|
Allene
In organic chemistry, allenes are organic compounds in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon centres (). Allenes are classified as cumulated dienes. The parent compound of this class is propadiene, which is itself also called ''allene''. Compounds with an allene-type structure but with more than three carbon atoms are members of a larger class of compounds called cumulenes with bonding. History For many years, allenes were viewed as curiosities but thought to be synthetically useless and difficult to prepare and to work with.The Chemistry of the Allenes (vol. 1−3); Landor, S. R., Ed.; cademic Press: London, 1982. Reportedly, the first synthesis of an allene, glutinic acid, was performed in an attempt to prove the non-existence of this class of compounds. The situation began to change in the 1950s, and more than 300 papers on allenes have been published in 2012 alone. These compounds are not just interesting intermediates but synthetica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doering–LaFlamme Allene Synthesis
In organic chemistry, the Doering–LaFlamme allene synthesis is a reaction of alkenes that converts them to allenes by insertion of a carbon atom. This name reaction is named for William von Eggers Doering and a co-worker, who first reported it. The reaction is a two-stage process, in which first the alkene is reacted with dichlorocarbene or dibromocarbene to form a dihalocyclopropane. This intermediate is then reacted with a reducing metal, such as sodium or magnesium, or with an organolithium reagent. Either approach results in metal-halogen exchange to convert the ''gem''-dihalogenated carbon to a 1-metallo-1-halocyclopropane. This species undergoes α-elimination of metal halide and ring-opening via an electrocyclic reaction (at least formally) to give the allene. Several different mechanisms for the electrocyclic In organic chemistry, an electrocyclic reaction is a type of pericyclic reaction, pericyclic rearrangement reaction, rearrangement where the net result is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propadiene
Propadiene () or allene () is the organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest allene, i.e. a compound with two adjacent carbon double bonds. As a constituent of MAPP gas, it has been used as a fuel for specialized welding. Production and equilibrium with methylacetylene Allene exists in equilibrium with methylacetylene (propyne) and the mixture is sometimes called MAPD for ''m''ethyl''a''cetylene-''p''ropa''d''iene: :H3CC#CH <<=> H2C=C=CH2 for which at 270 °C or 0.1 at 5 °C. MAPD is produced as a side product, often an undesirable one, of dehydrogenation of to produce propene, an important |
Glutinic Acid
Penta-2,3-dienedioic acid (one of two chemicals called glutinic acid), is in allene-containing dicarboxylic acid. It was the first allene to be synthesized, in 1887, but the structure of it was thought to be a propyne core instead of an allene. The correct structural isomeric identity was not determined until 1954. Literature confusion A diterpene, chemical name (4a''R'',5''S'',6''R'',8a''R'')-5- ''Z'')-4-carboxy-3-methylbut-3-enyl5,6,8a-trimethyl-3,4,4a,6,7,8-hexahydronaphthalene-1-carboxylic acid (), is also called ''glutinic acid''. Some database entries for "glutinic acid" incorrectly identify it as this diterpene Diterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of four isoprene units, often with the molecular formula C20H32. They are biosynthesized by plants, animals and fungi via the HMG-CoA reductase pathway, with geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate being ... rather than the allene meaning in the underlying publications.See patents listed for References {{organic-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
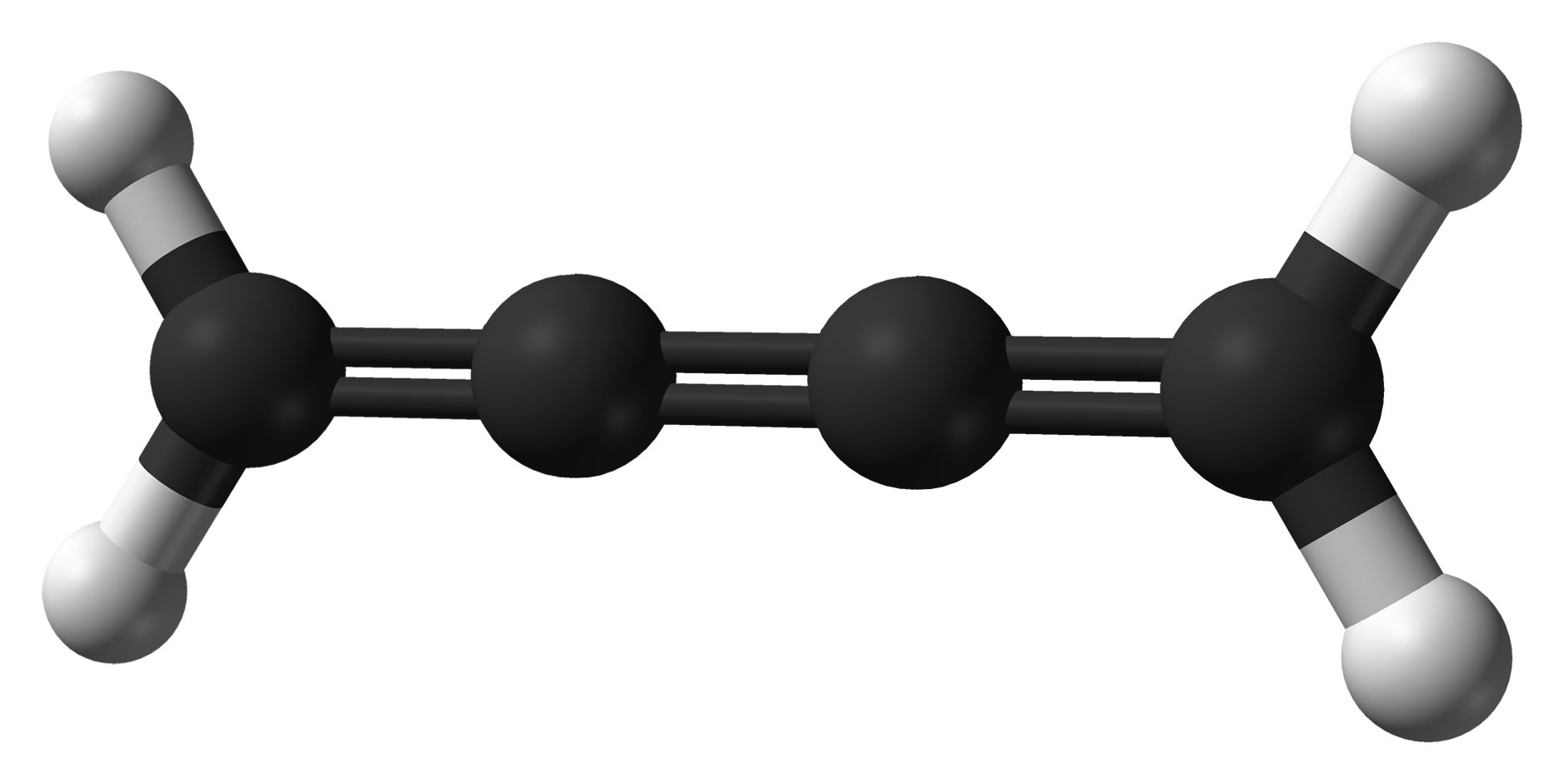
Cumulene
In organic chemistry, a cumulene is a compound having three or more ''cumulative'' (consecutive) double bonds. They are analogous to allenes, only having a more extensive chain. The simplest molecule in this class is butatriene (), which is also called simply ''cumulene''. Unlike most alkanes and alkenes, cumulenes tend to be rigid, comparable to polyynes. Cumulene carbenes for ''n'' from 3 to 6 have been observed in interstellar molecular clouds and in laboratory experiments by using microwave and infrared spectroscopy. (The more stable cumulenes are difficult to detect optically because they lack an electric dipole moment.) Cumulenes containing heteroatoms are called heterocumulenes; an example is carbon suboxide. Synthesis The first reported synthesis of a butatriene is that of tetraphenylbutatriene in 1921. The most common synthetic method for butatriene synthesis is based on reductive coupling of a geminal dihalo vinylidene. Tetraphenylbutatriene was reported sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skattebøl Rearrangement
The Skattebøl rearrangement is an organic reaction for converting a geminal dihalo cyclopropane to an allene using an organolithium base. This rearrangement reaction is named after its discoverer, Lars Skattebøl, Professor emeritus at the University of Oslo. It proceeds through a carbene reaction intermediate: When the cyclopropane ring is fitted with a 2-vinyl group, a cyclopentadiene is formed through a so-called foiled carbene intermediate.Leo A. Paquette and Mark L. McLaughlin Organic Syntheses ''Organic Syntheses'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1921. It publishes detailed and checked procedures for the synthesis of organic compounds. A unique feature of the review process is that all of the data and exper ..., CV 8, 22Link This process is more generally known as a vinylcyclopropane rearrangement. The reaction is closely related to the earlier Doering-LaFlamme procedure ( Doering-LaFlamme allene synthesis), in which a ''gem-''dibromocyclo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diene
In organic chemistry a diene ( ) (diolefin ( ) or alkadiene) is a covalent compound that contains two double bonds, usually among carbon atoms. They thus contain two alk''ene'' units, with the standard prefix ''di'' of systematic nomenclature. As a subunit of more complex molecules, dienes occur in naturally occurring and synthetic chemicals and are used in organic synthesis. Conjugated dienes are widely used as monomers in the polymer industry. Polyunsaturated fats are of interest to nutrition. Classes Dienes can be divided into three classes, depending on the relative location of the double bonds: #Cumulated dienes have the double bonds sharing a common atom. The result is more specifically called an allene. #Conjugated dienes have conjugated double bonds separated by one single bond. Conjugated dienes are more stable than other dienes because of resonance. #Unconjugated dienes have the double bonds separated by two or more single bonds. They are usually less stable than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirality (chemistry)
In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral () if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations, translations, and some conformational changes. This geometric property is called chirality (). The terms are derived from Ancient Greek χείρ (''cheir'') 'hand'; which is the canonical example of an object with this property. A chiral molecule or ion exists in two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other, called enantiomers; they are often distinguished as either "right-handed" or "left-handed" by their absolute configuration or some other criterion. The two enantiomers have the same chemical properties, except when reacting with other chiral compounds. They also have the same physical properties, except that they often have opposite optical activities. A homogeneous mixture of the two enantiomers in equal parts is said to be racemic, and it usually differs chemically and physically from the pure enantiomers. Chiral molecule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylacetylene
Propyne (methylacetylene) is an alkyne with the chemical formula . It is a component of MAPD gas—along with its isomer propadiene (allene), which was commonly used in gas welding. Unlike acetylene, propyne can be safely condensed.Peter Pässler, Werner Hefner, Klaus Buckl, Helmut Meinass, Andreas Meiswinkel, Hans-Jürgen Wernicke, Günter Ebersberg, Richard Müller, Jürgen Bässler, Hartmut Behringer, Dieter Mayer, "Acetylene" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2007 (). Production and equilibrium with propadiene Propyne exists in equilibrium with propadiene, the mixture of propyne and propadiene being called MAPD: :H3CC#CH H2C=C=CH2 The coefficient of equilibrium ''K''eq is 0.22 at 270 °C or 0.1 at 5 °C. MAPD is produced as a side product, often an undesirable one, by cracking propane to produce propene, an important feedstock in the chemical industry. MAPD interferes with the catalytic polymerization of propene. Laborat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 121 picometers is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (134 pm) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. The sigma bond contri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |