|
Artificial Bone
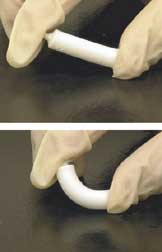
Artificial bone refers to bone-like material created in a laboratory that can be used in bone grafts, to replace human bone that was lost due to severe fractures, disease, etc. Bone fracture, which is a complete or partial break in the bone, is a very common condition that has more than three million US cases per year. Human bones have the ability to regenerate themselves by cycle of bone resorption and bone formation. The cell responsible for bone resorption is osteoclast, while the cell responsible for bone formation is osteoblast. That being said, the human body can regenerate fractured bone. However, if damage to bone is caused by a disease or severe injury, it becomes difficult for the body to repair itself. When the human body is unable to regenerate the lost bone tissue, surgeons come in and replace the missing bone using autografts, allografts, and synthetic grafts (artificial bone). When comparing artificial bone to autograft and allograft, it is less invasive and more bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preparation Of Chitin And Chitosan From Marine Crustaceans
Preparation may refer to: * Preparation (dental), the method by which a tooth is prepared when removing decay and designing a form that will provide adequate retention for a dental restoration * Preparation (music), treatment of dissonance in tonal music * Preparation, Iowa, a ghost town * Preparation time, time to prepare speeches in policy debate * ''The Preparation'', a 2017 South Korean film * ''Preparations'' (album), a 2007 album by Prefuse 73 * Prepared dosage form * Prepared drug * Prepared food * Prepared supplement * Special modifications to instruments, see **Prepared piano **Prepared guitar *Fossil preparation See also * Preparation H, popular hemorrhoids medicine * Preparation for the Gospel, early Christian book * * Prep (other) * Preparationism * Prepare (other) Prepare or ''variation'', may refer to: * PREPARE (Preparedness Against (Re-)emerging Epidemics) of the European Union (EU) * CONTEST#Prepare, Prepare strategy, part of the CONTEST an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricalcium Phosphate
Tricalcium phosphate (sometimes abbreviated TCP), more commonly known as Calcium phosphate, is a calcium salt of phosphoric acid with the chemical formula Ca3(PO4)2. It is also known as tribasic calcium phosphate and bone phosphate of lime (BPL). It is a white solid of low solubility. Most commercial samples of "tricalcium phosphate" are in fact hydroxyapatite. It exists as three crystalline polymorphs α, α′, and β. The α and α′ states are stable at high temperatures. Nomenclature ''Calcium phosphate'' refers to numerous materials consisting of calcium ions (Ca2+) together with orthophosphates (), metaphosphates or pyrophosphates () and occasionally oxide and hydroxide ions. Especially, the common mineral apatite has formula Ca5(PO4)3''X'', where ''X'' is F, Cl, OH, or a mixture; it is hydroxyapatite if the extra ion is mainly hydroxide. Much of the "tricalcium phosphate" on the market is actually powdered hydroxyapatite. Preparation Tricalcium phosphate is produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a triple helix of elongated fibril known as a collagen helix. It is mostly found in cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments, and skin. Vitamin C is vital for collagen synthesis. Depending on the degree of biomineralization, mineralization, collagen tissues may be rigid (bone) or compliant (tendon) or have a gradient from rigid to compliant (cartilage). Collagen is also abundant in corneas, blood vessels, the Gut (anatomy), gut, intervertebral discs, and the dentin in teeth. In muscle tissue, it serves as a major component of the endomysium. Collagen constitutes 1% to 2% of muscle tissue and 6% by weight of skeletal muscle. The fibroblast is the most common cell creating collagen in animals. Gelatin, which is used in food and industry, is collagen t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teratoma
A teratoma is a neoplasia, tumor made up of several types of biological tissue, tissue, such as hair, muscle, Human tooth, teeth, or bone. Teratomata typically form in the tailbone (where it is known as a sacrococcygeal teratoma), ovary, or testicle. Symptoms Symptoms may be minimal if the tumor is small. A testicular teratoma may present as a painless lump. Complications may include ovarian torsion, testicular torsion, or hydrops fetalis. They are a type of germ cell tumor (a tumor that begins in the cells that give rise to sperm or egg cell, eggs). They are divided into two types: mature and immature. Mature teratomas include dermoid cysts and are generally benign tumor, benign. Immature teratomas may be cancerous. Most ovarian teratomas are mature. In adults, testicular teratomas are generally cancerous. Definitive diagnosis is based on a tissue biopsy. Treatment of coccyx, testicular, and ovarian teratomas is generally by surgery. Testicular and immature ovarian terato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps. Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary science and is concerned with local detail in general, including not only relief, but also natural, artificial, and cultural features such as roads, land boundaries, and buildings. In the United States, topography often means specifically relief, even though the USGS topographic maps record not just elevation contours, but also roads, populated places, structures, land boundaries, and so on. Topography in a narrow sense involves the recording of relief or terrain, the three-dimensional quality of the surface, and the identification of specific landforms; this is also known as geomorphometry. In modern usage, this involves generation of elevation data in digital form ( DEM). It is often considered to include the graphic representation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodegradability
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradation occurs under a specific set of circumstances. The process of biodegradation is threefold: first an object undergoes biodeterioration, which is the mechanical weakening of its structure; then follows biofragmentation, which is the breakdown of materials by microorganisms; and finally assimilation, which is the incorporation of the old material into new cells. In practice, almost all chemical compounds and materials are subject to biodegradation, the key element being time. Things like vegetables may degrade within days, while glass and some plastics take many millennia to decompose. A standard for biodegradability used by the European Union is that greater than 90% of the original material must be converted into , water and minerals b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallinity
Crystallinity refers to the degree of structural order in a solid. In a crystal, the atoms or molecules are arranged in a regular, periodic manner. The degree of crystallinity has a large influence on hardness, density, transparency and diffusion. In an ideal gas, the relative positions of the atoms or molecules are completely random. Amorphous materials, such as liquids and glasses, represent an intermediate case, having order over short distances (a few atomic or molecular spacings) but not over longer distances. Many materials, such as glass-ceramics and some polymers, can be prepared in such a way as to produce a mixture of crystalline and amorphous regions. In such cases, crystallinity is usually specified as a percentage of the volume of the material that is crystalline. Even within materials that are completely crystalline, however, the degree of structural perfection can vary. For instance, most metallic alloys are crystalline, but they usually comprise many independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sintering
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, plastics, and other materials. The atoms/molecules in the sintered material diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing the particles together and creating a solid piece. Since the sintering temperature does not have to reach the melting point of the material, sintering is often chosen as the shaping process for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten and molybdenum. The study of sintering in metallurgy, metallurgical powder-related processes is known as powder metallurgy. An example of sintering can be observed when ice cubes in a glass of water adhere to each other, which is driven by the temperature difference between the water and the ice. Examples of pressure-driven sintering are the compacting of snowfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycaprolactone
Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a synthetic, semi-crystalline, biodegradable polyester with a melting point of about 60 °C and a glass transition temperature of about −60 °C. The most common use of polycaprolactone is in the production of speciality polyurethanes. Polycaprolactones impart good resistance to water, oil, solvent and chlorine to the polyurethane produced. This polymer is often used as an additive for resins to improve their processing characteristics and their end use properties (e.g., toughness, impact resistance). Being compatible with a range of other materials, PCL can be mixed with starch to lower its cost and increase biodegradation, biodegradability or it can be added as a polymeric plasticizer to polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Polycaprolactone is also used for splinting, modeling, and as a feedstock for prototyping systems such as fused filament fabrication 3D printers. Synthesis PCL is prepared by Ring-opening polymerization, ring opening polymerizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Chloride
Calcium chloride is an inorganic compound, a Salt (chemistry), salt with the chemical formula . It is a white crystalline solid at room temperature, and it is highly soluble in water. It can be created by neutralising hydrochloric acid with calcium hydroxide. Calcium chloride is commonly encountered as a Water of crystallization, hydrated solid with generic formula , where ''n'' = 0, 1, 2, 4, and 6. These compounds are mainly used for de-icing and dust control. Because the anhydrous salt is Hygroscopic, hygroscopic and deliquescent, it is used as a desiccant.Robert Kemp, Suzanne E. Keegan "Calcium Chloride" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2000, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. History Calcium chloride was apparently discovered in the 15th century but wasn't studied properly until the 18th century. It was historically called "fixed Salammoniac, sal ammoniac" () because it was synthesized during the distillation of ammonium chloride with lime and was nonvolatile (while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diammonium Phosphate
Diammonium phosphate (DAP; IUPAC name diammonium hydrogen phosphate; chemical formula (NH4)2(HPO4)) is one of a series of water- soluble ammonium phosphate salts that can be produced when ammonia reacts with phosphoric acid. Solid diammonium phosphate shows a dissociation pressure of ammonia as given by the following expression and equation: : At 100 °C, the dissociation pressure of diammonium phosphate is approximately 5 mmHg. According to the diammonium phosphate MSDS from CF Industries, Inc., decomposition starts as low as 70 °C: "Hazardous Decomposition Products: Gradually loses ammonia when exposed to air at room temperature. Decomposes to ammonia and monoammonium phosphate at around 70 °C (158 °F). At 155 °C (311 °F), DAP emits phosphorus oxides, nitrogen oxides and ammonia." Uses DAP is used as a fertilizer. When applied as plant fertilizer, it temporarily increases the soil pH, but over a long term the treated ground becomes more acidic than before, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |