|
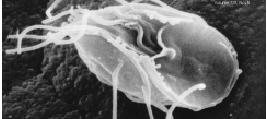
Acytostelium Leptosomum
''Acytostelium'' is a genus of dictyostelid. The genus ''Acytostelium'' inhabit surface humus and leaf mold of forest soils and are widely distributed in different forests of the world. Species include: * '' Acytostelium aggregatum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium amazonicum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium anastomosans'' Cavender et al. 2005 * '' Acytostelium digitatum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium irregularosporum'' Hagiw. 1971 * '' Acytostelium leptosomum'' Raper 1956 * '' Acytostelium longisorophorum'' Cavender et al. 2005 * '' Acytostelium magniphorum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium magnisorum'' Cavender et al. 2005 * '' Acytostelium minutissimum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium pendulum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium reticulatum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium serpentarium'' Cavender et al. 2005 * '' Acytostelium singulare'' Cavender et al. 2005 * ''Acytostelium subglobosum ''Acytostelium'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek language, Greek wikt:εὖ, εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and wikt:� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acytostelium Leptosomum
''Acytostelium'' is a genus of dictyostelid. The genus ''Acytostelium'' inhabit surface humus and leaf mold of forest soils and are widely distributed in different forests of the world. Species include: * '' Acytostelium aggregatum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium amazonicum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium anastomosans'' Cavender et al. 2005 * '' Acytostelium digitatum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium irregularosporum'' Hagiw. 1971 * '' Acytostelium leptosomum'' Raper 1956 * '' Acytostelium longisorophorum'' Cavender et al. 2005 * '' Acytostelium magniphorum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium magnisorum'' Cavender et al. 2005 * '' Acytostelium minutissimum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium pendulum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium reticulatum'' Cavender & Vadell 2000 * '' Acytostelium serpentarium'' Cavender et al. 2005 * '' Acytostelium singulare'' Cavender et al. 2005 * ''Acytostelium subglobosum ''Acytostelium'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional and currently no longer supported classification schemes, Amoebozoa is ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked " supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, variously named Unikonta, Amorphea or Opimoda. Amoebozoa includes many of the best-known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |