|
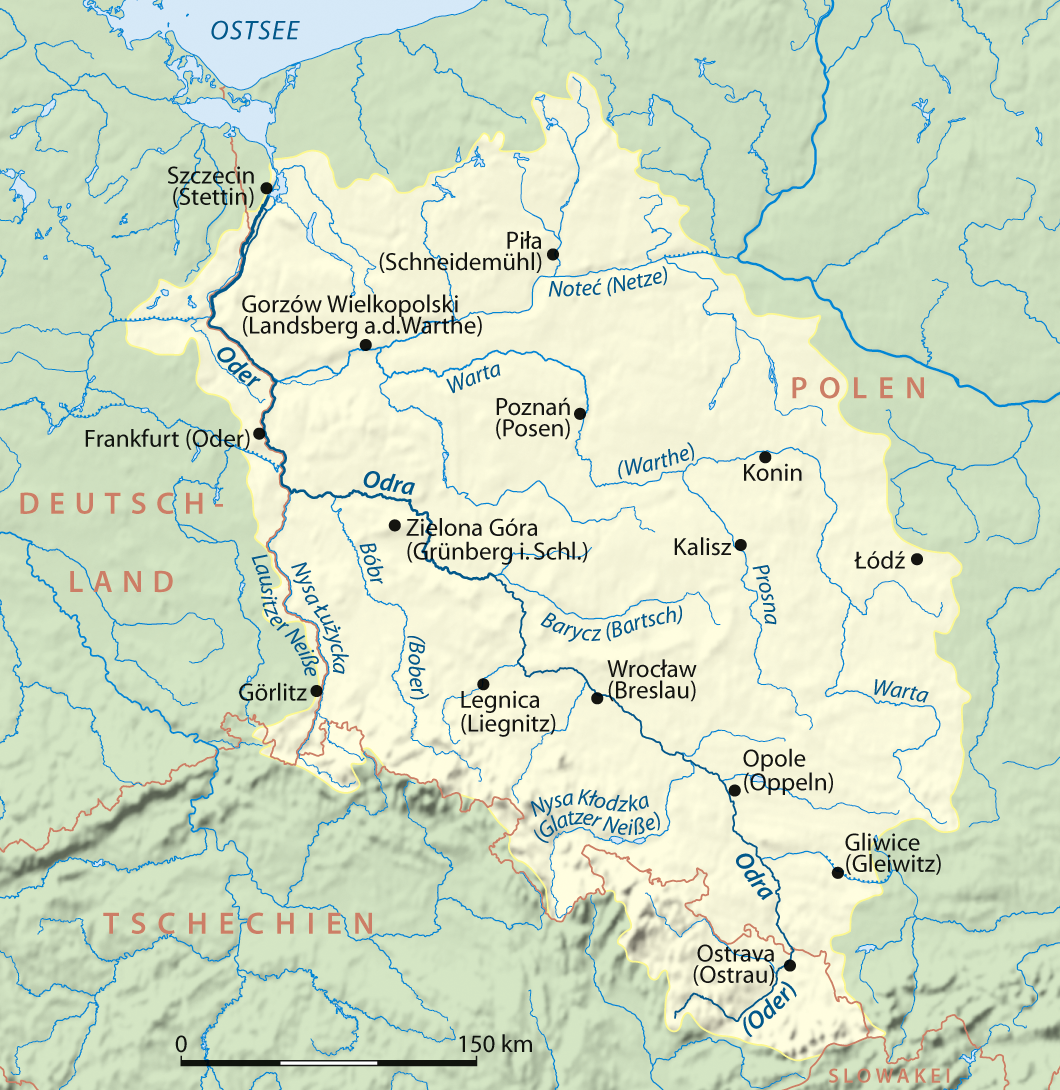
2022 Oder Environmental Disaster
During the summer of 2022, a mass mortality event involving fish, beavers, clams, crayfish and other wildlife occurred in the Oder river. Over 100 tonnes of fish kill, dead fish were removed from the Polish section of the river, and a further 35 tonnes from German sections, causing concern that the water was poisoned. At first the cause was not clear, theories included the effects of the summer heat and lower water levels due to the 2022 European drought, European drought, reduced oxygen levels due to the heat and nutrient loading, a spike in oxygen levels due to the introduction of an oxidizing agent, and pollution by chemicals including Mercury (element), mercury, mesitylene, salts or other sewage, as well as the possibility of an algal bloom. It was later determined to be an algal bloom, which was made possible by the discharge of saline industrial wastewater into the river on the Polish side, is now considered the probable cause of the disaster. The Polish authorities were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oława
Oława (, , ) is a historic town in south-western Poland with 33,029 inhabitants (2019). It is situated in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, within the Wrocław metropolitan area. It is the seat of Oława County and of the smaller administrative district of Gmina Oława (although it is not part of the territory of the latter, as the town is an urban gmina in its own right). Etymology The name of the city comes from the Polish word root el-, ol-, which in Polish lands took also the form of oła-, meaning "water". The association with water refers to the location of the settlement between two rivers: the Oder and the Oława, which are close to each other, but only connect in Wrocław, which is away. The location of the city between rivers, pools and forests, and at the same time in the place of crossing the Oder River, favored the creation of a market settlement of Ślęża, and later a stronghold, a town. The locality was mentioned in the Old Polish, Latinized form of Oleva in a Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, roughly from the Sudetes, Sudeten Mountains to the north. In 2023, the official population of Wrocław was 674,132, making it the third-largest city in Poland. The population of the Wrocław metropolitan area is around 1.25 million. Wrocław is the historical capital of Silesia and Lower Silesia. The history of the city dates back over 1,000 years; at various times, it has been part of the Kingdom of Poland, the Kingdom of Bohemia, the Kingdom of Hungary, the Habsburg monarchy of Austria, the Kingdom of Prussia and German Reich, Germany, until it became again part of Poland in 1945 immediately after World War II. Wrocław is a College town, university city with a student population of over 130,000, making it one of the most yo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jelcz
Jelcz (pronounced like ''Yelch'' after the town of the same name) is a Polish manufacturer of trucks, buses, trolleybuses and different types of dedicated chassis. Since 2013, the company has been part of the Polska Grupa Zbrojeniowa and focuses on manufacturing off-road military vehicles. History In 1952, a decision was made to use a former German armaments factory in Jelcz-Laskowice near Wrocław for production in western Poland. A company called Zakłady Budowy Nadwozi Samochodowych (Automobile Chassis Works) was established. After the factory was rebuilt, the company started to develop and build bus bodies for Lublin and Star trucks, including buses such as the Jelcz PR110D. In 1974, the Polish expedition to Lhotse used a Jelcz 316 car to travel from Warsaw to Nepal. In 1975, the expedition of the Wrocław Mountain Club to Broad Peak Central, in Pakistan, used a Jelcz 315-M car to travel from Wrocław to Islamabad, driving up to 9,000 km between 2 and 21 May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Neisse
The Eastern Neisse, also known by its Polish name of Nysa Kłodzka (, ), is a river in southwestern Poland, a left tributary of the Oder, with a length of 188 km (21st longest) and a basin area of 4,570 km2 (3,742 in Poland). Prior to World War II it was part of Germany. During the Yalta Conference it was discussed by the Western Allies as one possible line of the western Polish border. Attempts were made to negotiate a compromise with the Soviets on the new Polish-German frontier; it was suggested that the Eastern Neisse be made the line of demarcation. This would have meant that (East) Germany could have retained approximately half of Silesia, including most of Wrocław (formerly Breslau). However the Soviets rejected the suggestion at the Potsdam Conference and insisted that the southern boundary between Germany and Poland be drawn further west, at the Lusatian Neisse,Plokhy S.M. ''Yalta: The Price of Peace'', New York: Viking, 2010. in some way reintroducing the borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated population of over 449million as of 2024. The EU is often described as a ''sui generis'' political entity combining characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.5% of the world population in 2023, EU member states generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around €17.935 trillion in 2024, accounting for approximately one sixth of global economic output. Its cornerstone, the European Union Customs Union, Customs Union, paved the way to establishing European Single Market, an internal single market based on standardised European Union law, legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nowa Ruda
Nowa Ruda (, ) is a town in south-western Poland near the Czech Republic, Czech border, lying on the Włodzica river in the central Sudetes mountain range. it had 22,067 inhabitants. The town is located in Kłodzko County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the seat of the rural district of Gmina Nowa Ruda, but is not part of its territory (the town is a separate urban gmina in its own right). History Under Polish and Bohemian rule A Middle Ages, medieval village situated in the rich Kłodzko Valley, Nowa Ruda developed in the mid-13th century as part of the Kingdom of Bohemia. Germans, German-speaking immigrants settled there as part of the ''Ostsiedlung''. The oldest known mention of the settlement comes from 1337 from a document issued in nearby Kłodzko, when it was part of the Polish Piast dynasty, Piast-ruled Duchy of Ziębice, Duchy of Ziębice/Münsterberg under the suzerainty of the Bohemian Crown, Bohemian (Czech) Crown of the Holy Roman Empire. It passed directly to B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opole
Opole (; ; ; ) is a city located in southern Poland on the Oder River and the historical capital of Upper Silesia. With a population of approximately 127,387 as of the 2021 census, it is the capital of Opole Voivodeship (province) and the seat of Opole County. Its metropolitan area was home to 146,522 inhabitants. It is the largest city in its province. Its history dates to the 8th century, and Opole is one of the oldest cities in Poland. An important stronghold in Poland, it became a capital of a Duchy of Opole, duchy within medieval Poland in 1172, and in 1217 it was granted city rights by Duke Casimir I of Opole, the great-grandson of Polish Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth. During the Medieval Period and the Renaissance, the city was known as a centre of commerce; several main trade routes intersected here, which helped to generate steady profits from transit trade. The rapid development of the town was also caused by the establishment of a seat of regency in Opole in 1816. The fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zdzieszowice
Zdzieszowice (; , 1936–1945: ''Odertal O.S.''; ) is a town in Krapkowice County, Opole Voivodeship, Poland Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ..., with 11,445 inhabitants (2019). The synthetic oil plant at "Schaffgotsch Benzin GmbH in Deschowitz-Beuthen, Odertal (Upper Silesia)" began production in 1939 and was a target of the Oil Campaign of World War II. Twin towns – sister cities See twin towns of Gmina Zdzieszowice. Gallery File:Dworzec kolejowy Zdzieszowice.jpg , Train station File:Zdzieszowice, kościół św. Antoniego.jpg , Saint Anthony church File:Zdzieszowice, Urząd Miasta i Gminy, stary kościół.jpg, Town hall File:Oder in Deschowitz.jpg, Odra River References Cities and towns in Opole Voivodeship Krapkowice County Oil campaign of World W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coke (fuel)
Coke is a grey, hard, and porous coal-based fuel with a high carbon content. It is made by heating coal or petroleum in the absence of air. Coke is an important industrial product, used mainly in iron ore smelting, but also as a fuel in stoves and forges. The unqualified term "coke" usually refers to the product derived from low-ash and low-sulphur bituminous coal by a process called coking. A similar product called petroleum coke, or pet coke, is obtained from crude petroleum in oil refinery, petroleum refineries. Coke may also be formed naturally by geology, geologic processes.B. Kwiecińska and H. I. Petersen (2004): "Graphite, semi-graphite, natural coke, and natural char classification — ICCP system". ''International Journal of Coal Geology'', volume 57, issue 2, pages 99-116. It is the residue of a destructive distillation process. Production Industrial coke furnaces The industrial production of coke from coal is called coking. The coal is baked in an airless k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kędzierzyn-Koźle
Kędzierzyn-Koźle () is a city in south-western Poland, the administrative center of Kędzierzyn-Koźle County. With 58,899 inhabitants as of 2021, it is the second most-populous city in the Opole Voivodeship. Founded from the merger of the previously separate towns of Kędzierzyn and Koźle, both dating back to the Middle Ages, the city is a major river port and center of chemical industry, and is particularly known for ZAKSA Kędzierzyn-Koźle, one of the top volleyball clubs in Europe in the 2020s. Geography and economy Kędzierzyn-Koźle is located in the historic Silesia (Upper Silesia) region at the confluence of the Oder River and its Kłodnica tributary. Situated on the lower reaches of the Gliwice Canal, it is a place of a major river port, has rail connections with all major cities of Poland and lies close to the west of the Metropolis GZM. The town is a major location of chemical industry, the site of several factories and a power plant at Blachownia Śląska. Zakłady ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kłodnica
The Kłodnica is a river in the Upper Silesia region. It is about 75 km long and a right tributary of the Odra river. Along Kłodnica's shore are Polish cities of Katowice, Kędzierzyn-Koźle, Ruda Śląska, Gliwice, and Zabrze Zabrze (; German: 1915–1945: , full form: , , ) is an industrial city put under direct government rule in Silesia in southern Poland, near Katowice. It lies in the western part of the Metropolis GZM, a metropolis with a population of around 2 m .... There was also a Kłodnica Canal that opened in 1806. This water transport facility has been replaced by the Gliwice Canal. Rivers of Poland Rivers of Silesian Voivodeship {{Poland-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heavy industry (mining and metallurgy). Geography Upper Silesia is situated on the upper Oder River, north of the Eastern Sudetes mountain range and the Moravian Gate, which form the southern border with the historic Moravia region. Within the adjacent Silesian Beskids to the east, the Vistula River rises and turns eastwards, the Biała and Przemsza tributaries mark the eastern border with Lesser Poland. In the north, Upper Silesia borders on Greater Poland, and in the west on the Lower Silesian lands (the adjacent region around Wrocław also referred to as Middle Silesia). It is currently split into a larger Polish and the smaller Czech Silesian part, which is located within the Czech regions of Moravia-Silesia and Olomouc. The P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |