|
Arboriculture
Arboriculture (, from ) is the cultivation, management, and study of individual trees, shrubs, vines, and other perennial woody plants. The science of arboriculture studies how these plants grow and respond to cultural practices and to their environment. The practice of arboriculture includes cultural techniques such as selection, planting, training, fertilizer, fertilization, pest and pathogen control, pruning, Tree shaping, shaping, and felling, removal. Overview A person who practices or studies arboriculture can be termed an ''arborist'' or an ''arboriculturist''. A ''tree surgeon'' is more typically someone who is trained in the physical maintenance and manipulation of trees and therefore more a part of the arboriculture process rather than an arborist. Risk management, legal issues, and aesthetic considerations have come to play prominent roles in the practice of arboriculture. Businesses often need to hire arboriculturists to complete "tree hazard surveys" and generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arborist
An arborist, or (less commonly) arboriculturist, is a professional in the practice of arboriculture, which is the Plant cultivation, cultivation, management, and study of individual trees, shrubs, vines, and other perennial woody plants in dendrology and horticulture. Arborists generally focus on the health and safety of individual plants and trees, rather than managing forests or harvesting wood (silviculture or forestry). An arborist's scope of work is therefore distinct from that of either a forester or a lumberjack, logger. Scope of work In order for arborists to work near power wires, either additional training is required or they need to be certified as a Qualified Line Clearance Arborist or Utility Arborist (there may be different terminology for various countries). There is a variety of minimum distances that must be kept from power wires depending on voltage, however the common distance for low voltage lines in urban settings is 10 feet (about 3 metres). Arborists w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Chartered Foresters
The Institute of Chartered Foresters (ICF) is the professional body for foresters and arboriculturists in the United Kingdom. Its royal charter A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but ... was granted in 1982. The Institute grants chartered status to individuals following an examination process that includes a period of management or supervisory experience resulting in them being promoted to professional membership. Chartered members are recognised by the designations 'Chartered Arboriculturist' or 'Chartered Forester' and by the postnominals letters MICFor (Member of the Institute of Chartered Foresters). Fellows of the institute bear the postnominals FICFor (Fellow of the Institute of Chartered Foresters) in addition to their designation. Members of the Institute of Chart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
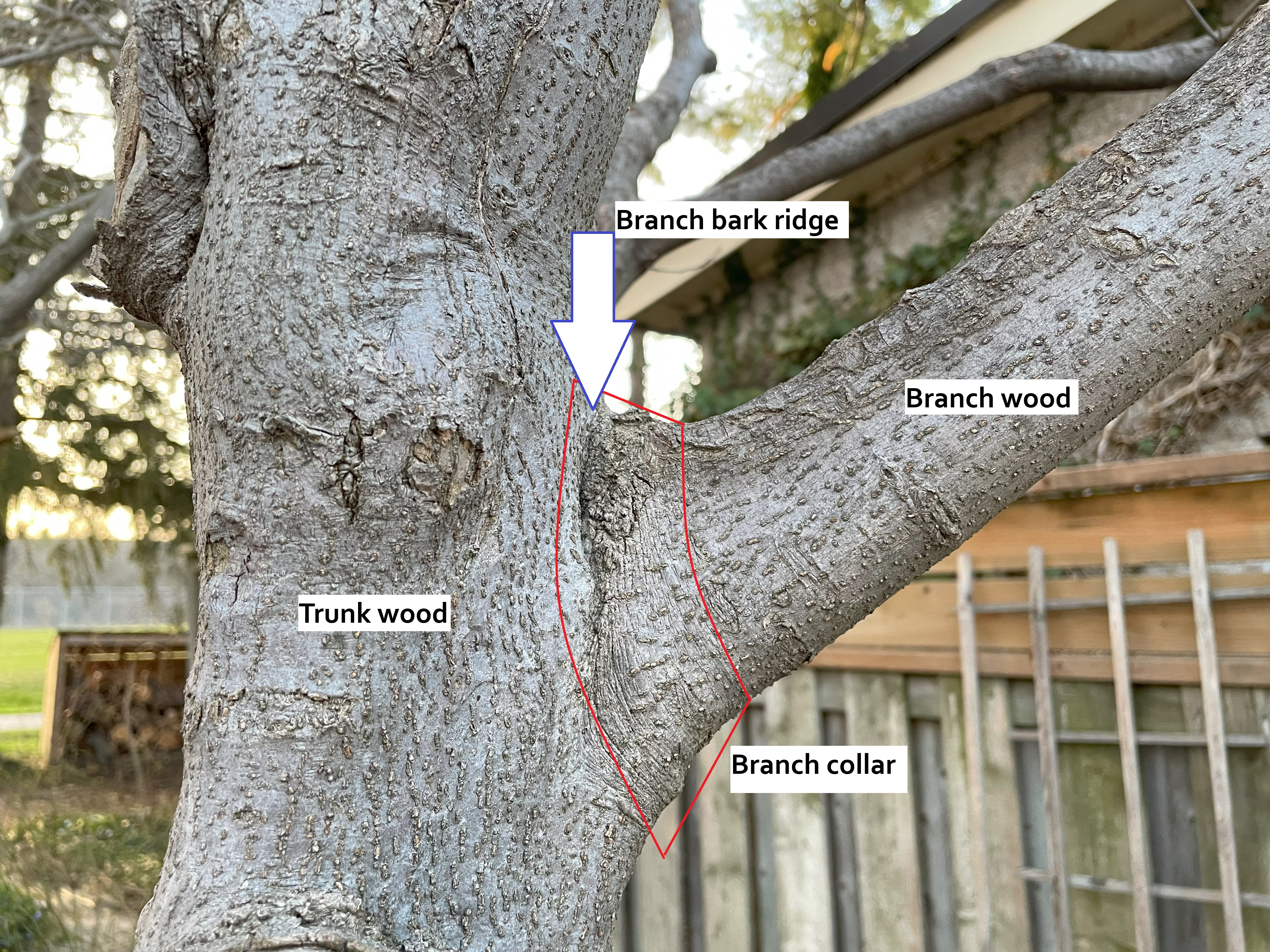
Pruning
Pruning is the selective removal of certain parts of a plant, such as branches, buds, or roots. It is practiced in horticulture (especially fruit tree pruning), arboriculture, and silviculture. The practice entails the targeted removal of diseased, damaged, dead, non-productive, structurally unsound, or otherwise unwanted plant material from crop and landscape plants. In general, the smaller the branch that is cut, the easier it is for a woody plant to compartmentalize the wound and thus limit the potential for pathogen intrusion and decay. It is therefore preferable to make any necessary formative structural pruning cuts to young plants, rather than removing large, poorly placed branches from mature plants. Woody plants may undergo a process referred to as ''self-pruning'', where they will drop twigs or branches which are no longer producing more energy than they require. It is theorized that this process can also occur in response to lack of water, in order to reduce the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Forestry
Urban forestry is the care and management of single trees and tree populations in Urban area, urban settings for the purpose of improving the urban environment. Urban forestry involves both planning and management, including the programming of care and maintenance operations of the urban forest. Urban forestry advocates the role of trees as a critical part of the urban infrastructure. Urban foresters plant and maintain trees, support appropriate tree and forest preservation, conduct research and promote the many benefits trees provide. Urban forestry is practiced by municipal and commercial arborists, municipal and utility foresters, environmental policymakers, city planners, consultants, educators, researchers and community activists. Benefits Environmental and health impacts Heat waves cause 1,300 deaths each year in the United States alone, which is more than any other weather-related event. As temperatures continue to rise due to global warming, we can expect to see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felling
Felling is the process of cutting down trees,"Feller" def. 2. and "Felling", def. 1. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' 2nd ed. via CD-ROM (v. 4.0) © Oxford University Press. 2009. an element of the task of logging. The person cutting the trees is a lumberjack Lumberjack is a mostly North American term for workers in the logging industry who perform the initial harvesting and transport of trees. The term usually refers to loggers in the era before 1945 in the United States, when trees were felled us .... A feller buncher is a machine capable of felling a single large tree or grouping and felling several small ones simultaneously. Methods Hand felling In hand felling, an axe, saw, or chainsaw is used to fell a tree, followed up by limbing and bucking in traditional applications. In the modern commercial logging industry, felling is typically followed by limbing and skidding. Feller buncher A feller-buncher is a motorized vehicle with an attachment which rapidly cut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Employment
Employment is a relationship between two party (law), parties Regulation, regulating the provision of paid Labour (human activity), labour services. Usually based on a employment contract, contract, one party, the employer, which might be a corporation, a not-for-profit organization, a co-operative, or any other entity, pays the other, the employee, in return for carrying out assigned work. Employees work in return for wage, wages, which can be paid on the basis of an hourly rate, by piecework or an annual salary, depending on the type of work an employee does, the prevailing conditions of the sector and the bargaining power between the parties. Employees in some sectors may receive gratuity, gratuities, bonus payments or employee stock option, stock options. In some types of employment, employees may receive benefits in addition to payment. Benefits may include health insurance, housing, and disability insurance. Employment is typically governed by Labour law, employment laws, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aesthetics Of Nature
Aesthetics of nature is a sub-field of ethics, philosophical ethics, and refers to the study of natural objects from their aesthetics, aesthetical perspective. History Aesthetics of nature developed as a sub-field of philosophical ethics. In the 18th and 19th century, the aesthetics of nature advanced the concepts of disinterestedness, the pictures, and the introduction of the idea of positive aesthetics. The first major developments of nature occurred in the 18th century. The concept of disinterestedness had been explained by many thinkers. Anthony Ashley-Cooper, 3rd Earl of Shaftesbury, Anthony Ashley-Cooper introduced the concept as a way of characterizing the notion of the aesthetic, later magnified by Francis Hutcheson (philosopher), Francis Hutcheson, who expanded it to exclude personal and utilitarianism interests and associations of a more general nature from aesthetic experience. This concept was further developed by Archibald Alison (author), Archibald Alison who refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town Planning
Urban planning (also called city planning in some contexts) is the process of developing and designing land use and the built environment, including air, water, and the infrastructure passing into and out of urban areas, such as transportation, communications, and distribution networks, and their accessibility. Traditionally, urban planning followed a top-down approach in master planning the physical layout of human settlements. The primary concern was the public welfare, which included considerations of efficiency, sanitation, protection and use of the environment, as well as taking account of effects of the master plans on the social and economic activities. Over time, urban planning has adopted a focus on the social and environmental " bottom lines" that focuses on using planning as a tool to improve the health and well-being of people and maintain sustainability standards. In the early 21st century, urban planning experts such as Jane Jacobs called on urban planners to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The UK includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and most of List of islands of the United Kingdom, the smaller islands within the British Isles, covering . Northern Ireland shares Republic of Ireland–United Kingdom border, a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the UK is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. It maintains sovereignty over the British Overseas Territories, which are located across various oceans and seas globally. The UK had an estimated population of over 68.2 million people in 2023. The capital and largest city of both England and the UK is London. The cities o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenity
In property and land use planning, amenity (lat. ''amoenitās'' “pleasantness, delightfulness”) is something considered to benefit a location, contribute to its enjoyment, and thereby increase its value. Tangible amenities can include the number and nature of guest rooms and the provision of facilities such as elevators (lifts), internet access, restaurants, parks, community centres, swimming pools, golf courses, health club facilities, party rooms, theatre or media rooms, bike paths or garages. Amenities are often provided or used as an instance to justify price increases on a specific property, leading to higher demand and thus scarcity for the selling property. Intangible amenities include well-integrated public transport Public transport (also known as public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) are forms of transport available to the general public. It typically uses a fixed schedule, route and charges a fixed fare. There is no rigid definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |