|
Advancement Of Learning
thumbnail, Title page of 1640 edition ''The Advancement of Learning'' (full title: ''Of the Proficience and Advancement of Learning, Divine and Human'') is a 1605 book by Francis Bacon which introduces and popularizes the scientific method of observation, skepticism and testability. Origin Bacon (a Protestant) lived during a period of great social turmoil as well as the expansion of scientific and social knowledge. In 1605 Bacon sent a draft to his friend Tobie Matthew who was in Florence where he was baptized as a Roman Catholic. Two years later, in 1607, Matthew returned to England, where he was imprisoned for his alleged " Papist views" The book is addressed as a plea to King James I and is in two parts or books, each with separate chapters: * Part I praises the king for his appreciation of knowledge and outlines Bacon's ideas as how strict bondage to the past (notably study of Greek and Roman language and form) was a hindrance to optimizing Christian values, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Views On Poverty And Wealth
Christian views on poverty and wealth vary. At one end of the spectrum is a view which casts wealth and materialism as an evil to be avoided and even combated. At the other end is a view which casts prosperity and well-being as a blessing from God. Many taking the former position address the topic in relation to the modern neoliberal capitalism that shapes the Western world. American theologian John B. Cobb has argued that the "economism that rules the West and through it much of the East" is directly opposed to traditional Christian doctrine. Cobb invokes the teaching of Jesus that "man cannot serve both God and Mammon (wealth)". He asserts that it is obvious that "Western society is organized in the service of wealth" and thus wealth has triumphed over God in the West. Scottish theologian Jack Mahoney has characterized the sayings of Jesus in Mark 10:23–27 as having "imprinted themselves so deeply on the Christian community through the centuries that those who are well o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks." It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital library. Most of the items in its collection are the full texts of books or individual stories in the public domain. All files can be accessed for free under an open format layout, available on almost any computer. , Project Gutenberg had reached over 75,999 items in its collection of free eBooks. The releases are available in plain text as well as other formats, such as HTML, PDF, EPUB, MOBI, and Plucker wherever possible. Most releases are in the English language, but many non-English works are also available. There are multiple affiliated projects that provide additional content, including region- and language-specific works. Project Gutenberg is closely affiliated with Distributed Proofreaders, an Internet-based community for proofr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American 501(c)(3) organization, non-profit organization founded in 1996 by Brewster Kahle that runs a digital library website, archive.org. It provides free access to collections of digitized media including websites, Application software, software applications, music, audiovisual, and print materials. The Archive also advocates a Information wants to be free, free and open Internet. Its mission is committing to provide "universal access to all knowledge". The Internet Archive allows the public to upload and download digital material to its data cluster, but the bulk of its data is collected automatically by its web crawlers, which work to preserve as much of the public web as possible. Its web archiving, web archive, the Wayback Machine, contains hundreds of billions of web captures. The Archive also oversees numerous Internet Archive#Book collections, book digitization projects, collectively one of the world's largest book digitization efforts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
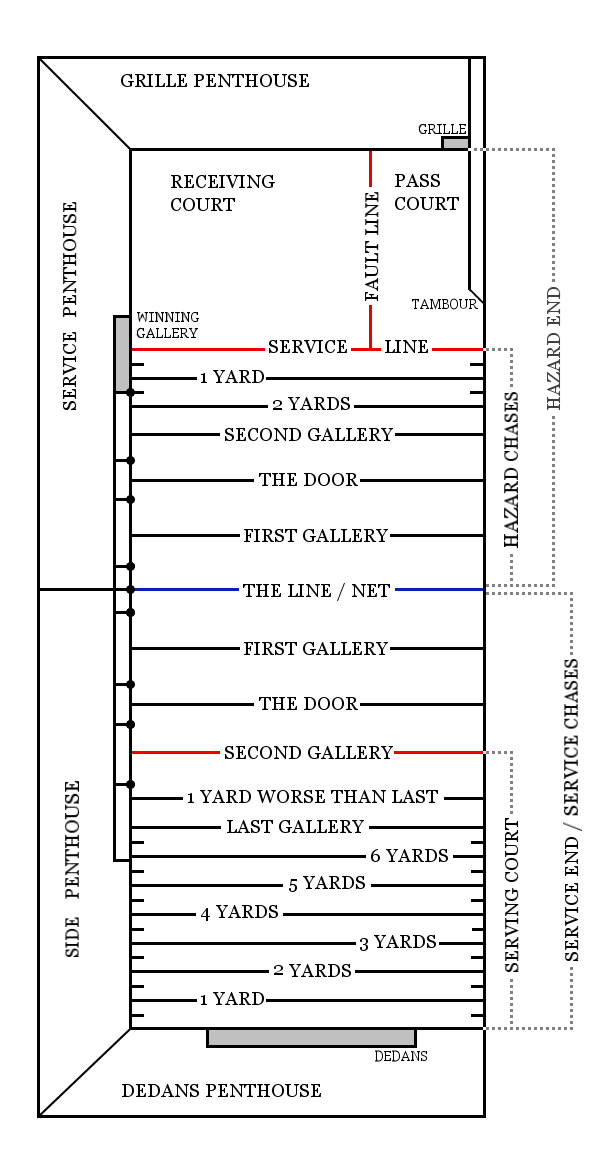
Real Tennis
Real tennis – one of several games sometimes called "the sport of kings" – is the original racquet sport from which the modern game of tennis (also called "lawn tennis") is derived. It is also known as court tennis in the United States, royal tennis in England and Australia, and ''courte-paume'' in France (to distinguish it from longue-paume, and in reference to the older, racquetless game of '' jeu de paume'', the ancestor of modern handball and racquet games). Many French real tennis courts are at ''jeu de paume'' clubs. The term ''real'' was first used by journalists in the early 20th century as a retronym to distinguish the ancient game from modern ''lawn'' tennis (even though, at present, the latter sport is seldom contested on lawns outside the few social-club-managed estates such as Wimbledon). There are just 45 active real tennis courts in the world, located in the United Kingdom, Australia, the United States and France. There are also currently six disu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Ludlam
William Ludlam (1717–1788) was an English clergyman and mathematician. Life Born at Leicester, he was elder son of the physician Richard Ludlam (1680–1728), who practised there; Thomas Ludlam, the clergyman, was his youngest brother. (His son was also called Thomas Ludlam, see below.) His mother was Anne, daughter of William Drury of Nottingham. His uncle, Sir George Ludlam, was Chamberlain of the city of London, and died in 1726. One of his sisters became stepmother of Joseph Cradock, and one of his first cousins, Isabella, daughter of John Ludlam, married Gerrard Andrewes, and was mother of Gerrard Andrewes the dean of Canterbury. Ludlam, after attending Leicester grammar school, became scholar of St. John's College, Cambridge, and was elected to a fellowship in 1744. He matriculated in 1734 and graduated B.A. 1738, M.A. 1742, and B.D. 1749. In 1749 he was instituted to the vicarage of Norton-by-Galby in Leicestershire, on the nomination of Bernard Whalley. From 1754 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empiricism
In philosophy, empiricism is an epistemological view which holds that true knowledge or justification comes only or primarily from sensory experience and empirical evidence. It is one of several competing views within epistemology, along with rationalism and skepticism. Empiricists argue that empiricism is a more reliable method of finding the truth than purely using logical reasoning, because humans have cognitive biases and limitations which lead to errors of judgement. Empiricism emphasizes the central role of empirical evidence in the formation of ideas, rather than innate ideas or traditions. Empiricists may argue that traditions (or customs) arise due to relations of previous sensory experiences. Historically, empiricism was associated with the " blank slate" concept (''tabula rasa''), according to which the human mind is "blank" at birth and develops its thoughts only through later experience. Empiricism in the philosophy of science emphasizes evidence, especi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine Drinker Bowen
Catherine Drinker Bowen (January 1, 1897 – November 1, 1973) was an American writer best known for her biographies. She won the National Book Award for Nonfiction in 1958. Biography Bowen was born Catherine Drinker on the Haverford College campus in Haverford, Pennsylvania, on January 1, 1897, to a prominent Quaker family. She was an accomplished violinist who studied for a musical career at the Peabody Institute and the Juilliard School of Music, but ultimately decided to become a writer. She had no formal writing education and no academic career, but became a bestselling American biographer and writer despite criticism from academics. Her earliest biographies were about musicians. Bowen did all her own research, without hiring research assistants, and sometimes took the controversial step of interviewing subjects without taking notes. A number of Bowen's books were chosen as Book of the Month Club selections, including ''Beloved Friend'' (1937), ''Yankee from Olympus'' (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denis Diderot
Denis Diderot (; ; 5 October 171331 July 1784) was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer, best known for serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. He was a prominent figure during the Age of Enlightenment. Diderot initially studied philosophy at a Society of Jesus, Jesuit college, then considered working in the church clergy before briefly studying law. When he decided to become a writer in 1734, his father disowned him. He lived a Bohemianism, bohemian existence for the next decade. In the 1740s he wrote many of his best-known works in both fiction and non-fiction, including the 1748 novel ''The Indiscreet Jewels, Les Bijoux indiscrets'' (The Indiscreet Jewels). In 1751 Diderot co-created the ''Encyclopédie'' with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. It was the first encyclopedia to include contributions from many named contributors and the first to describe the mechanical arts. Its secular tone, which included articles skepti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Le Rond D'Alembert
Jean-Baptiste le Rond d'Alembert ( ; ; 16 November 1717 – 29 October 1783) was a French mathematician, mechanician, physicist, philosopher, and music theorist. Until 1759 he was, together with Denis Diderot, a co-editor of the ''Encyclopédie''. D'Alembert's formula for obtaining solutions to the wave equation is named after him. The wave equation is sometimes referred to as d'Alembert's equation, and the fundamental theorem of algebra is named after d'Alembert in French. Early years Born in Paris, d'Alembert was the natural son of the writer Claudine Guérin de Tencin and the chevalier Louis-Camus Destouches, an artillery officer. Destouches was abroad at the time of d'Alembert's birth. Days after birth his mother left him on the steps of the church. According to custom, he was named after the patron saint of the church. D'Alembert was placed in an orphanage for foundling children, but his father found him and placed him with the wife of a glazier, Madame Rousseau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopédie
, better known as ''Encyclopédie'' (), was a general encyclopedia published in France between 1751 and 1772, with later supplements, revised editions, and translations. It had many writers, known as the Encyclopédistes. It was edited by Denis Diderot and, until 1759, co-edited by Jean le Rond d'Alembert. The ''Encyclopédie'' is most famous for representing the thought of the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment. According to Denis Diderot in the article "Encyclopédie", the ''Encyclopédie'' aim was "to change the way people think" and for people to be able to inform themselves and to know things. He and the other contributors advocated for the secularization of learning away from the Jesuits. Diderot wanted to incorporate all of the world's knowledge into the ''Encyclopédie'' and hoped that the text could disseminate all this information to the public and future generations. Thus, it is an example of democratization of knowledge. It was also the first encyclopedia to include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |