|
Alpine Marmot
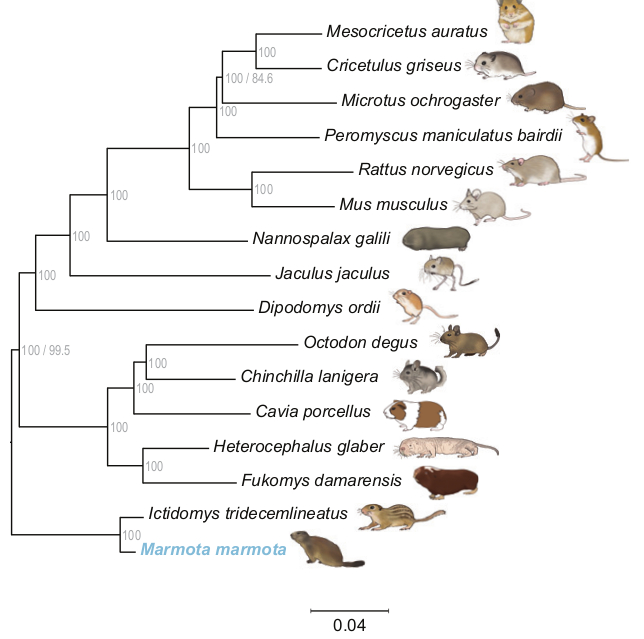
The alpine marmot (''Marmota marmota'') is a large ground-dwelling squirrel, from the genus of marmots. It is found in high numbers in mountainous areas of central and southern Europe, at heights between in the Alps, Carpathians, Tatras and Northern Apennines. In 1948 they were reintroduced with success in the Pyrenees, where the alpine marmot had disappeared at end of the Pleistocene epoch. Evolution The alpine marmot originates as an animal of Pleistocene cold steppe, exquisitely adapted to this ice-age climate. As such, alpine marmots are excellent diggers, able to penetrate soil that even a pickaxe would have difficulty with, and spend up to nine months per year in hibernation. Since the disappearance of the Pleistocene cold steppe, the alpine marmot persists in the high altitude alpine meadow. During the colonisation of Alpine habitat, the alpine marmot has lost most of its genetic diversity through a bottleneck effect. It could not rebuild its genetic diversity ever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Muveran
The Grand Muveran is a mountain of the Bernese Alps, located on the border between the cantons of Vaud and Valais. At 3,051 metres, it is the highest summit of the group lying between the Rhone knee and the Pas de Cheville and the westernmost three-thousander of the Bernese Alps. The closest localities are Les Plans-sur-Bex (municipality of Bex, Vaud) and Ovronnaz (Valais). It is accompanied by the smaller peak of Petit Muveran. Overlooking the Rhone valley from a height of about 2,600 metres, the Grand Muveran is the high point of a group (referred to as the ''Muverans'') composed of several summits approaching 3,000 metres, including to the southwest the Dent de Morcles and the Dent Favre, and to the northeast the Tête à Pierre Grept and the Haut de Cry. The Muverans are the second highest massif of the canton of Vaud, after the Diablerets, and one of the four distinct and glaciated massifs of the Bernese Alps that lie between the Rhone elbow and the Gemmi Pass, Gemmi Pass. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Heterozygosity Levels In The Alpine Marmot
Low or LOW or lows, may refer to: People * Low (surname), listing people surnamed Low Places * Low, Quebec, Canada * Low, Utah, United States * Lo Wu station (MTR code LOW), Hong Kong; a rail station * Salzburg Airport (ICAO airport code: LOWS), Austria Music * Low (band), an American indie rock group from Duluth, Minnesota * Low (English band), an English duo featuring Frankie Goes to Hollywood guitarist Brian Nash Albums * ''Low'' (David Bowie album), 1977 * ''Low'' (Testament album), 1994 * ''Low'' (Low EP), 1994 Songs * "Low" (Cracker song), 1993 * "Low" (Flo Rida song), 2007 * "Low" (Foo Fighters song), 2002 * "Low" (Juicy J song), 2014 * "Low" (Kelly Clarkson song), 2003 * "Low" (Lenny Kravitz song), 2018 * "Low" (Sara Evans song), 2008 * "Low" (SZA song), 2022 * "Low", by Camp Mulla * "Low", by Coldplay from the 2005 album '' X&Y'' * "Low", by I Prevail from the 2019 album '' Trauma'' * "Low", by Inna from her 2015 self-titled album * "Low", by Marianas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Carpathians
The Romanian Carpathians () are a section of the Carpathian Mountains, within the borders of modern Romania. The Carpathians are a "subsystem" of the Alps-Himalaya System and are further divided into "provinces" and "subprovinces". This is an overview of the geological subdivisions of the Romanian section of the Carpathian Mountains. The broadest divisions are shown in the map on the right. The last level of the division, i.e. the actual mountain ranges and basins, is usually called "units". The lowest-level detail for those units is maintained on separate pages. Naming conventions Traditional Romanian naming conventions differ from this list. In Romania, it is usual to divide the Eastern Carpathians in Romanian territory into three geographical groups (North, Centre, South), instead in Outer and Inner Eastern Carpathians. The Transylvanian Plateau is encircled by, and geologically a part of, the Carpathians, but it is not a mountainous region and its inclusion is disputed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apennine Mountains
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains ( ; or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; or – a singular with plural meaning; )Latin ''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which would be segmented ''Apenn-inus'', often used with nouns such as ("mountain") or Greek (), but ''Apenninus'' is just as often used alone as a noun. The ancient Greeks and Romans typically but not always used "mountain" in the singular to mean one or a range; thus, "the Apennine mountain" refers to the entire chain and is translated "the Apennine mountains". The ending can vary also by gender depending on the noun modified. The Italian singular refers to one of the constituent chains rather than to a single mountain, and the Italian plural refers to multiple chains rather than to multiple mountains. are a mountain range consisting of parallel smaller chains extending the length of peninsular Italy. In the northwest they join the Ligurian Alps at Altare. In the southwest they end at Reggio di Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Forest
The Black Forest ( ) is a large forested mountain range in the States of Germany, state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is the source of the Danube and Neckar rivers. Its highest peak is the Feldberg (Black Forest), Feldberg with an elevation of above sea level. Roughly oblong in shape, with a length of and breadth of up to , it has an area of about . Historically, the area was known for forestry and the mining of ore deposits, but tourism has now become the primary industry, accounting for around 300,000 jobs. There are Baroque fortifications in the Black Forest, several ruined military fortifications dating back to the 17th century. History In ancient times, the Black Forest was known as , after the Celtic deity, Abnoba. In Roman times (Late antiquity), it was given the name ("Marcynian Forest", from the Germanic word ''marka'', "border"). The Black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vosges
The Vosges ( , ; ; Franconian and ) is a range of medium mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a single geomorphological unit and low mountain range of around in area. It runs in a north-northeast direction from the Burgundian Gate (the Belfort– Ronchamp– Lure line) to the Börrstadt Basin (the Winnweiler– Börrstadt– Göllheim line), and forms the western boundary of the Upper Rhine Plain. The Grand Ballon is the highest peak at , followed by the Storkenkopf (), and the Hohneck ().IGN maps available oGéoportail/ref> Geography Geographically, the Vosges Mountains are wholly in France, far above the Col de Saverne separating them from the Palatinate Forest in Germany. The latter area logically continues the same Vosges geologic structure but traditionally receives this different name for historical and political reasons. From 1871 to 1918 the Vos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jura Mountains
The Jura Mountains ( ) are a sub-alpine mountain range a short distance north of the Western Alps and mainly demarcate a long part of the French–Swiss border. While the Jura range proper (" folded Jura", ) is located in France and Switzerland, the range continues northeastwards through northern Switzerland and Germany as the Table Jura ("not folded Jura", ), which is crossed by the High Rhine. Name The mountain range gives its name to the French department of Jura, the Swiss canton of Jura, the Jurassic period of the geologic timescale, and the Montes Jura of the Moon. It is first attested as ''mons Iura'' in book one of Julius Caesar's '' Commentarii de Bello Gallico''. Strabo uses a Greek masculine form ("through the Jura mountains", ) in his ''Geographica'' (4.6.11). Based on suggestions by Ferdinand de Saussure, early celticists such as Georges Dottin tried to establish an etymon "iura-, iuri" as a Celtic word for mountains, with similar putative etymologies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squirrel
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae (), a family that includes small or medium-sized rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrels. Squirrels are indigenous to the Americas, Eurasia, and Africa, and were introduced by humans to Australia. The earliest known fossilized squirrels date from the Eocene epoch, and among other living rodent families, the squirrels are most closely related to the mountain beaver and dormice. Etymology The word ''squirrel'', first attested in 1327, comes from the Anglo-Norman which is from the Old French , the reflex of a Latin language">Latin word , which was taken from the Ancient Greek word (; from ) 'shadow-tailed', referring to the long bushy tail which many of its members have. ''Sciurus'' is also the name of one of its genuses. The native Old English language, Old English word for the squirrel, , only survived into Middle Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottleneck Effect
A population bottleneck or genetic bottleneck is a sharp reduction in the size of a population due to environmental events such as famines, earthquakes, floods, fires, disease, and droughts; or human activities such as genocide, speciocide, widespread violence or intentional culling. Such events can reduce the variation in the gene pool of a population; thereafter, a smaller population, with a smaller genetic diversity, remains to pass on genes to future generations of offspring. Genetic diversity remains lower, increasing only when gene flow from another population occurs or very slowly increasing with time as random mutations occur. This results in a reduction in the robustness of the population and in its ability to adapt to and survive selecting environmental changes, such as climate change or a shift in available resources. Alternatively, if survivors of the bottleneck are the individuals with the greatest genetic fitness, the frequency of the fitter genes within the gene p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hibernation
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic reduction entered by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It is most commonly used to pass through winter months – called overwintering. Although traditionally reserved for "deep" hibernators such as rodents, the term has been redefined to include animals such as bears and is now applied based on active metabolic suppression rather than any absolute decline in body temperature. Many experts believe that the processes of daily torpor and hibernation form a continuum and use similar mechanisms. The equivalent during the summer months is aestivation. Hibernation functions to conserve energy when sufficient food is not available. To achieve this energy saving, an endothermic animal decreases its metabolic rate and thereby its body temperature. Hibernation may last days, weeks, or months—depending on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |