|
2015 Upper Austrian State Election
The 2015 Upper Austrian state election was held on 27 September 2015 to elect the members of the Landtag of Upper Austria. The election saw major losses for the Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) and Social Democratic Party of Austria (SPÖ), the traditional major parties of Austrian politics. This was matched by huge gains for the right-wing populist Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ), which doubled its vote share to 30% and overtook the SPÖ to become the second largest party. The Greens – The Green Alternative, The Greens also made small gains, while the liberal NEOS – The New Austria (NEOS) failed to enter the Landtag on its first attempt, taking 3.5%. Background The Upper Austrian constitution mandates that cabinet positions in the state government (state councillors, ) be allocated between parties proportionally in accordance with the share of votes won by each; this is known as Proporz. As such, the government is a perpetual coalition of all parties that qualify for at least on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josef Pühringer
Josef Pühringer (; born 30 October 1949 in Traun) is a former Austrian politician. From 2 March 1995 to 6 April 2017 he was the governor (Landeshauptmann) of Upper Austria. He is a member of the Austrian People's Party (ÖVP). He is a member of several Roman Catholic student Fraternities and sororities, fraternities that belong to the Österreichischer Cartellverband, ÖCV and the Mittelschüler-Kartell-Verband, MKV. Pühringer is imperial Knight of Honor of the Order of St. George (Habsburg-Lorraine), Order of St. George. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D'Hondt Method
The D'Hondt method, also called the Jefferson method or the greatest divisors method, is an apportionment method for allocating seats in parliaments among federal states, or in proportional representation among political parties. It belongs to the class of highest-averages methods. Compared to ideal proportional representation, the D'Hondt method reduces somewhat the political fragmentation for smaller electoral district sizes, where it favors larger political parties over small parties. The method was first described in 1792 by American Secretary of State and later President of the United States Thomas Jefferson. It was re-invented independently in 1878 by Belgian mathematician Victor D'Hondt, which is the reason for its two different names. Motivation Proportional representation systems aim to allocate seats to parties approximately in proportion to the number of votes received. For example, if a party wins one-third of the votes then it should gain about one-third of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traunviertel
The Traunviertel is an Austrian region belonging to the state of Upper Austria. It is one of four "quarters" of Upper Austria and its name refers to the river Traun which passes through the area. Region The district includes the Linz-Land, Steyr-Land, Kirchdorf, Gmunden, Steyr, and the city of Linz Linz (Pronunciation: , ; ) is the capital of Upper Austria and List of cities and towns in Austria, third-largest city in Austria. Located on the river Danube, the city is in the far north of Austria, south of the border with the Czech Repub .... Major towns in Traunviertel include the capital of Upper Austria Linz, Gmunden, Kirchdorf an der Krems, and Steyr. References Geography of Upper Austria {{UpperAustria-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hausruckviertel
The Hausruckviertel is one of the four traditional "quarters" () of the Austrian province of Upper Austria Upper Austria ( ; ; ) is one of the nine States of Austria, states of Austria. Its capital is Linz. Upper Austria borders Germany and the Czech Republic, as well as the other Austrian states of Lower Austria, Styria, and Salzburg (state), Salzbur .... The region is named after a range of hills, the Hausruck. Cities in the Hausruckviertel include Wels, Eferding, Grieskirchen, and Vöcklabruck. Notes References * * Geography of Upper Austria {{UpperAustria-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innviertel
The Innviertel (literally German language, German for "Inn Quarter"; officially called the ; ) is a traditional Austrian region southeast of the Inn (river), Inn river. It forms the western part of the States of Austria, state of Upper Austria and borders the Germany, German state of Bavaria. The Innviertel is one of the four traditional "quarters" of Upper Austria, the others being Hausruckviertel, Mühlviertel, and Traunviertel. The Innviertel is the northwestern quarter of Upper Austria and includes the districts Braunau am Inn District, Braunau am Inn, Ried im Innkreis District, Ried im Innkreis and Schärding District, Schärding. Since the formation of the District Captaincy (Austria), political districts in 1868, the quarters in Upper Austria no longer have a legal basis and are purely regional names. The older Habsburg districts (), which were still based on the old quarters, were superseded. Unlike the rest of Upper Austria, most of the area was part of Duchy of Bavaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linz-Land
Bezirk Linz-Land is a Districts of Austria, district of Upper Austria in Austria. Municipalities Towns (''Städte'') are indicated in boldface; market towns (''Marktgemeinden'') in ''italics''; suburbs, hamlets and other subdivisions of a municipality are indicated in small characters. * Allhaming * Ansfelden * ''Asten, Austria, Asten'' * Eggendorf im Traunkreis * Enns (city), Enns * Hargelsberg * Hofkirchen im Traunkreis * ''Hörsching'' * Kematen an der Krems * Kirchberg-Thening * ''Kronstorf'' * Leonding * ''Neuhofen an der Krems'' * Niederneukirchen * Oftering * Pasching * Piberbach * ''Pucking'' * ''Sankt Florian'' * Sankt Marien * Traun * ''Wilhering'' External links * {{Authority control Linz-Land District, Districts of Upper Austria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linz
Linz (Pronunciation: , ; ) is the capital of Upper Austria and List of cities and towns in Austria, third-largest city in Austria. Located on the river Danube, the city is in the far north of Austria, south of the border with the Czech Republic. As of 1 January 2024, the city has a population of 212,538. It is the seventh-largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. History Linz originated as a Roman Empire, Roman fort named ''Lentia'', established in the first century. The name reflects its location at a bend in the Danube (Celtic languages, Celtic root ''lentos'' = "bendable"). This strategic position on the river made it the first Roman fort in the Noricum region, protecting a vital transportation route. The name "Linz" in its present form was first documented in 799. Linz was mentioned as a fortified city in 1236 and was granted city rights in 1324. Johannes Kepler spent several years of his life in the city teaching m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landtag Of Upper Austria 2015
A ''Landtag'' (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non-federal matters. The States of Germany and Austria are governed by ''Landtage''. In addition, the legislature of the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol is known in German as a ''Landtag''. Historically, states of the German Confederation also established ''Landtage''. The Landtag of Liechtenstein is the nation's unicameral assembly. Name The German word Landtag is composed of the words ''Land'' (state, country or territory) and ''Tag'' (day). The German word ''Tagung'' (meeting) is derived from the German word ''Tag'', as such meetings were held at daylight and sometimes spanned several days. Historic Landtag assemblies States of the Holy Roman Empire In feudal society, the formal class system was reflected in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Party Of Austria
The Christian Party of Austria (, CPÖ; formerly the Christians – ) is a minor political party in Austria, founded on 15 October 2005. It changed its name under its new chairman Rudolf Gehring in late 2009, to avoid the use of the term "Christians" to mean only the party. History The party was registered on 23 January 2006, and presented to the public on 27 September 2007, when it announced a popular initiative ("Volksbegehren") on the topic of children and families and that it would contest the 2008 election in Lower Austria. In the 2008 parliamentary election, the party received 0.64% of the vote. Rudolf Gehring, the party's chairman, announced he would run for president in the 2010 election. He received 5.44% of the vote for third place, the party's highest vote percentage in a national election to date. Goals The party is oriented mainly on Christian politics, advocating, for example: * Revoking the recognition of same-sex unions * Giving parents the right to vote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of Austria
The Communist Party of Austria (, KPÖ) is a communist party in Austria. Established in 1918 as the Communist Party of Republic of German-Austria, German-Austria (KPDÖ), it is one of the world's oldest Communist party, communist parties. The KPÖ was banned between 1933 and 1945 under both the Austrofascism, Austrofascist regime and the Nazi Germany, Nazi German administration of Austria after the 1938 ''Anschluss''. The party currently holds two seats in the Styrian and four seats in the Salzburg (federal state), Salzburg (States of Austria, state parliament), but has not had representation in the National Council (Austria), National Council (, Austria's federal parliament) since 1959. In the 2019 Austrian legislative election, legislative election held on 29 September 2019, it won only 0.7% of the votes (32,736 out of a total of 4,835,469), well below the 4% minimum to obtain seats in the National Council. The party's vote share increased markedly to 2.4% in 2024 Austrian legi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
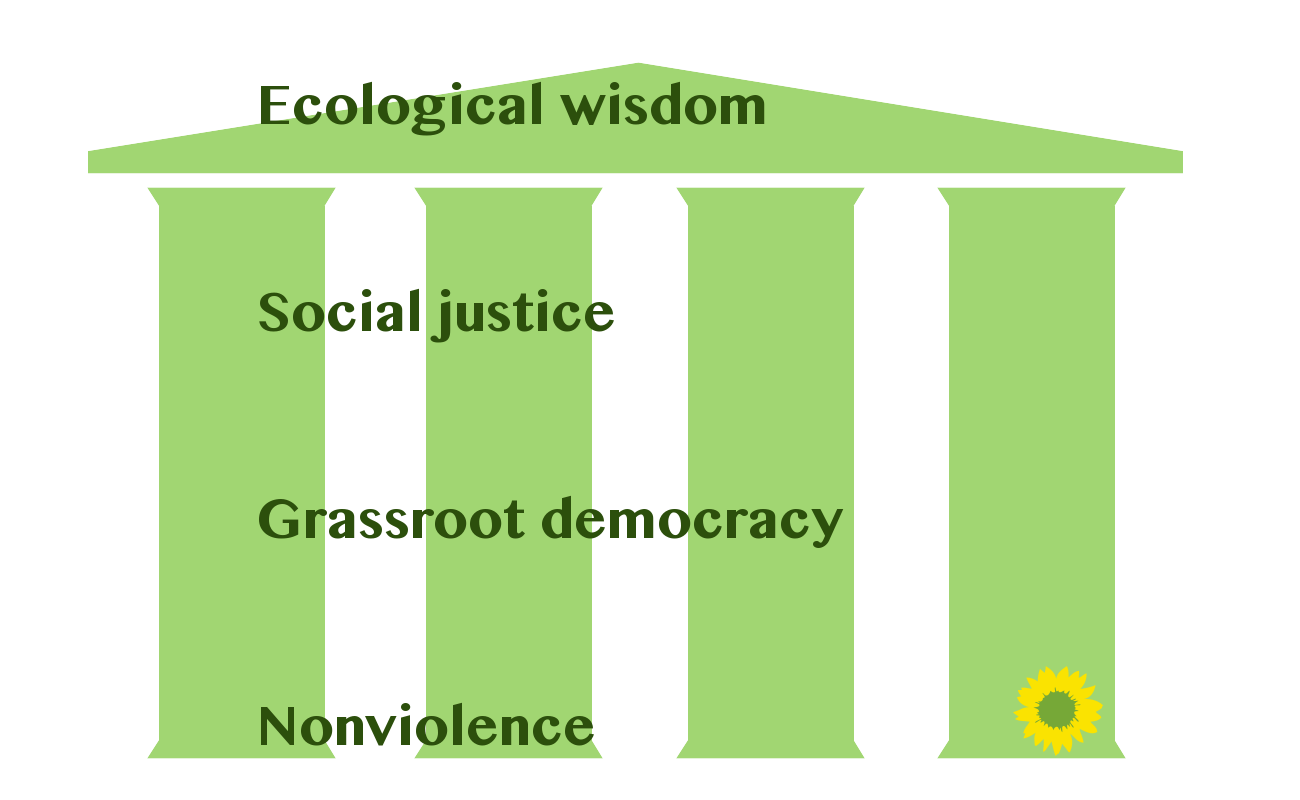
Green Politics
Green politics, or ecopolitics, is a political ideology that aims to foster an ecologically sustainable society often, but not always, rooted in environmentalism, nonviolence, social justice and grassroots democracy.#Wal10, Wall 2010. p. 12-13. It began taking shape in the Western world in the 1970s; since then, green parties have developed and established themselves in many countries around the globe and have achieved some electoral success. The political term ''green'' was used initially in relation to ''Alliance 90/The Greens, die Grünen'' (German for "the Greens"), a green party formed in the late 1970s. The term ''political ecology'' is sometimes used in academic circles, but it has come to represent an interdisciplinary field of study as the academic discipline offers wide-ranging studies integrating ecological social sciences with political economy in topics such as degradation and marginalization, environmental conflict, conservation and control and environmental identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euroscepticism
Euroscepticism, also spelled as Euroskepticism or EU-scepticism, is a political position involving criticism of the European Union (EU) and European integration. It ranges from those who oppose some EU institutions and policies and seek reform (''Eurorealism'', ''Eurocritical'', or ''soft Euroscepticism''), to those who oppose EU membership and see the EU as unreformable (''anti-European Unionism'', ''anti-EUism'', or ''hard Euroscepticism''). The opposite of Euroscepticism is known as ''pro-Europeanism''. The main drivers of Euroscepticism have been beliefs that integration undermines national sovereignty and the nation state, that the EU is elitist and Democratic deficit in the European Union, lacks democratic legitimacy and Transparency (behavior), transparency, that it is too bureaucratic and wasteful,(Op-Ed that it encourages high levels of immigration, or perceptions that it is a neoliberal organisation serving the big business elite at the expense of the working class, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |