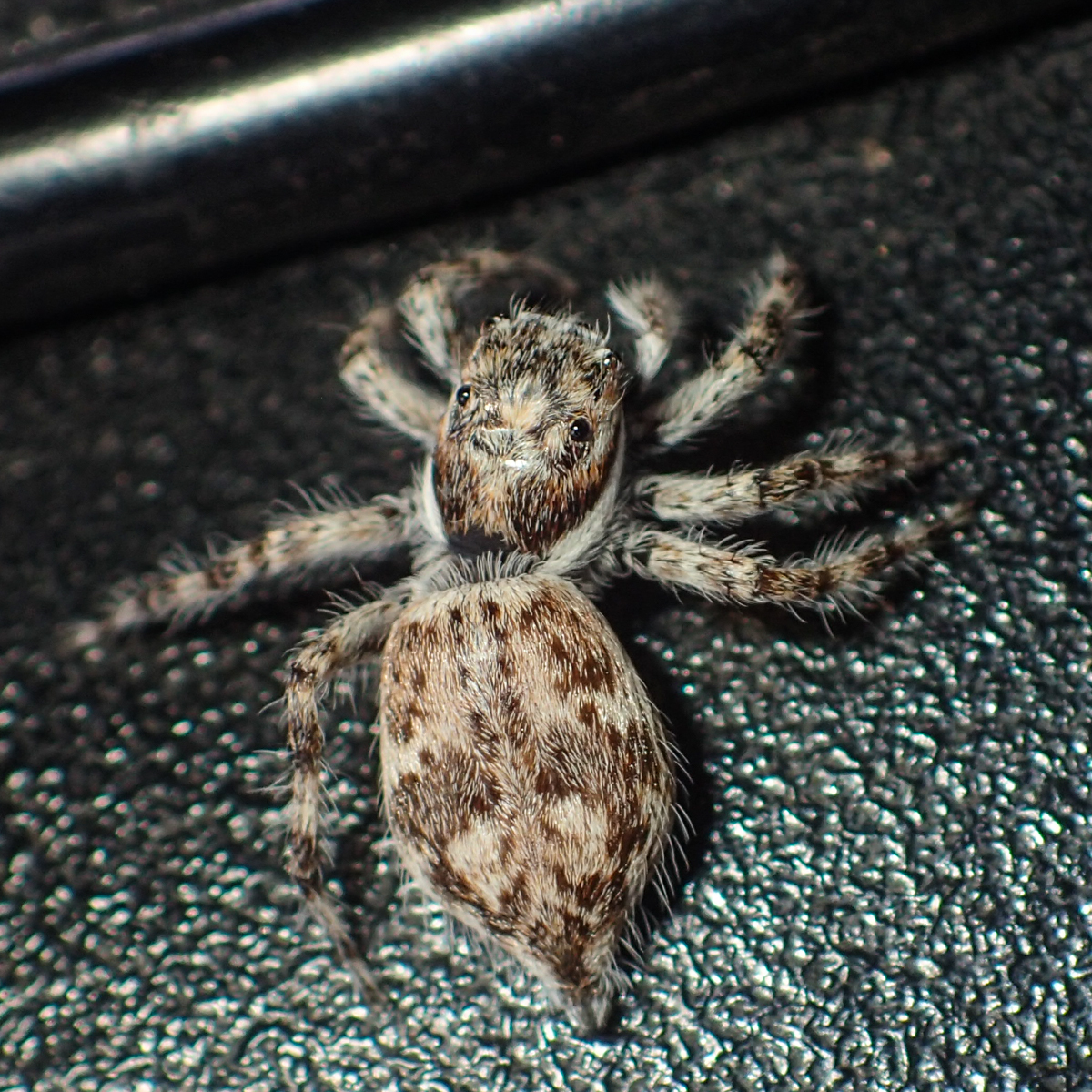
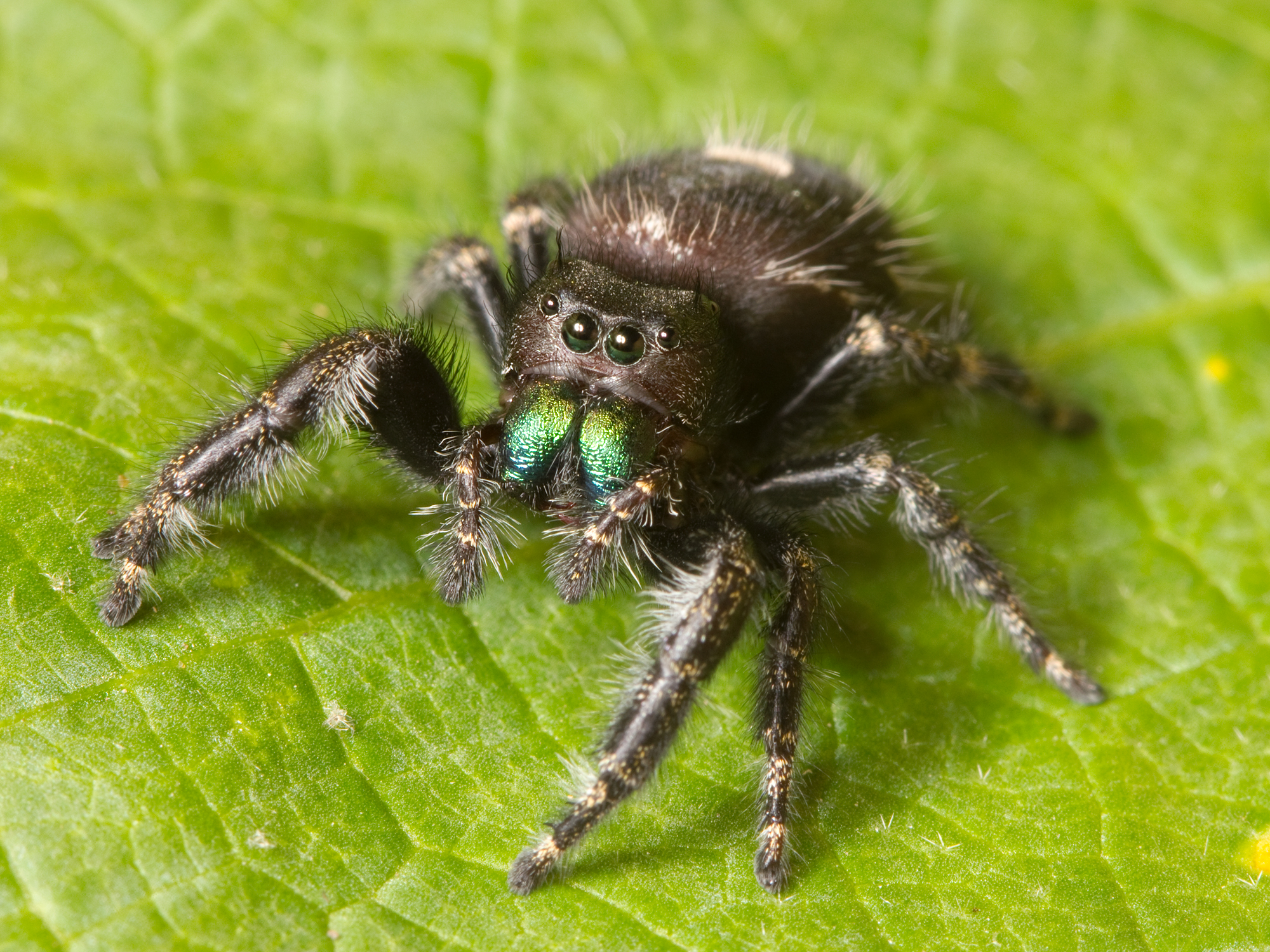
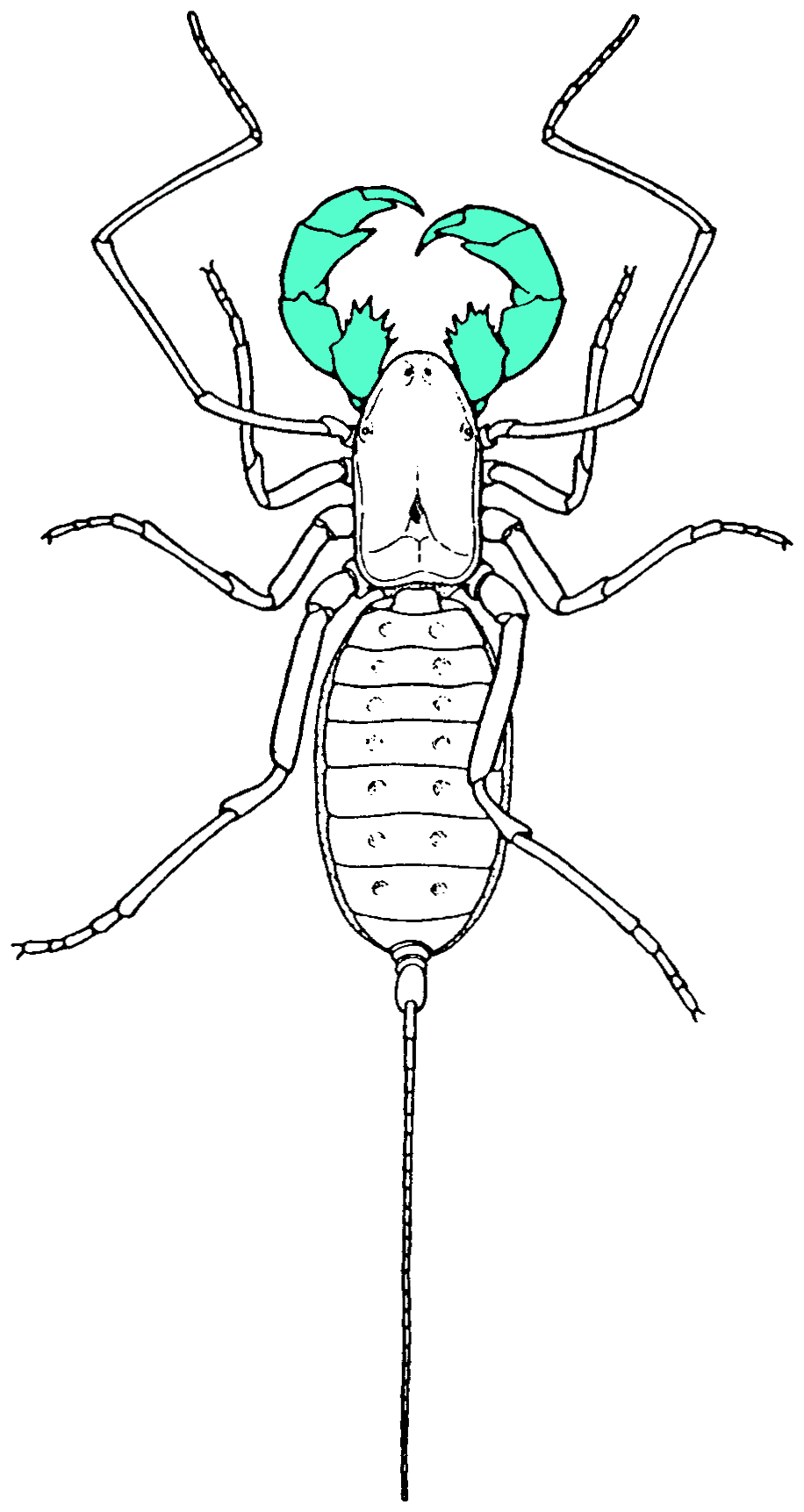
''Asemonea clara'', the Oribi Gorge Asemonea Jumping Spider, is a species of jumping spider that lives in Mozambique and South Africa. It can be found in forests near the coast and in lowland areas. A member of the genus '' Asemonea'', the spider is small, with a cephalothorax that is between long and an abdomen that is between long, the male being smaller than the female. It has distinctive colouration, with the female being generally lime-green and the male black. The female has a white carapace that is pear-shaped, an abdomen that is white apart from two dark lines across the front, a small round dot in the middle and a black dot towards the back, and long thin white legs. The male is darker, apart from a creamy patch on its carapace, although some specimen have a grey abdomen that has black dots. Wanda Wesołowska and Charles Haddad first described the female in 2013, the male not being described until eleven years later in 2024. Taxonomy and etymology The Oribi Gorge Asem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wanda Wesołowska
Wanda Wesołowska (born 11 August 1950) is a Polish zoologist known for her work with jumping spiders. She has described more species of jumping spider than any contemporary writer, and is second only to Eugène Simon in the history of arachnology. Originally a student of ornithology, she developed an interest in jumping spiders while still a student at the Siedlce University of Natural Sciences and Humanities in the 1970s. Wesołowska published her first work in 1981, which included the description of nine new species of spiders, the first in what would be a prolific career. She moved to the University of Wrocław to continue her studies, and completed her doctoral thesis that described 44 new species of the genus ''Heliophanus''. She joined the faculty of the University of Wrocław in 1985, received a habilitation in 2000, and remained a Academic tenure, tenured professor at the university until her retirement in 2020. Her research has focused on the description, taxonomy and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayne Maddison
Wayne Paul Maddison (born 1958) is a Canadian evolutionary biologist, arachnologist, and biological illustrator. He is Canada Research Chair in Biodiversity and a professor at the departments of zoology and botany at the University of British Columbia, and the Director of the Spencer Entomological Collection at the Beaty Biodiversity Museum. Education and career Maddison was born in London, Ontario and his interests in studying spiders started while he was a teenager exploring Lake Ontario. Maddison studied zoology at the University of Toronto, where he obtained his BSc in 1980. He went on to study at Harvard University in the Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, where he obtained his PhD in 1988 under the supervision of Herbert W. Levi. He was a NSERC postdoctoral fellow at the University of California, Berkeley from 1988 to 1990, where he worked with Montgomery Slatkin. Maddison became an assistant professor and later associate professor at the University o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cymbium (spider Anatomy)
The two palpal bulbs – also known as palpal organs and genital bulbs – are the copulatory organs of a male spider. They are borne on the last segment of the pedipalps (the front "limbs" of a spider), giving the spider an appearance often described as like wearing boxing gloves. The palpal bulb does not actually produce sperm, being used only to transfer it to the female. Palpal bulbs are only fully developed in adult male spiders and are not completely visible until after the final moult. In the majority of species of spider, the bulbs have complex shapes and are important in identification. Structure The palpal bulb of a mature male spider is borne on the last segment of the pedipalp. This segment usually has touch-sensitive hairs (setae) with nerves leading to them. The bulb itself is entirely without nerves, and hence without sensory organs and muscles, since these depend on nerves for their functioning, although some spiders have one or two muscles external to the bulb and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the secondary pair of forward appendages among Chelicerata, chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles. From the proximal end (where they are attached to the body) to the distal, they are: the coxa, the Arthropod leg#Trochanter, trochanter, the Arthropod leg#Femur, femur, the short Glossary_of_spider_terms#patella, patella, the Glossary_of_spider_terms#tibia, tibia, and the Arthropod_leg#Tarsus, tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called Glossary_of_spider_terms#maxilla , maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior arthropod leg, legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clypeus (arthropod Anatomy)
The clypeus is one of the sclerites that make up the face of an arthropod. In insects, the clypeus delimits the lower margin of the face, with the labrum articulated along the ventral margin of the clypeus. The mandibles bracket the labrum, but do not touch the clypeus. The dorsal margin of the clypeus is below the antennal sockets. The clypeus is often well-defined by sulci ("grooves") along its lateral and dorsal margins, and is most commonly rectangular or trapezoidal in overall shape. The post-clypeus is a large nose-like structure that lies between the eyes and makes up much of the front of the head in cicadas. In spider Spiders (order (biology), order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight limbs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude spider silk, silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and ran ...s, the clypeus is generally the area between the anterior edge of the carapace and the anterior eyes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerotization
Sclerotization is a biochemical process that produces the rigid shell of sclerotin that comprises an insect's chitinous exoskeleton. It is prominent in the thicker, armored parts of insects and arachnid Arachnids are arthropods in the Class (biology), class Arachnida () of the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, opiliones, harvestmen, Solifugae, camel spiders, Amblypygi, wh ...s, especially in the biting mouthparts and sclerites of scorpions and beetles. Molecular mechanism Sclerotization entails crosslinking of oxygen-reactive derivatives of dopamine. The reaction of the dopamine derivatives toward oxygen is catalyzed by diverse enzymes such as laccase, which convert the catechol groups to quinones. The resulting quinones are susceptible to nucleophilic attack by amines and thiols, which decorate the side-chains of proteins. These reactions gives rise to color (typically brown), loss of solubili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigyne
The epigyne or epigynum is the external genital structure of female spiders. As the epigyne varies greatly in form in different species, even in closely related ones, it often provides the most distinctive characteristic for recognizing species. It consists of a small, hardened portion of the exoskeleton located on the underside of the abdomen, in front of the epigastric furrow and between the epigastric plates. Functions The primary function of the epigyne is to receive and direct the palpal organ of the male during copulation. The various specific forms of epigynes are correlated, in each case, with corresponding specific differences in the palpus of the male. This specialization prevents individuals of different species from mating. The epigyne covers or accompanies the openings of the spermathecae, which are pouches for receiving and retaining sperm. Frequently, the openings of the spermathecae are on the outer face of the epigyne and can be easily seen. A secondary funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spider Anatomy
The anatomy of spiders includes many characteristics shared with other arachnids. These characteristics include bodies divided into two tagmata (sections or segments), eight jointed legs, no wings or antennae, the presence of chelicerae and pedipalps, simple eyes, and an exoskeleton, which is periodically shed. Spiders also have several adaptations that distinguish them from other arachnids. All spiders are capable of producing silk of various types, which many species use to build webs to ensnare prey. Most spiders possess venom, which is injected into prey (or defensively, when the spider feels threatened) through the fangs of the chelicerae. Male spiders have specialized pedipalps that are used to transfer sperm to the female during mating. Many species of spiders exhibit a great deal of sexual dimorphism. External anatomy Spiders, unlike insects, have only two main body parts ( tagmata) instead of three: a fused head and thorax (called a cephalothorax or prosoma) and an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinneret
A spinneret is a silk-spinning organ of a spider or the larva of an insect. Some adult insects also have spinnerets, such as those borne on the forelegs of Embioptera. Spinnerets are usually on the underside of a spider's opisthosoma, and are typically segmented. While most spiders have six spinnerets, some have two, four, or eight. They can move both independently and in concert. Most spinnerets are not simple structures with a single orifice producing a single thread, but complex structures of many microscopic spigots, each producing one filament. This produces the necessary orientation of the protein molecules, without which the silk would be weak and useless. Spigots can be singular or found in groups, which also permits spiders to combine multiple filaments in different ways to produce many kinds of silk for various purposes. Spinneret morphology can help arachnologists identify the taxon of a specimen and the specific morphology of a spigot can determine its use as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelicerae
The chelicerae () are the arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts of the subphylum Chelicerata, an arthropod group that includes arachnids, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. Commonly referred to as "jaws", chelicerae may be shaped as either articulated fangs, or as a type of pincer_(biology), pincers. Some chelicerae, such as those found on nearly all spiders, are hollow and contain (or are connected to) venom glands, used to inject venom into prey or a perceived threat. Both pseudoscorpions and Opiliones , harvestmen have additional structures on their chelicerae that are used for grooming (papillae in pseudoscorpions, cheliceral teeth in Opiliones). In ''Paratrechalea'', males and females have shown to have a chelicerae dimorphism, because the chelicerae is used as a mating signal for females. Types Chelicerae can be divided into three kinds: jackknife chelicerae, scissor chelicerae, and three-segmented wikt:chelate, chelate chelicerae. Jackknife chelicerae The jackknife chelicer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternum (arthropod Anatomy)
The sternum (: sterna) is the ventral portion of a segment of an arthropod thorax or abdomen. In insects, the sterna are usually single, large sclerites, and external. However, they can sometimes be divided in two or more, in which case the subunits are called sternites, and may also be modified on the terminal abdominal segments so as to form part of the functional genitalia, in which case they are frequently reduced in size and development, and may become internalized and/or membranous. For a detailed explanation of the terminology, see Kinorhynchs have tergal and sternal plates too, though seemingly not homologous with those of arthropods.Sørensen, M. V. et al. Phylogeny of Kinorhyncha based on morphology and two molecular loci. PLoS One 10, 1–33 (2015). Ventrites are externally visible sternites. Usually the first sternite is covered up, so that ventrite numbers do not correspond to sternite numbers. The term is also used in other arthropod groups such as crustaceans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spider Vision
The eyes of spiders vary significantly in their structure, arrangement, and function. They usually have eight, each being a simple eye with a single lens (optics), lens rather than multiple units as in the compound eyes of insects. The specific arrangement and structure of the eyes is one of the features used in the identification and classification of different species, genera, and families. Most Haplogynae, haplogynes have six eyes, although some have eight (Plectreuridae), four (e.g., ''Tetrablemma'') or even two (most Caponiidae). In some cave species, there are no eyes at all (e.g. ''Stalita taenaria''). Sometimes one pair of eyes is better developed than the rest. Several families of hunting spiders, such as jumping spiders and wolf spiders, have fair to excellent vision. The main pair of eyes in jumping spiders even sees in colour. Structure and anatomy Spiders' eyes are Simple eye in invertebrates, simple eyes, or ''ocelli'' (singular ''ocellus''), meaning their eyes have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |