|
2020 PP1
is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group, that is a stable quasi-satellite of the Earth. There are over a dozen known Earth quasi-satellites, some of which switch periodically between the quasi-satellite and horseshoe co-orbital states. Discovery was discovered on 12 August 2020 by the Pan-STARRS 1 survey at the Haleakalā Observatory. It was later recovered by the Karl Schwarzschild Observatory in August 2021, which allowed for precovery in earlier Pan-STARRS observations from 24 July 2017. Orbit and orbital evolution is currently an Apollo asteroid (Earth-crossing but with a period longer than a year). Its semi-major axis (currently 1.001715 AU) is similar to that of Earth (0.999789 AU), but it has both low eccentricity (0.07384) and low orbital inclination (5.827°). It alternates between being an Aten asteroid and being an Apollo asteroid, although its orbital evolution is not fully stable and it can be considered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-STARRS 1
The Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System (Pan-STARRS1; obs. code: F51 and Pan-STARRS2 obs. code: F52) located at Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii, US, consists of astronomical cameras, telescopes and a computing facility that is surveying the sky for moving or variable objects on a continual basis, and also producing accurate astrometry and photometry of already-detected objects. In January 2019 the second Pan-STARRS data release was announced. At 1.6 petabytes, it is the largest volume of astronomical data ever released. Description The Pan-STARRS Project is a collaboration between the University of Hawaiʻi Institute for Astronomy, MIT Lincoln Laboratory, Maui High Performance Computing Center and Science Applications International Corporation. Telescope construction was funded by the U.S. Air Force. By detecting differences from previous observations of the same areas of the sky, Pan-STARRS is discovering many new asteroids, comets, variable stars, sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precovery
In astronomy, precovery (short for pre-discovery recovery) is the process of finding the image of a celestial object in images or photographic plates predating its discovery, typically for the purpose of calculating a more accurate orbit. This happens most often with minor planets, but sometimes a comet, a dwarf planet, a natural satellite, or a star is found in old archived images; even exoplanet precovery observations have been obtained. "Precovery" refers to a pre-discovery image; "recovery" refers to imaging of a body which was lost to our view (as behind the Sun), but is now visible again ''(also see lost minor planet and lost comet)''. Orbit determination requires measuring an object's position on multiple occasions. The longer the interval between observations, the more accurately the orbit can be calculated; however, for a newly discovered object, only a few days' or weeks' worth of measured positions may be available, sufficient only for a preliminary (imprecise) orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Co-orbital Asteroids
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet Object Articles (unnumbered)
Minor may refer to: Common meanings * Minor (law), a person not under the age of certain legal activities. * Academic minor, a secondary field of study in undergraduate education Mathematics * Graph minor, Minor (graph theory), a relation of one graph to another * Matroid minor, Minor (matroid theory), a relation of one matroid to another * Minor (linear algebra), the determinant of a square submatrix Music * Minor chord * Minor interval * Minor key * Minor scale People * Minor (given name), a masculine given name * Minor (surname), a surname Places in the United States * Minor, Alabama, a census-designated place * Minor, Virginia, an unincorporated community * Minor Creek (California) * Minor Creek (Missouri) * Minor Glacier, Wyoming Sports * Glossary of Gaelic games terms#M, Minor, a grade in Gaelic games; also, a person who qualifies to play in that grade * Minor league, a sports league not regarded as a premier league ** Minor League Baseball or "the minors", the North Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo Asteroids
The Apollo asteroids are a group of near-Earth asteroids named after 1862 Apollo, discovered by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth in the 1930s. They are Earth-crosser asteroid, Earth-crossing asteroids that have an orbital semimajor axis, semi-major axis greater than that of the Earth (a > 1 Astronomical unit, AU) but perihelion distances less than the Earth's aphelion distance (q < 1.017 AU). , the number of known Apollo asteroids is 21,083, making the class the largest group of near-Earth objects (''cf''. the Aten asteroid, Aten, Amor asteroid, Amor and Atira asteroid, Atira asteroids), of which 1,742 are Minor planet designation, numbered (asteroids are not numbered until they have been observed at two or more Opposition (planets), oppositions), 81 are named, and 2,130 are identified as potentially hazardous asteroids. The closer their semi-major axis is to Earth's, the less Eccentricit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in astronomy, astrophysics and related fields. It publishes original research in two formats: papers (of any length) and letters (limited to five pages). MNRAS publishes more articles per year than any other astronomy journal. The learned society journal has been in continuous existence since 1827 and became online only in 2020. It operates as a partnership between the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS), who select and peer-review the contents, and Oxford University Press (OUP), who publish and market the journal. Despite its name, MNRAS is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the RAS. In 2024 MNRAS became a purely gold open access journal. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet Center
The Minor Planet Center (MPC) is the official body for observing and reporting on minor planets under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Founded in 1947, it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. Function The Minor Planet Center is the official worldwide organization in charge of collecting observational data for minor planets (such as asteroids), calculating their orbits and publishing this information via the '' Minor Planet Circulars''. Under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU), it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, which is part of the Center for Astrophysics along with the Harvard College Observatory. The MPC runs a number of free online services for observers to assist them in observing minor planets and comets. The complete catalogue of minor planet orbits (sometimes referred to as the "Minor Planet Catalogue") may also be freely downloaded. In addition to astrometric data, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Las Cumbres Observatory
Las Cumbres Observatory (LCO) is a network of astronomical observatories run by a non-profit private operating foundation directed by the technologist Wayne Rosing. Its offices are in Goleta, California. The telescopes are located at both northern and southern hemisphere sites distributed in longitude around the Earth. For some astronomical objects, the longitudinal spacing of telescopes allows continuous observations over 24 hours or longer. The operating network currently consists of two 2 meter telescopes, nine 1 meter telescopes, and seven 40 cm telescopes, placed at six astronomical observatories. The network operates as a single, integrated, observing facility, using a software scheduler that continuously optimizes the planned observing schedule of each individual telescope. History Rosing incorporated Las Cumbres Observatory in 1993 with the goal of aiding universities, observatories, and individuals in the acquisition and improvement of telescopes, opt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) in La Cañada Flintridge, California, Crescenta Valley, United States. Founded in 1936 by California Institute of Technology (Caltech) researchers, the laboratory is now owned and sponsored by NASA and administered and managed by Caltech. The primary function of the laboratory is the construction and operation of planetary robotic spacecraft, though it also conducts Earth-orbit and astronomy missions. It is also responsible for operating the NASA Deep Space Network (DSN). Among the major active projects at the laboratory, some are the Mars 2020 mission, which includes the ''Perseverance (rover), Perseverance'' rover; the Mars Science Laboratory mission, including the ''Curiosity (rover), Curiosity'' rover; the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter''; the ''Juno (spacecraft), Juno'' spacecraft orbiting Jupiter; the ''Soil Moisture Active P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
54509 YORP
54509 YORP ( provisional designation ) is an Earth co-orbital asteroid discovered on 3 August 2000 by the Lincoln Laboratory Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR) Team at Lincoln Laboratory Experimental Test Site in Socorro, New Mexico. Measurements of the rotation rate of this object provided the first observational evidence of the YORP effect, hence the name of the asteroid. The asteroid's rate of rotation is increasing at the rate of (2.0 ± 0.2) × 10−4 deg/day2 which between 2001 and 2005 caused the asteroid to rotate about 250° further than its spin rate in 2001 would have predicted. Simulations of the asteroid suggest that it may reach a rotation period of ~20 seconds near the end of its expected lifetime, which has a 75% probability of happening within the next 35 million years. The simulations also ruled out the possibility that close encounters with the Earth have been the cause of the increased spin rate. On 2 January 2104, asteroid YORP will pass within from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
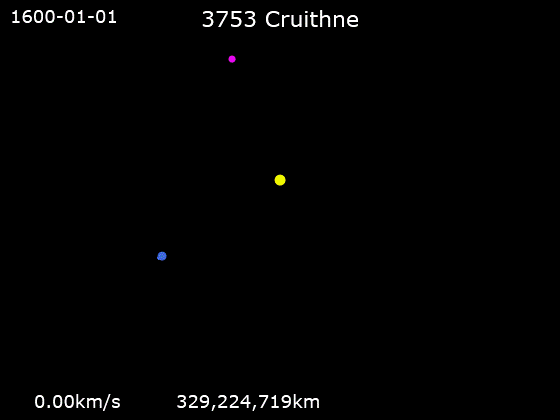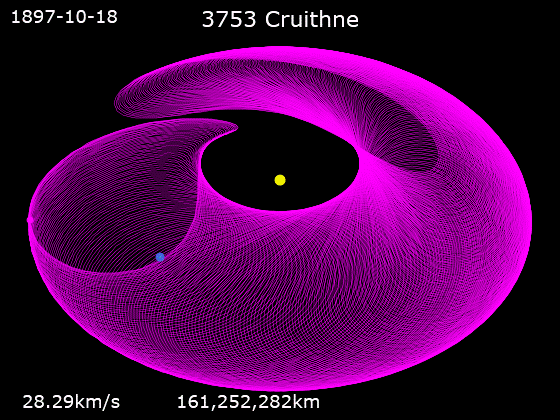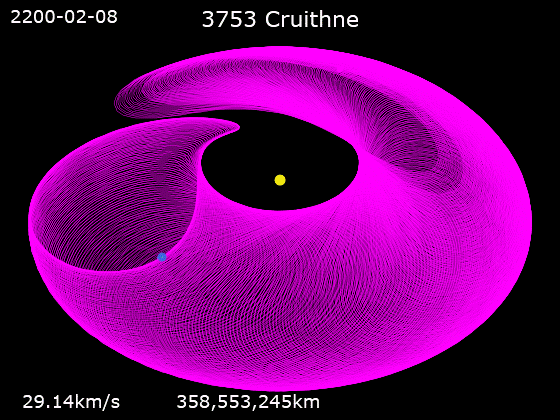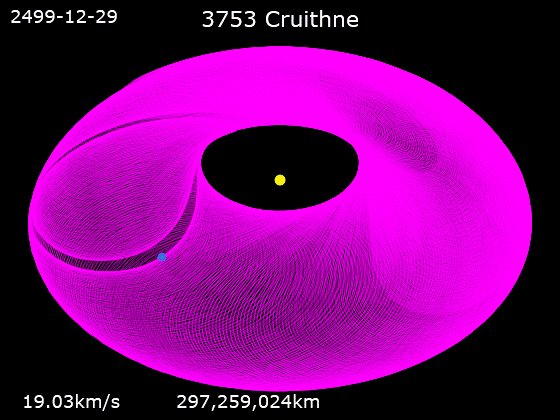
3753 Cruithne
3753 Cruithne is a Q-type, Aten asteroid in orbit around the Sun in 1:1 orbital resonance with Earth, making it a co-orbital object. It is an asteroid that, relative to Earth, orbits the Sun in a bean-shaped orbit that effectively describes a horseshoe, and that can change into a quasi-satellite orbit. Cruithne does not orbit Earth and at times it is on the other side of the Sun, placing Cruithne well outside of Earth's Hill sphere. Its orbit takes it near the orbit of Mercury and outside the orbit of Mars. Cruithne orbits the Sun in about one Earth year, but it takes 770 years for the series to complete a horseshoe-shaped movement around Earth. The asteroid takes its name from the Cruithne, a people mentioned in early Irish annals.Cruithne: Asteroid 3753 . Western Washington University Planetarium. Retrieved 27 January 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |