|
Aminoacetonitrile
Aminoacetonitrile is the organic compound with the formula . The compound is a colorless liquid. It is unstable at room temperature, owing to the incompatibility of the amine nucleophile and the nitrile electrophile. For this reason it is usually encountered as the chloride and bisulfate salts of the ammonium derivative, i.e., CCH2NH3sup>+Cl− and CCH2NH3sup>+HSO4−. Production and applications Industrially aminoacetonitrile is produced from glycolonitrile by reaction with ammonia: :HOCH2CN + NH3 → H2NCH2CN + H2O The aminoacetonitrile can be hydrolysed to give glycine: Being bifunctional, it is useful in the synthesis of diverse nitrogen-containing heterocycles. Aminoacetonitrile derivatives are useful antihelmintics. They act as nematode specific ACh agonists causing a spastic paralysis and rapid expulsion from the host. Occurrence in the interstellar medium Using radio astronomy, aminoacetonitrile was discovered in the Large Molecule Heimat, a giant gas cloud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycolonitrile
Glycolonitrile, also called hydroxyacetonitrile or formaldehyde cyanohydrin, is the organic compound with the formula HOCH2CN. It is the simplest cyanohydrin and it is derived from formaldehyde. It is a colourless liquid that dissolves in water and ether. Because glycolonitrile decomposes readily into formaldehyde and hydrogen cyanide, it is listed as an List of extremely hazardous substances, extremely hazardous substance. In January 2019, astronomers reported the detection of glycolonitrile, another possible Abiogenesis, building block of life among List of interstellar and circumstellar molecules, other such molecules, in outer space. Synthesis and reactions Glycolonitrile is produced by reacting formaldehyde with hydrogen cyanide at near-neutral pH, but with small amounts of catalytic base.Peter Pollak, Gérard Romeder, Ferdinand Hagedorn, Heinz-Peter Gelbke "Nitriles" ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'' 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Glycolonitrile polymerizes und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile (hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not classed as organic). It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture. It is used as a polar aprotic solvent in organic synthesis and in the purification of butadiene. The skeleton is linear with a short distance of 1.16 Å. Acetonitrile was first prepared in 1847 by the French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas. Applications Acetonitrile is used mainly as a solvent in the purification of butadiene in refineries. Specifically, acetonitrile is fed into the top of a distillation column filled with hydrocarbons including butadiene, and as the acetonitrile falls down through the column, it absorbs the butadiene which is then sent from the bottom of the tower to a second separating tower. Heat is then employed in the separa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanogen
Cyanogen is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula . Its structure is . The simplest stable carbon nitride, it is a Transparency and translucency, colorless and highly toxic gas with a pungency, pungent odor. The molecule is a pseudohalogen. Cyanogen molecules are linear molecular geometry, linear, and consist of two CN groups ‒ analogous to diatomic halogen molecules, such as chlorine, Cl, but far less oxidizing. The two cyanide, cyano groups are bonded together at their carbon atoms, though other isomers have been detected. The name is also used for the CN radical, and hence is used for compounds such as cyanogen bromide () (but see also ''Cyano radical''). When burned at increased pressure with oxygen, it is possible to get a blue tinted flame, the temperature of which is about 4800°C (a higher temperature is possible with ozone). It is as such regarded as the gas with the second highest temperature of burning (after dicyanoacetylene). Cyanogen is the anhy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminopropionitrile
Aminopropionitrile, also known as β-aminopropionitrile (BAPN), is an organic compound with both amine and nitrile functional groups. It is a colourless liquid. The compound occurs naturally and is of interest in the biomedical community. Biochemical and medical occurrence BAPN is the toxic constituent of peas from Lathyrus plants, e.g., '' Lathyrus odoratus''. Lathyrism, a disease known for centuries, encompasses 2 distinct entities: a disorder of connective tissue, causing either bone deformity (osteolathyrism) or aortic aneurisms (angiolathyrim). BAPN causes osteolathyrism and angiolathyrism when ingested in large quantities." It can cause osteolathyrism, neurolathyrism, and/or angiolathyrism. It is an antirheumatic agent in veterinary medicine. It has attracted interest as an anticancer agent. Production Aminopropionitrile is prepared by the reaction of ammonia with acrylonitrile.Karsten Eller, Erhard Henkes, Roland Rossbacher, Hartmut Höke "Amines, Aliphatic" in ''Ullma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocycle
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Standards And Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into Outline of physical science, physical science laboratory programs that include Nanotechnology, nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagittarius (constellation)
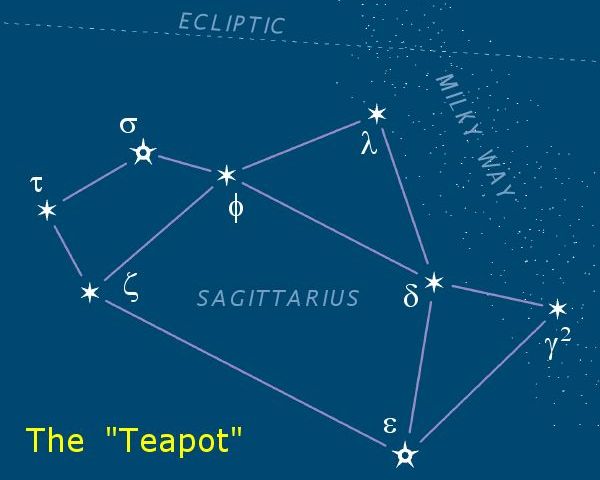
Sagittarius is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Southern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its old astronomical symbol is (♐︎). Its name is Latin for "archery, archer". Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow. It lies between Scorpius and Ophiuchus to the west and Capricornus and Microscopium to the east. The center of the Milky Way lies in the westernmost part of Sagittarius (see Sagittarius A). Visualizations As seen from the northern hemisphere, the constellation's brighter stars form an easily recognizable asterism (astronomy), asterism known as "the Teapot". The stars Delta Sagittarii, δ Sgr (Kaus Media), Epsilon Sagittarii, ε Sgr (Kaus Australis), Zeta Sagittarii, ζ Sgr (Ascella), and Phi Sagittarii, φ Sgr form the body of the pot; Lambda Sagittarii, λ Sgr (Kaus Borealis) is the point of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Center
The Galactic Center is the barycenter of the Milky Way and a corresponding point on the rotational axis of the galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact Astronomical radio source, radio source which is almost exactly at the galactic rotational center. The Galactic Center is approximately away from Earth in the direction of the constellations Sagittarius (constellation), Sagittarius, Ophiuchus, and Scorpius, where the Milky Way appears brightest, visually close to the Butterfly Cluster (M6) or the star Shaula, south to the Pipe Nebula. There are around 10 million stars within one parsec of the Galactic Center, dominated by red giants, with a significant population of massive supergiants and Wolf–Rayet stars from star formation in the region around 1 million years ago. The core stars are a small part within the much wider central region, called ''galactic bulge''. Discovery Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Molecule Heimat
The Large Molecule Heimat is a dense gas cloud located in the molecular cloud Sagittarius B2. Many species of molecule, including aminoacetonitrile (a molecule related to glycine Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...), ethyl formate, and butyronitrile, have been detected in the Large Molecule Heimat. References Milky Way Astrochemistry Sagittarius (constellation) {{nebula-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Planck Institute For Radio Astronomy
The Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy (MPIfRA) (German: ''Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie'') is located in Bonn, Germany. It is one of 80 institutes in the Max Planck Society (German: Max-Planck-Gesellschaft). History By combining the already existing radio astronomy faculty of the University of Bonn led by Otto Hachenberg with the new Max Planck institute the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy was formed. In 1972 the 100-m Effelsberg 100-m Radio Telescope, radio telescope in Effelsberg was opened. The institute building was enlarged in 1983 and 2002. The southern wing of the whole complex is occupied by the Argelander Institute of Astronomy of the University of Bonn. Structure The Institute has three main research groups, each with its own Director Departments * Fundamental Physics (Michael Kramer (astronomer), Michael Kramer) * VLBI and Radio Astronomy (Anton Zensus) * Millimetre Astronomy (Karl Martin Menten, Karl Menten) Independent Resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. IUPAC's executive director heads this administrative office, currently Greta Heydenrych. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine disrupts the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure. Its small side chain causes it to favor random coils instead. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a '' Clostridium tetani'' infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into both hydrophilic and hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. History and etymology Glycine was discovered in 1820 by French chemist Henri Braconnot when he hydrolyzed gelatin by boiling it with sulfuric acid. He originally called it "sugar of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |