|
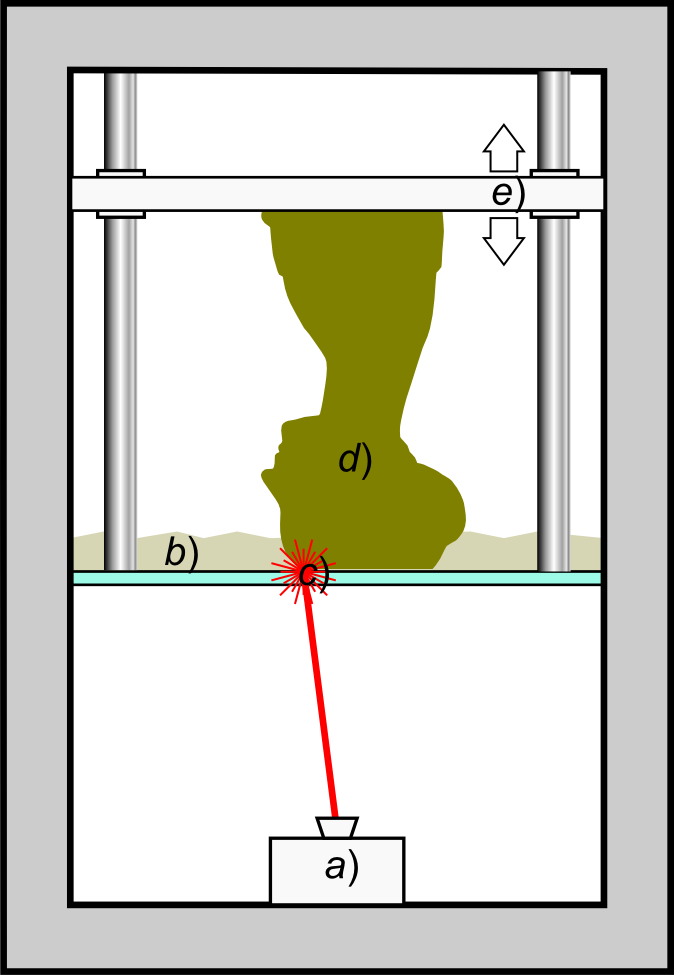
3D Bioprinting
Three dimensional (3D) bioprinting is the utilization of 3D printing–like techniques to combine cells, growth factors, and/or biomaterials to fabricate biomedical parts, often with the aim of imitating natural tissue characteristics. Generally, 3D bioprinting can utilize a layer-by-layer method to deposit materials known as bio-inks to create tissue-like structures that are later used in various medical and tissue engineering fields. 3D bioprinting covers a broad range of bioprinting techniques and biomaterials. Currently, bioprinting can be used to print tissue and organ models to help research drugs and potential treatments. Nonetheless, translation of bioprinted living cellular constructs into clinical application is met with several issues due to the complexity and cell number needed to create functional organs. However, innovations span from bioprinting of extracellular matrix to mixing cells with hydrogels deposited layer by layer to produce the desired tissue. In addition, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereolithography
Stereolithography (SLA or SL; also known as vat photopolymerisation, optical fabrication, photo-solidification, or resin printing) is a form of 3D printing technology used for creating models, prototypes, patterns, and production parts in a layer by layer fashion using photochemical processes by which light causes chemical monomers and oligomers to cross-link together to form polymers.U.S. Patentbr>4,575,330(“Apparatus for Production of Three-Dimensional Objects by Stereolithography”) Those polymers then make up the body of a three-dimensional solid. Research in the area had been conducted during the 1970s, but the term was coined by Chuck Hull in 1984 when he applied for a patent on the process, which was granted in 1986. Stereolithography can be used to create prototypes for products in development, medical models, and computer hardware, as well as in many other applications. While stereolithography is fast and can produce almost any design, it can be expensive. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alginate
Alginic acid, also called algin, is a naturally occurring, edible polysaccharide found in brown algae. It is hydrophilic and forms a viscous gum when hydrated. With metals such as sodium and calcium, its salts are known as alginates. Its colour ranges from white to yellowish-brown. It is sold in filamentous, granular, or powdered forms. It is a significant component of the biofilms produced by the bacterium ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', a major pathogen found in the lungs of some people who have cystic fibrosis. The biofilm and ''P. aeruginosa'' have a high resistance to antibiotics, but susceptible to inhibition by macrophages. Structure Alginic acid is a linear copolymer with homopolymeric blocks of (1→4)-linked β-D- mannuronate (M) and α-L- guluronate (G) residues, respectively, covalently linked together in different sequences or blocks. The monomers may appear in homopolymeric blocks of consecutive G-residues (G-blocks), consecutive M-residues (M-blocks) or alternati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomaterials
A biomaterial is a substance that has been engineered to interact with biological systems for a medical purpose, either a therapeutic (treat, augment, repair, or replace a tissue function of the body) or a diagnostic one. As a science, biomaterials is about fifty years old. The study of biomaterials is called biomaterials science or biomaterials engineering. It has experienced steady and strong growth over its history, with many companies investing large amounts of money into the development of new products. Biomaterials science encompasses elements of medicine, biology, chemistry, tissue engineering and materials science. Note that a biomaterial is different from a biological material, such as bone, that is produced by a biological system. Additionally, care should be exercised in defining a biomaterial as biocompatible, since it is application-specific. A biomaterial that is biocompatible or suitable for one application may not be biocompatible in another. Introduction B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
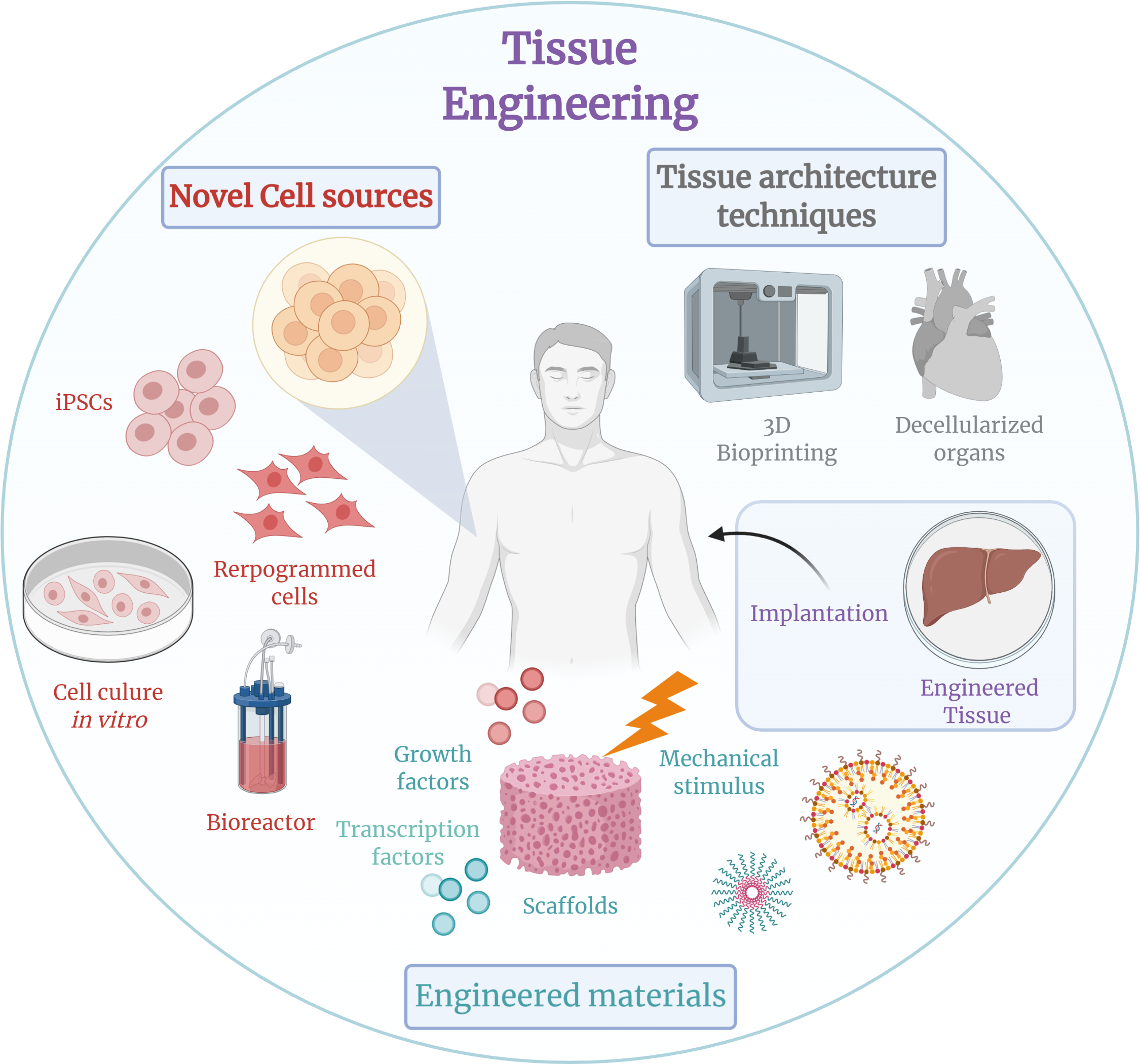
Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of cells, engineering, materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintain, improve, or replace different types of biological tissues. Tissue engineering often involves the use of cells placed on tissue scaffolds in the formation of new viable tissue for a medical purpose but is not limited to applications involving cells and tissue scaffolds. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field of its own. While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e. bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wagyu
Wagyu ( ja, 和牛, Hepburn: ''wagyū'', ) is the collective name for the four principal Japanese breeds of beef cattle. All wagyū cattle derive from cross-breeding in the early twentieth century of native Japanese cattle with imported stock, mostly from Europe. In several areas of Japan, Wagyu beef is shipped carrying area names. Some examples are Matsusaka beef, Kobe beef, Yonezawa beef, Ōmi beef, and Sanda beef. In recent years, Wagyu beef has increased in fat percentage due to decrease in grazing and an increase in using feed, resulting in larger, fattier cattle. History Cattle were brought to Japan from China at the same time as the cultivation of rice, in about the second century AD, in the Yayoi period. Until about the time of the Meiji Restoration in 1868, they were used only as draught animals, in agriculture, forestry, mining and for transport, and as a source of fertilizer. Milk consumption was unknown, and – for cultural and religious reasons – mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
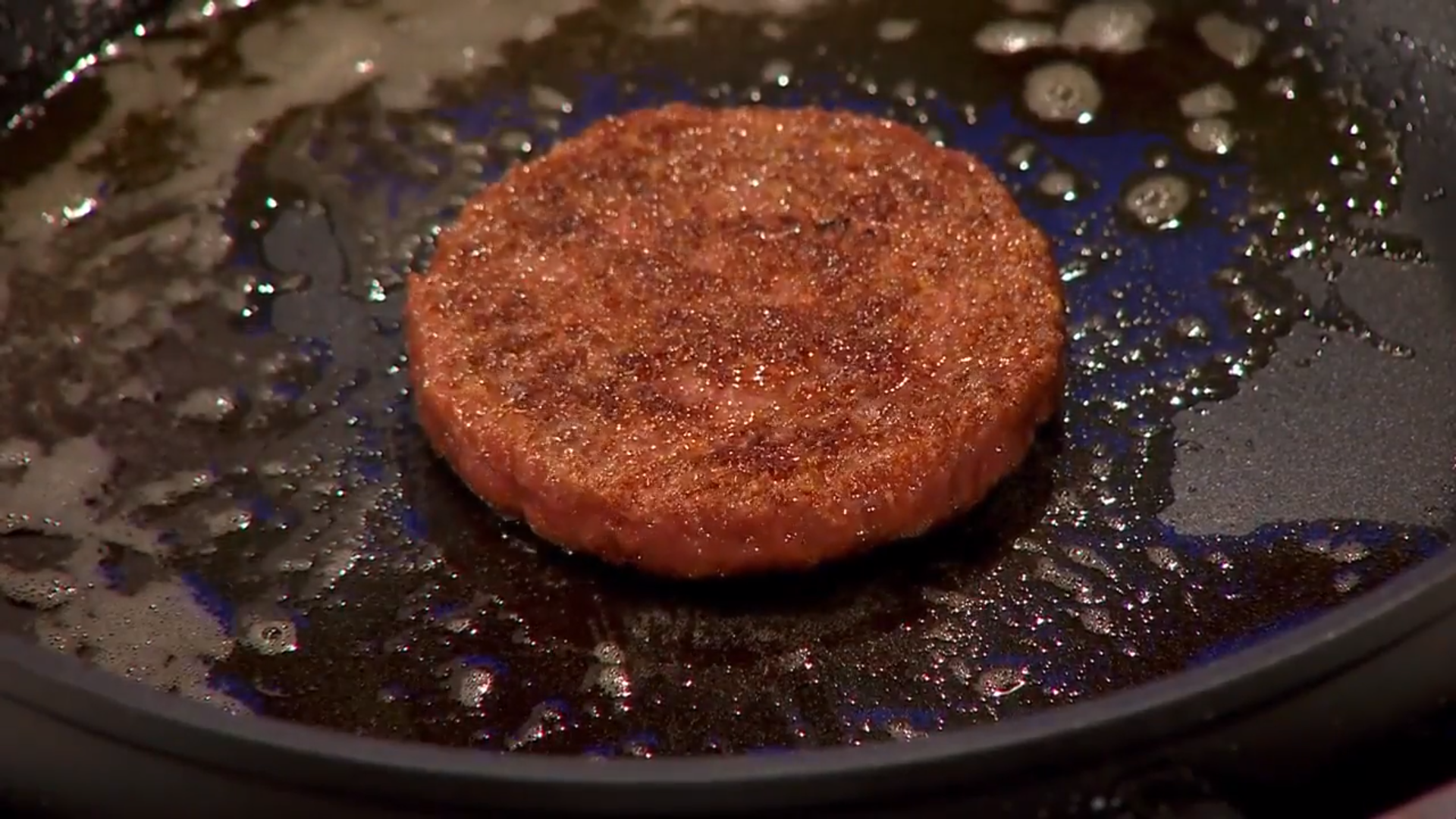
Cultured Meat
Cultured meat (also known by other names) is meat produced by culturing animal cells ''in vitro''. It is a form of cellular agriculture. Cultured meat is produced using tissue engineering techniques pioneered in regenerative medicine. Jason Matheny popularized the concept in the early 2000s after he co-authored a paper on cultured meat production and created New Harvest, the world's first nonprofit organization dedicated to ''in-vitro'' meat research. Cultured meat has the potential to address the environmental impact of meat production, animal welfare, food security and human health. in addition to its potential mitigation of climate change. In 2013, Mark Post created a hamburger patty made from tissue grown outside of an animal. Since then, other cultured meat prototypes have gained media attention: SuperMeat opened a farm-to-fork restaurant called "The Chicken" in Tel Aviv to test consumer reaction to its "Chicken" burger, while the "world's first commercial sale of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assembly Of Fibrous Muscle, Fat, And Vascular Tissues To Cultured Steak
Assembly may refer to: Organisations and meetings * Deliberative assembly, a gathering of members who use parliamentary procedure for making decisions * General assembly, an official meeting of the members of an organization or of their representatives * House of Assembly, a name given to the legislature or lower house of a bicameral legislature * National Assembly, either a legislature or the lower house of a bicameral legislature in some countries ** National Assembly (other) * Popular assembly, a localized citizen gathering to address issues of importance to the community * Qahal, or assembly, an Israelite organizational structure * People's Assembly (other) * Assembly of Experts, the deliberative body empowered to designate and dismiss the Supreme Leader of Iran * Freedom of assembly, the individual right to come together and collectively express, promote, pursue and defend common interests * School assembly, a gathering of all or part of a school Science, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtia
Microtia is a congenital deformity where the auricle (external ear) is underdeveloped. A completely undeveloped pinna is referred to as anotia. Because microtia and anotia have the same origin, it can be referred to as microtia-anotia. Microtia can be unilateral (one side only) or bilateral (affecting both sides). Microtia occurs in 1 out of about 8,000–10,000 births. In unilateral microtia, the right ear is most commonly affected. It may occur as a complication of taking Accutane (isotretinoin) during pregnancy. Classification According to the Altman-classification, there are four grades of microtia: *Grade I: A less than complete development of the external ear with identifiable structures and a small but present external ear canal *Grade II: A partially developed ear (usually the top portion is underdeveloped) with a closed stenotic external ear canal producing a conductive hearing loss. *Grade III: Absence of the external ear with a small peanut-like vestige structure a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auricle (anatomy)
The auricle or auricula is the visible part of the ear that is outside the head. It is also called the pinna ( Latin for " wing" or "fin", plural pinnae), a term that is used more in zoology. Structure The diagram shows the shape and location of most of these components: * ''antihelix'' forms a 'Y' shape where the upper parts are: ** ''Superior crus'' (to the left of the ''fossa triangularis'' in the diagram) ** ''Inferior crus'' (to the right of the ''fossa triangularis'' in the diagram) * ''Antitragus'' is below the ''tragus'' * ''Aperture'' is the entrance to the ear canal * ''Auricular sulcus'' is the depression behind the ear next to the head * ''Concha'' is the hollow next to the ear canal * Conchal angle is the angle that the back of the ''concha'' makes with the side of the head * ''Crus'' of the helix is just above the ''tragus'' * ''Cymba conchae'' is the narrowest end of the ''concha'' * External auditory meatus is the ear canal * ''Fossa triangularis'' is the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheobronchomalacia
Tracheobronchomalacia or TBM is a condition characterized by flaccidity of the tracheal support cartilage which leads to tracheal collapse. This condition can also affect the bronchi. There are two forms of this condition: primary TBM and secondary TBM. Primary TBM is congenital and starts as early as birth. It is mainly linked to genetic causes. Secondary TBM is acquired and starts in adulthood. It is mainly developed after an accident or chronic inflammation. Tracheobronchomalacia may also occur in people who have normal cartliginous structure of the trachea, but significant atrophy of the posterior wall, causing significant invagination of the trachea on expiration. In these cases it is more commonly known as Excessive Dynamic Airway Collapse (EDAC). Signs and symptoms Initially TBM may be asymptomatic or some patients do not experience symptoms at all. In a progressive TBM case symptoms include: * shortness of breath * a cough * mucus build up * stridor (a wheeze-like sound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photo Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many forms of polymerization and different systems exist to categorize them. In chemical compounds, polymerization can occur via a variety of reaction mechanisms that vary in complexity due to the functional groups present in the reactants and their inherent steric effects. In more straightforward polymerizations, alkenes form polymers through relatively simple radical reactions; in contrast, reactions involving substitution at a carbonyl group require more complex synthesis due to the way in which reactants polymerize. Alkanes can also be polymerized, but only with the help of strong acids. As alkenes can polymerize in somewhat straightforward radical reactions, they form useful compounds such as polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
