|
1912 Republican Party Presidential Primaries
From March 19 to June 4, 1912, delegates to the 1912 Republican National Convention were selected through a series of primaries and caucuses to determine the party's nominee for President in the 1912 election. Incumbent President William Howard Taft was chosen over former President Theodore Roosevelt. Taft's victory at the national convention precipitated a fissure in the Republican Party, with Roosevelt standing for the presidency as the candidate of an independent Progressive Party, and the election of Democrat Woodrow Wilson over the divided Republicans. For the first time, a large number of delegates were selected through direct primary elections rather than local or state party conventions. Primary elections were a progressive reform supported by Roosevelt and his allies, and the primaries were largely dominated by Roosevelt or Robert M. La Follette, a fellow progressive who entered the race early. However, President Taft was equally dominant under the traditional caucus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Convention
The terms party conference (UK English), political convention ( US and Canadian English), and party congress usually refer to a general meeting of a political party. The conference is attended by certain delegates who represent the party membership. In most political parties, the party conference is the highest decision-making body of the organization, tasked with electing or nominating the party's leaders or leadership bodies, deciding party policy, and setting the party's platform and agendas. The definitions of all of these terms vary greatly, depending on the country and situation in which they are used. The term ''conference'' or '' caucus'' may also refer to the organization of all party members as a whole. The term ''political convention'' may also refer to international bilateral or multilateral meetings on state-level, like the convention of the Anglo-Russian Entente (1907). Leadership roles Within party conferences, there might be different offices or bodies fulfil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorbonne (building)
The name Sorbonne (French: ''La Sorbonne''; , , ) is commonly used to refer to the historic University of Paris in Paris, France or one of its successor institutions (see below). It is also the name of a building in the Latin Quarter of Paris which from 1253 onwards housed the College of Sorbonne, part of one of the first universities in the Western world, later renamed University of Paris and commonly known as "the Sorbonne". Today, it continues to house the successor universities of the University of Paris, such as Panthéon-Sorbonne University, Sorbonne University, Sorbonne Nouvelle University and Paris City University, as well as the . Sorbonne Université is also now the university resulting from the merger on 1 January 2018 of Paris 6 UPMC and Paris 4 Sorbonne.. Collège de Sorbonne The college was founded in 1253 by Robert de Sorbon. Louis IX of France confirmed the foundation in 1257. It was one of the first significant colleges of the medieval University of Paris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citizenship In A Republic
Citizenship in a Republic is the title of a speech given by Theodore Roosevelt, former President of the United States, at the Sorbonne in Paris, France, on April 23, 1910. One notable passage from the speech is referred to as "The Man in the Arena": It is not the critic who counts; not the man who points out how the strong man stumbles, or where the doer of deeds could have done them better. The credit belongs to the man who is actually in the arena, whose face is marred by dust and sweat and blood; who strives valiantly; who errs, who comes short again and again, because there is no effort without error and shortcoming; but who does actually strive to do the deeds; who knows great enthusiasms, the great devotions; who spends himself in a worthy cause; who at the best knows in the end the triumph of high achievement, and who at the worst, if he fails, at least fails while daring greatly, so that his place shall never be with those cold and timid souls who neither know victory no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Portsmouth
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal persons. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms. However, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties vary on the basis of obligations (the extent to which states are bound to the rules), precision (the extent to which the rules are unambiguous), and delegation (the extent to which third parties have authority to interpret, apply and make rules). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations, with the first known example being a border agreement between the Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiology or Medicine and Literature. Since March 1901, it has been awarded annually (with some exceptions) to those who have "done the most or the best work for fraternity between nations, for the abolition or reduction of standing armies and for the holding and promotion of peace congresses". In accordance with Alfred Nobel's will, the recipient is selected by the Norwegian Nobel Committee, a five-member committee appointed by the Parliament of Norway. Since 2020 the prize is awarded in the Atrium of the University of Oslo, where it was also awarded 1947–1989; the Abel Prize is also awarded in the building. The prize was previously awarded in Oslo City Hall (1990–2019), the Norwegian Nobel Institute (1905–1946), and the Parliament (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing north from Lake Victoria, and the Blue Nile, flowing west from Lake Tana in Ethiopia. The place where the two Niles meet is known as ''al-Mogran'' or ''al-Muqran'' (; English: "The Confluence"). From there, the Nile continues north towards Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea. Divided by these two parts of the Nile, Khartoum is a tripartite metropolis with an estimated population of over five million people, consisting of Khartoum proper, and linked by bridges to Khartoum North ( ) and Omdurman ( ) to the west. Khartoum was founded in 1821 as part of Egypt, north of the ancient city of Soba. While the United Kingdom exerted power over Egypt, it left administration of the Sudan to it until Mahdist forces took over Khartoum. The British at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
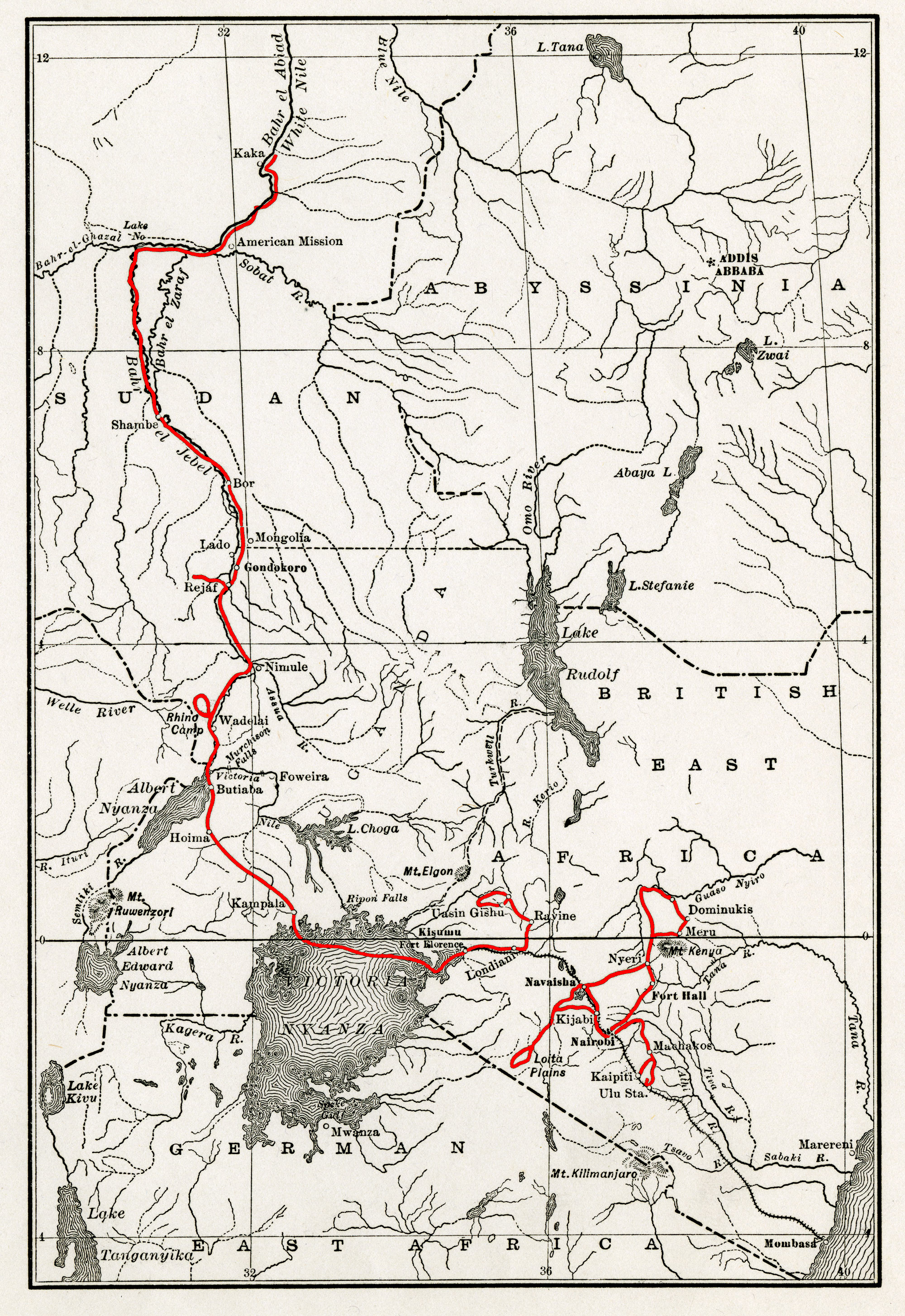
Smithsonian–Roosevelt African Expedition
The Smithsonian–Roosevelt African Expedition was an expedition to tropical Africa in 1909-1911 led by former United States president Theodore Roosevelt, funded by Andrew Carnegie and sponsored by the Smithsonian Institution. Its purpose was to collect specimens for the Smithsonian's new Natural History museum, now known as the National Museum of Natural History. The expedition collected around 11,400 animal specimens which took Smithsonian naturalists eight years to catalog. Following the expedition, Roosevelt chronicled it in his book ''African Game Trails''. Participants and resources The group was led by the legendary hunter-tracker R. J. Cunninghame. Participants on the Expedition included Australian sharpshooter Leslie Tarlton; three American naturalists, Edgar Alexander Mearns, a retired U.S. Army surgeon; Stanford University taxidermist Edmund Heller, and mammalologist John Alden Loring; and Roosevelt's 19-year-old son Kermit, on a leave of absence from Harvard. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan (March 19, 1860 – July 26, 1925) was an American lawyer, orator and politician. Beginning in 1896, he emerged as a dominant force in the Democratic Party, running three times as the party's nominee for President of the United States in the 1896, 1900, and the 1908 elections. He served in the House of Representatives from 1891 to 1895 and as the Secretary of State under Woodrow Wilson. Because of his faith in the wisdom of the common people, Bryan was often called "The Great Commoner", and because of his rhetorical power and early notoriety, "The Boy Orator". Born and raised in Illinois, Bryan moved to Nebraska in the 1880s. He won election to the House of Representatives in the 1890 elections, served two terms, and made an unsuccessful run for the Senate in 1894. At the 1896 Democratic National Convention, Bryan delivered his "Cross of Gold" speech which attacked the gold standard and the eastern moneyed interests and crusaded for inflatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elihu Root
Elihu Root (; February 15, 1845February 7, 1937) was an American lawyer, Republican politician, and statesman who served as Secretary of State and Secretary of War in the early twentieth century. He also served as United States Senator from New York and received the 1912 Nobel Peace Prize. Root is sometimes considered the prototype of the 20th century political " wise man," advising presidents on a range of foreign and domestic issues. Root was a leading New York City lawyer who moved frequently between high-level appointed government positions in Washington, D.C., and private-sector legal practice in New York City. His private clients included major corporations and such powerful players as Andrew Carnegie. Root served as president or chairman of the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, the Carnegie Institution of Washington, and the Carnegie Corporation of New York. Root was a prominent opponent of women's suffrage and worked to ensure the New York state constituti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assassination Of William McKinley
William McKinley, the 25th president of the United States, was shot on the grounds of the Pan-American Exposition at the Temple of Music in Buffalo, New York, on September 6, 1901, six months into his second term. He was shaking hands with the public when anarchist Leon Czolgosz shot him twice in the abdomen. McKinley died on September 14 of gangrene caused by the wounds. He was the third American president to be assassinated, following Abraham Lincoln in 1865 and James A. Garfield in 1881. McKinley enjoyed meeting the public and was reluctant to accept the security available to his office. Secretary to the President George B. Cortelyou feared that an assassination attempt would take place during a visit to the Temple of Music and took it off the schedule twice, but McKinley restored it each time. Czolgosz had lost his job during the economic Panic of 1893 and turned to anarchism, a political philosophy adhered to by recent assassins of foreign leaders. He regarded McKinley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Roosevelt With A Waterbuck Trophy, Signed 'To R
Theodore may refer to: Places * Theodore, Alabama, United States * Theodore, Australian Capital Territory * Theodore, Queensland, a town in the Shire of Banana, Australia * Theodore, Saskatchewan, Canada * Theodore Reservoir, a lake in Saskatchewan People * Theodore (given name), includes the etymology of the given name and a list of people * Theodore (surname), a list of people Fictional characters * Theodore "T-Bag" Bagwell, on the television series ''Prison Break'' * Theodore Huxtable, on the television series ''The Cosby Show'' Other uses * Theodore (horse), a British Thoroughbred racehorse * Theodore Racing, a Formula One racing team See also * Principality of Theodoro, a principality in the south-west Crimea from the 13th to 15th centuries * Thoros (other), Armenian for Theodore * James Bass Mullinger James Bass Mullinger (1834 or 1843 – 22 November 1917), sometimes known by his pen name Theodorus, was a British author, historian, lecturer and scholar. A l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |